NEW! The Gist (APR-24) | E-BOOKS |
(IGP) GS Paper 1 - India & World Geography - "South America"
Integrated Guidance Programme of General Studies for IAS (Pre)
Subject - India & World Geography
Chapter : South America
South America:
Situation : Situated to the south of North America, mostly in the Southern Hemsphere. It is surrounded by the Caribbean Sea in the north, Atlantic Ocean in the east, Antarctic Ocean in the south and Pacific Ocean in the west.
South America as well as Mexico, Central America and West Indies are collectively known as Latin America.
Important Gulfs, Peninsulas and Straits:
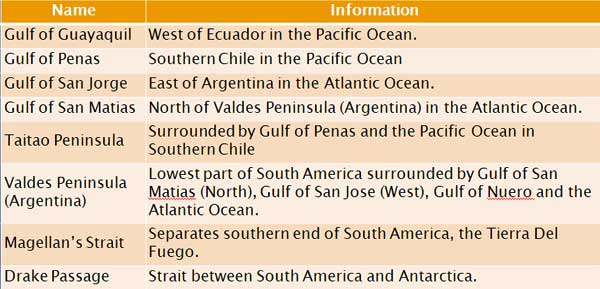
Important River Basin of South America:
Amazon River Basin
- Source : Andes Mountain, Peru
- Mouth : Macapa (Brazil) in the Atlantic Ocean
- 6,500 km long river flowing through Peru and Brazil to the Atlantic Ocean.
- World’s second longest river after Nile and has the greatest volume.
- Madeira is the largest tributary of the Amazon River.
- The river basin is covered with dense equatorial forest which are locally called Selvas.
- Rubber was first discovered in its wild state as Para rubber in the Amazon basin.
- Guicas practice subsistence agriculture in the river basin.
For Detail Description, Analysis and More MCQs of the Chapter Buy this Study Notes:
Orinoco River Basin
- Source : Guiana highlands.
- Mouth : Enters the Atlantic Ocean via huge delta.
- The river basin is covered with Lianos, Savanna like vegetation.
- Angel Falls, the highest in the world is located on the river.
The Western Mountains:
- Forms the second highest mountain system in the world, next to the Himalaya.
The Andes Mountain System
- Aconcagu (6960 m), an extinct volcano is the highest peak of Western Hemisphere lies in Argentina.
- A part of seven countries; Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Bolivia, Peru, Chile and Argentina.
- The Andes range is widest in Bolivia (640 km) and comprises two chain
(Cordillera Occident al and Oriental); the Altiplano (high plateau) lies
between these two chains.
(i) Cordillera Occidental
(ii) Cordillera Central
(iii) Cordillera Oriental - Three parallel north-south ranges of the Andes dominate the western part of Colombia with altitudes between 3,000 m and 5,000m.
- The two parallel north-south ranges of the Andes dominate the Central Ecuador.
- Chimborazo (6,310 m) is the highest peak of Ecuador and Mt Ojas del Salado the highest active volcano in the world, is in Argentina.
BRAZILIAN HIGHLANDS:
- Rising from Brazil’s Atlantic coast and levels off into high towards the western side of Brazil.
- Rich in mines, coffee plantation, and cattle ranches.
- Highland region is characterized by coniferous forest while the drier region is covered with Savanna-like grassland (Campos).
GRAN CHACO:
- A great lowland centred on western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and south eastern Bolivia.
- It has warm temperate forest and grassland to the south of Selvas.
- Dry scrubland used mainly for cattle rearing.
- It means ‘The Hunting Land’ in the local language.
ATACAMA DESERT:
- A coastal desert in Chile.
- The world’s driest desert.
- It contains a number of salt lakes.
- Rich in gold, nitrate (caliche), copper and sulphur.
PAMPA:
- Vast monotonous temperate grassland that covers about 20% area of Argentina’s heartland.
- One of the world’s greatest agricultural regions for grain and beef.
- Alfa-Alfa, a nutritious leguminous grass is grown for commercial grazing.
PATAGONIA PLATEAU:
- Piedmont plateau of the Southern Argentina, rain shadow region with little rain called Patagonia desert.
- Grazing land for sheep and cattle.
For Detail Description, Analysis and More MCQs of the Chapter Buy this Study Notes:

