NEW! The Gist (FREE) | E-BOOKS |
Environment Performance Index : Important Topics for UPSC Exams
Environment Performance Index : Important Topics for UPSC Exams
The Environmental Performance Index (EPI) is a method of quantifying and numerically marking the environmental performance of a state's policies. This index was developed from the Pilot Environmental Performance Index, first published in 2002, and designed to supplement the environmental targets set forth in the United Nations Millennium Development Goals.
The EPI was preceded by the Environmental Sustainability Index (ESI), published between 1999 and 2005. Both indexes were developed by Yale University (Yale Center for Environmental Law and Policy) and Columbia University (Center for International Earth Science Information Network) in collaboration with the World Economic Forum and the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission
Methodology
|
Buy Printed Complete Study Materials for UPSC IAS PRELIMS Exam
Online Crash Course for UPSC PRE Exam
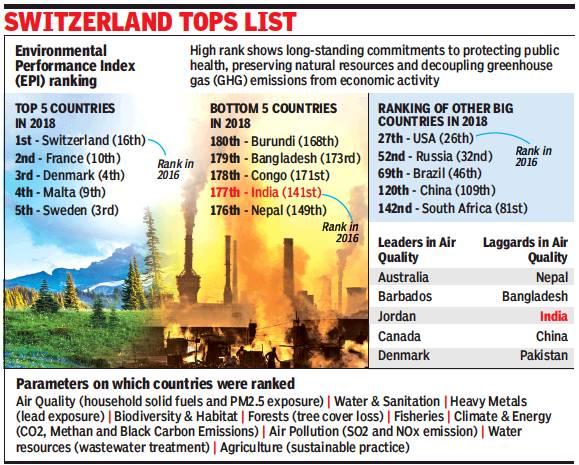
Leaders and others
-
Environment Performance Index 2018 top ranking countries: Switzerland, France, Denmark, Malta, Malta
-
Environment Performance Index 2018 – Bottom 5: Burundi, Burundi, Congo, India,
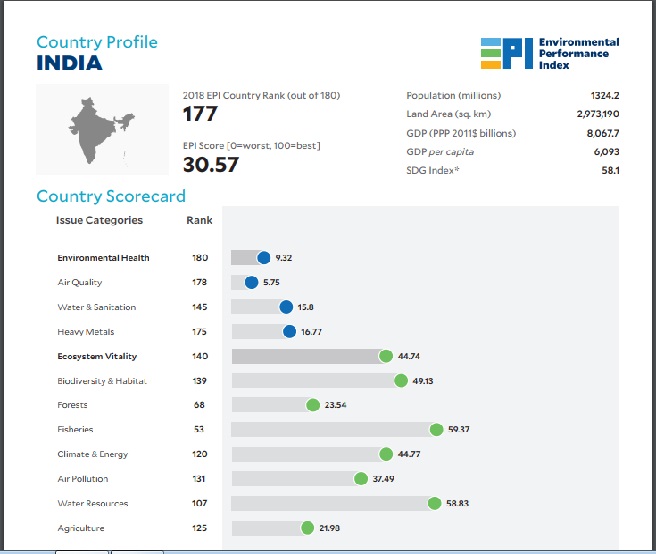
Causes of concern mentioned in the report
-
India’s low scores are influenced by poor performance in the in Environmental Health policy objective.
-
Deaths attributed to PM2.5 have risen over the past decade and are estimated at 1,640,113, annually (Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, 2017).
-
Despite government action, pollution from solid fuels, coal and crop residue burning, and emissions from motor vehicles continue to severely degrade the air quality for millions of Indians.
Consequences of degrading situation
A. Health:
-
Deaths attributed to PM 2.5 have risen
-
Health of children and women are more prone to be affected due to longer exposure and weak immune system which adversely affects the potential of India’s demographic dividend.
B. Economy:
-
Productivity of labour declines due to illness and mortalities, This is reported to be an estimated loss of 0.8% GDP
What has the government done?
-
Government has decided to implement Bharat Stage VI emission norms directly from BS IV from 2020.
-
New transport policy and various missions like smart cities have provisions for promoting cleaner transport sources. This is supplemented by new metro policy. Transit oriented development is increasingly being emphasized Ex: Pod taxi project in gurugram
-
National solar mission: revising the target for setting up solar capacity from 20 GW to 100 GW by 2021-22.
-
Color coding of industries according to the level of industrial pollution for easy regulation of such industries.
-
Pollutants like Fly-ash are being harnessed for economic uses Ex: Maharashtra’s policy
-
At international level the government has set ambitious targets in Intended nationally determined contributions (INDC’s) in the Paris deal 2015.
-
Recently Environment pollution control authority prepared a graded plan to be followed in Delhi-NCR for controlling the pollution from PM 2.5, PM 10 etc as per the mandate of Supreme Court.
-
Clean Ganga Mission has set ambitious targets of cleaning Ganga by 2018.
-
The 8 components under National action plan on climate change cater to almost all the parameters listed under environment performance index.
-
The report has termed ‘Ujjwala’ scheme Cited As Potentially Life Changing
About UJJWALA:Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana is a scheme of the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas, the government aims to provide cooking gas to poor households. The scheme aims to replace cooking fuels used mostly in rural India with clean liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). The scheme allows the government to provide cooking gas connections to poor women along with financial assistance over a period of three years. Eligible families are identified through the Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011 data. Ujjwala scheme provides financial support of Rs1,600 for each cooking gas connection to eligible households. The connections are given in the name of the women heads of households. The government also provides an equated monthly instalment facility for meeting the cost of stove and refills. In the recent budget Finance minister expanded the ambit of the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (Ujjwala scheme) to include 80 million poor families who will be given free cooking gas connections.
|
What needs to be done?
-
India has set ambitious targets in the policy framework as well as INDC’s but the ground realities and implementation do not reflect the enthusiasm which is reflected while framing them.
-
India faces the challenge of balancing development targets and preserving environment which is highlighted in relaxed norms for ex in power plant emission, electronic waste collections and relaxed wetland conservation rules, compensatory afforestation fund to name a few. This needs to be checked.
-
Adoption of REDD+ measures is a cost effective way of increasing forest cover and also fulfilling the targets under Paris deal.
-
User based governance needs to be adopted for managing environment threats.
-
ZLD’s or zero liquid discharge can be made mandatory for industries.
-
Transition to renewable sources should be accelerated and the costs of biodiversity must be incorporated in the development costs.
MODEL QUESTIONS
:: MCQ’s ::
1. Which of the following organizations participate in the preparation of Environment performance Index?
A. Yale University
B. WEF
C. Columbia University...
D. Joint Research Centre of the European Commission.
Which of the above are correct?
-
B and D only
-
A and B only
-
A,B and C only
-
All of the above
Correct Answer: d (All of the above)
2. Which of the following statements about Pradhan mantri ujjwala yojna are correct?
A. The scheme is being implemented by ministry of Environment.
B. The scheme aims to provide LPG connection to 8crore households.
Choose the correct answer
-
A only
-
B only
-
A and B
-
None of the above
Correct Answer: c (A and B)
:: Mains Questions ::

