NEW! The Gist (FREE) | E-BOOKS |
(IGP) IAS Pre Paper - 2: GS - Basic Numeracy - Unitary Method
Basic Nmeracy
Unitary Method
Unitary method is the basic area of arithmetic. In the CSAT paper this portion of Basic numeracy will help you to solve myriad problems.
Direct Proportion
Two quantities are said to be directly proportional, if on the increase in
one the other increases proportionally or on the decrease in one the other
decreases proportionally.
eg, More the numbers of articles, More is the cost.
More the number of workers, More is the work done.
Less the number of articles, Less is the cost.
Less the number of workers, Less is the work done.
Indirect Proportion
Two quantities are said to be indirectly proportional, if on the increase in one the other decreases proportionally or on the decrease in one the other increases proportionally.
eg, More the number of workers, less is the number of days required to finish a work. More the speed, less is the time taken to cover a certain distance.
Less the number of workers,more is the number of days required to finish a work. Less the speed, more is the time taken to cover a certain distance.
Chain Rule
When a series of variables are connected with one another, that we know how much of the first kind is equivalent to a given quantity of second, how much of the second is equivalent to a given quantity of the third and so on. The rule by which we can find how much of the last kind is equivalent to a given quantity of the first kind is called the Chain Rule.
Example 1: If 12 apples cost Rs 216, what is the cost of 3 dozen
apples ?
Solution. Let the required cost be Rs x. Also, 3 dozen apples = 35 apples
more apples, more cost (Direct Proportion);
Apples
Cost in Rs
12
216
36
x
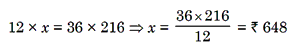
Example 2: A man completes 3/5 of a job in 18 days. At this rate, how many more days will it take him to finish the job?
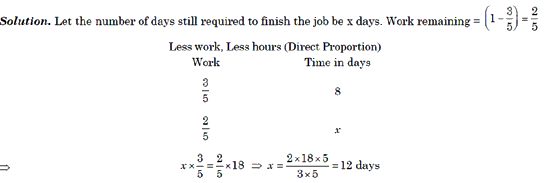
Example 3: A wheel that has 5 cogs is meshed with a larger wheel of 15
cogs. When the smaller wheel has made 27 revolutions, then the number of
revolution made by the larger wheel is
Solution. Let the required number of revolutions made by larger wheel be
x.
More cogs, Less revolutions (Indirect Proportion)
Cogs
Revolutions made
5
27
5
x
![]()
Example 4: If the wages for 8 men for 24 days be Rs 3040, then find
the wages of 6 men for 18 days.
Solution. Let the required wages be 7 x.
Less men, Less wages (Direct Proportion)
Less days, Less wages (Direct Proportion)
Men Days
Wages in Rs
8
24
3040
6
18
x
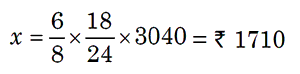
Example 5: If a man walks a certain distance in 20 days when he rests
10 h each day, how long, will it take him to walk three times as far, if he
walks twice as fast and rest 12 h each day?
Solution. In the first case the man walks (24 –10)hr = 14h each day. Let
the distance travelled bed and the speed be s. In the second case the man walks
(24 –12) hr = 12 hr each day. The distance travelled is 3d and the speed is 2 s
Let the required number of days be x.
More distance, More days (Direct Proportion)
More speed, Less days (Indirect Proportion)
Less hours, More days (Indirect Proportion)
Distance
Speed
Hours Days
d s
14
20
3d
2s
12 x
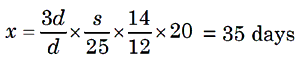
Example 6: A contractor undertakes to complete a road 420 m long in
140 days and employ men for the work. After 70 days he finds that only 140 m of
the road is made. How many men should the contractor employ more so that the
work may be completed in time?
Solution. In the second case in (140–70) days ie, 70 days the length of
the road to be construct (420-140) m ie, 280 m. Let the number of men employed
be x.
More length of road, More men (Direct Proportion)
Days Length of road in
metre
Men
70
140
28
70
280
x
![]()
© UPSCPORTAL.COM

