NEW! The Gist (FREE) | E-BOOKS |
(Online Course) CSAT Paper - II : Basic Numeracy: Volume & Surface Area of Solid Figures
Basic Numeracy
Volume & Surface Area of Solid Figures
Solid
Anything that occupies space is calleda Solid. In addition to area, a solid figure has volume also. It has three dimensions namely, length, breadth and height. For solid two different types of areas namely, lateral surface area or curved surface area and total surface area are defined.1.Prism
A solid having two congruent and parallel faces, called bases and whose other faces, the lateral faces are parallelograms, formed by joining corresponding vertices of the bases is called a Prism.2. Right Prism
A prismin which bases are perpendicular to the lateral edges is calleda Right
Prism. The base of the prism can be a polygon.
In a right prism
(ii) Total number of surfaces of a prism = Number of lateral surfaces + 2
(iii) Lateral surface area = Perimeter of base × Height
(iv) Total surface area = Lateral surface area + 2 (Area of base)
(v) Volume = Area of base × Height
3. Cuboid
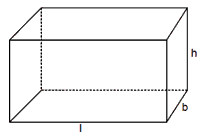
A right prism in which the base is a rectangle is called a Cuboid. If l is the length and b the breadth of the base and h the height, then
Lateral surface area = 2 (l + b)h sq unit
Total surface area = 2(l + b)h + 2lb = 2 (lb + bh + lh) sq unit
Volume = lbh cu unit
The longest diagonal of the cuboid = Öl2
+ b2 + h2 unit
4. Cube
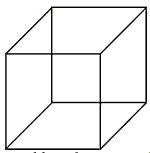
A right prismin which the base is a square and height is equal to the side of
the base is alled a cube. If x is the
side of the cube, then lateral surface area = 4x× x = 4x2sq unit
Total surface area = 4x2 + 2(x2) = 6x2 sq unit
Volume = x2 × x = x3 cu unit
The longest diagonal of the cube = Ö3x unit
5. Cylinder
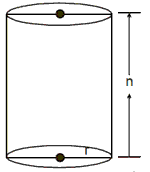
If the base of a right prism is circular, then it becomes a cylinder. The
lateral surface area c the cylinder is a single curved surface called the curved
surface area. If r is the radius of the has and h is the height of the cylinder,
then
Curved surface area = 2Πrh sq unit
Total surface area = 2Πrh + 2Πr2 = 2Πr (r + h) sq unit
Volume of cylinder =Πr2h cu unit
6. Cone
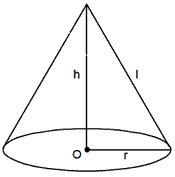
If the base of a right pyramid is circular, then it becomes a cone. The lateral
surface area of the cone is a single curved surface. If r is the radius of the
base h is the height of the cone and 1 the slant height of the cone,
then slant height, l =Öh2 + r2 unit
Curved surface area = Πrl sq unit
Total surface area = Πrl+ Πr2= Πr (l+ r) sq unit
Volume of cylinder =1/3 Πr2h cu unit.
7. Frustrum of a Cone
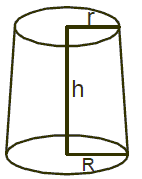
If a cone is cut parallel to base at a hight h then the remaining part is called the frustrum of the cone. If radius of base and vertex of the frustrum of a cone be R and r respectively and height and slant height of it be h and l then
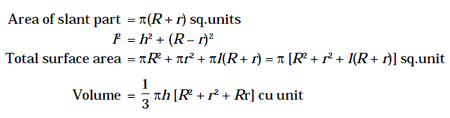
8. Sphere
A sphere is a solid in which any point on the surface of sphere is equidistant
from the centre of the sphere.
Surface area = 4Πr2 sq unit
Volume =4/3Πr3 cu unit
9. Hemisphere
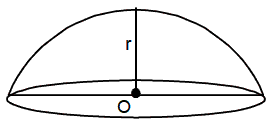
When a sphere is cut into two equal halves, each half is an hemisphere in which the base is circular with radius r and height is equal to the radius.
Curved surface area = 2Πr2 sq. unit
Total surface area = 2Πr2+Πr2sq. unit = 3Πr2 sq. unit
Volume = 2Πr3 cu unit
1 L = 1000cm3
10. Pyramids
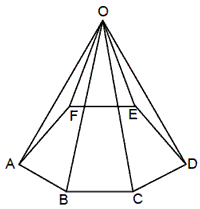
If a point O is joined to the end points of each side of a polygon by straight
lines, then it is called a pyramid.
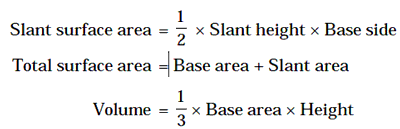
Base area depends on the shape of polygon in the base.
Example 1: Find the volume and total surface area of a cube of side 7 m.
Solution. Here, x =7 m
Surface area = 6 × 2 = (6 × 72) m2 = 294 m2
Volume = x3 = (73) m3 = 343 m3
Example 3: Find the length of the longest pole that can be put in a
room 15m long, 8m broad and 7m high.
Solution. Here, l = 15 m, b = 8 m and h = 7 m
Required length = Öl2 + b2 + h2 = ( 15)2
+(8 )2+ ( 7 )2= Ö388 = 13Ö2
m
Example 4: The length, breadth and height of a room are in the ratio 3
: 2 : 1. The length, breadth and height of the room are increased by 300%, 200%
and 100% respectively. Find, how many number of times the volume of the room is
increased?
Solution. Let the length, breadth and height of the room are 3x, 2x and x
respectively.
Volume of the room = 3x × 2x × x = 6x2 After increase
length = 3x + 300% of 3x = 12x
breadth = 2x + 200% of 2x = 6x
height = x + 100% of x = 2x
New volume =12x + 6x + 2x = 144x3
Increase in volume = 144x3– 6x3 = 138x3
Required number of times = 138x3/6x3 = 23 times
Solution. Clearly, height of the cylinder = diameter of the sphere = 14 cm
Example 6: The base radius of a cylinder is 14 cm and its height is 30
cm. Find (a) Volume (b) Curved surface area (c) Total surface area
Solution.
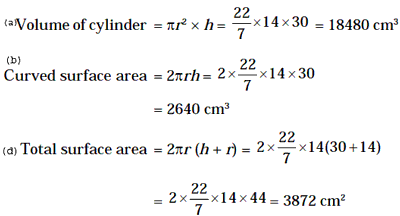
Example 7: How many cubic metres of earth must be dug to make a well
14 m deep and 4 m in diameter?
Solution. Each to be dugout from the well = volume of the cylindrical
well =Πr2h = = 176 m3
Example 8: The radius of the base of a right cone is 35 cm and its
height is 84 cm. Find
(a) Slant Height (b) Curved Surface Area (c) Total Surface Area (d) Volume
Solution. (a)

(d).