NEW! The Gist (FREE) | E-BOOKS |
(Sample Material) UPSC Mains Philosophy (Optional) Study Kit "Western Philosophy (Philosophy)"

Sample Material of UPSC Mains Philosophy (Optional) Study Kit
Topic: Western Philosophy (Philosophy)
The Term Philosophy is derived from Philosophy and Sophia i.e. love and wisdom or knowledge respectively. It literally means ‘Lover of Wisdom’ Etymologically it is derived so.
Many thinkers have defined philosophy in their own individual way. But basically Philosophy is the intellectual (rational, logical) enquiry of the life and the universe (vision or holistic, constructive, evaluative neutral, critical).
PURPOSE OF PHILOSOPHY
Fundamental elements behind the life and Unin & its creation and their aim or its end.
PLOBMELS IN PHILO.
Two problems regarding these elements:
(1) How many fundamental elements (FE) are there? (Numbers)
(2) What is the nature of these FE? (Nature)
Click Here for UPSC Mains Philosophy Study Material
(1) Monoism – only single element behind life and universe. Propagated by
SPINOZA and SHANKARACHARYA They are called Monocist.
(2) Dualism – Two types of basic element Propagated by DESCARTE and SANKHYA and
MADHWUCHARYA (3) Pluralism many types of basic element propagated by LEIBNIZ and
NYAYA VAISESHIKA
(1) Materialism – emphasizing on the material elements (body and not soul)
behind life and universe KARL MARY and CHARYAKA (CARVAKA)
(2) Spiritualism – People emphasising on conscious elements behind life and
universe. LIEBNIZ and SHANKARACHARYA (3) Dualism – People emphasising equally on
both material and conscious SANKHYA and DESCARTES
Thus Philosophy is the study (co structure study) of the beginning and end of life and universe (Traditionally)
- In many religions HEAVEN is the highest end of life.
- But in Philosophy LIBERATION is the highest end of life.
- But in Humanism HUMAN WELFARE is the highest end of life.
But in wo Vedanta i.e. practical and scientific explanation of Vendanta. Supporters are Arvinda, Tagore , Radha Krishna
Philosophical study of religious aspect is called Philosophy of religion (Philosophical enquiry) (Science is related with is Philosophy is related with OUGNI TO BE)
Why to take Philosophy as an optional?
- Short syllabus
- Only 500 pages
- Conceptual (Without studying the entire syllabus you can’t answer any single question. (All interlinked question) (2009 pattern).
- Helpful in essay (No of topics in the syllabus all related to the subject matter of essay)
- Common portions of Paper I & Paper II
TECHNICAL TERMS IN PHILOSOPHY
(1) EPISTOMOLOGY: Theory of knowledge. It is an important branch of
philosophy where we discuss the source of knowledge validity of knowledge nature
of know limit know etc. and relation between knower and knowable.
(2) METAPHYSICS: an important branch of philosophy where we discuss the no. of
fundamental stuff (FS) (minimum dualism pluralism) nature of FE (materialism
fundamental element spiritualism dualism) In Metaphysics we generally discuss
GOD SOUL, SUBSTANCE REALITY MATTER, WORLD etc.
(3) RATIONALISM: is an epistemological theory according To which reason is the
only source of valid knowledge recognition supporters are DESCARTES SPINOZA and
LEIBNIZ.
(4) EMPIRICISM: an important epistemological theory according To which
experience is the only source of valid knowledge LOCKE BERKELEY and HUME.
Q: Plato’s recollection theory of knowledge.
(5) INDUCTION: When we find universal conclusion from particular premises. Eg.
Ram is mortal. Mohan is mortal. Therefore all men are mortal on this his proceed
from particular to universal (science) Particular – Universal
(6) DEDUCTION: When we find particular conclusion on the basis of universal
premises. All men are mortal Ram is a main Therefore Ram is mortal. When
premises provide conclusive evidence of the truthfulness of its conclusion it is
called
DEDUCTION
Universal – Particular
We can always create doubt on inductive conc. Elusion (Science) because of uncertainly but deduction can never be doubt upon (Maths) because of certainly and universalize.
(7) JUDGEMENT CAN BE OF 3 TYPES (KNOWLEDGE)
- Always true (212 =4)
TAUOLOGY (Maths)
- Always false (242 =5) CONTRADICTION (Maths)
- Sometimes true sometimes false (Rose is red)
CONTINGENT (SCIENCE): Existence is always based on experience. Religious statements cannot be put under any category eg. God is omniponent.
(8) SUBJECTIVE: It depends on our self subjectivity is directly related with different reference. Subjective verification.
(9) OBJECTIVE: It depends on something outside objective is directly related to uniformity objective (public) verification.
(10) CAUSAL THEORY: It accepts the theory that every fact must have a cause. It is the foundation of scientific belief.
Anything which doesn’t have a cause is considered as a miracle by religious people.
(11) MATERIAL: Material cause is that through which effect is constituted.
(12) EFFICIENT: Efficient cause is that which creates effect with the help of material cause. It sets in motion or provides harmony to material cause and creates the effect.
Eg: In a pot Made by day. Cray is the material cause and pother is the efficient cause Material cause is always eminent with the object Efficient cause is always outside the object. Q: What do eminent and transcendent mean in the context of God? (2003M)
Eg: In the context of world. If God is the material cause he is eminent in the world (he is present everywhere). Problem will be there be no different between right or wrongs good or evil etc. If Lord is the efficient cause he is always outside the universe. Problem will be there will be no fruits of our deeds all will be evil.
(13) SIMPLE: Parties, Indivisible, Eternal (eg. Soul) Immortal.
(14) SUBSTANCE: Independent existence (metaphysically and epistemologically both) For eg. God has been accepted as substance.
(15) REALISM: Knowable (object) exists outside and independently from knower. We find the knower of object as it is.
(16) IDEALISM: From epistemological point view idealism indicates that knowable (object) doesn’t exist outside and independently from knower (ourself). When we pricier any object we come across many ideas about that object which (ideas) come out of our brains. Thus if there are no ideas there doesn’t exist any object (Eg. Berkley).
Q: To be is to percieved said by Berkley Explain (2009 M) (existence) (idea)
(17) UNIVERSAL: Common and essential quality of a particular thing or group Eg. Manners Cowness.
(18) INFINITE REGRESS
Q: God is the first reason of things (2006 M)
It means to go infinite in finite continuance.
No final or ultimate cause.
(19) LAW OF KARMA: Good deeds good fruits
- Bad deeds bad fruits
It is the backbone (cornet stone) of Indian philosophy.
It is universally accepted fact by all the religion.
It is one of the proofs of existence of God.
(Religion says so but there are practical contradictions (The explanation of the cause of rebirth will explain these contradictions clearly)
Law of karma is the practical explanation of causal theory in the field of morality.
Rebirth: To take birth again & again- Indian religion. But in Sematic religion (i.e. Islam, Christianity, Jenes) resuesection (One more life) is to be believed to happen.
(20) BONDAGE- It means presence of sufferings in life and presence of cycle of birth and death. Ignorance is the main cause of bondage.
(21) LIBERATION: Universally it is accepted that it is the absence of sufferings and stoppage of the cycle of birth and death, when we get away from ignorance and becomes aware then we are liberated. body is the accidental quality of one soul)
CREATION THEORY AND EVOLUTION THEORY
Q: Analyse the technological arguments of the proof of existence of God (2009 m) (30)
Order
System – purpose – concious creator
Harmony
(22) Creation theory says that God is the creator of the world (Religious person), (God is like absence landlord)
(23) Evolution theory says that evolution is the reason behind the creation of world. (Scientific Person)
(24) DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INDIAN AND WESTERN PHILOSOPHY
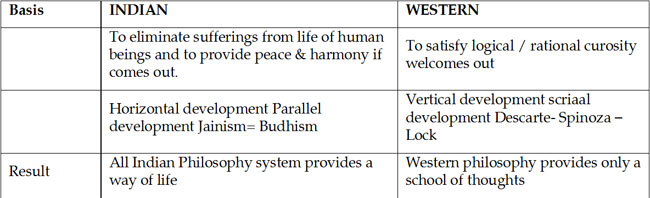
(25) IDEALS- These are whatever is should be they are the aims of anybody’s life, which (ideals) differentiate between right and wrong. They are something what we want to actualise. Figure
(26) EXISTENCE- Existence can be of two types. Mental and real. Everything which has existence has some space and time and thus it is limited and changable and finite.

