(FREE) UPSC Current Affairs 2025 PDF
NEW! The Gist (MAY-2025) | E-BOOKS
(IGP) IAS Pre: GS - Indian History - Ancient India : The Vedic (Part - 2)
Ancient India
The Vedic (Part -2)
RELIGION AND PHILOSOPHY
Philosophical schools
Nastik - Athestic
Astik — Thestic
Nastik - (a) Carvak -
(b) Jainism -
(c) Buddhism -
SCHOOLS OF PHILOSOPHY CHIEF EXPOUNDER
Astik -
(a) Sankhya - Kapil
(b) Yoga - Patanjali
(c) Nyayay - Gautam
(d) Vaisesika - Kannad
(e) Mimansa - Jaimini
(f) Vedant - Bhadrayan and Shankaracharya
UNORTHODOX RELIGIOUS MOVEMENTS
Early Buddhist texts speak of six foremost opponents of Lord Buddha who were
(1) Ajit Kesh Kamblin - (Believed in Materialsm)
(2) Maskari Gosal - (Founder of Ajivaka sect)
(3) Puran Kasyap - Atomist)
(4) Pakudh Katyayam - (Believed in fatalism)
(5) Sanjay Vethaliputta - (Believed in materialismsynicism)
(6) Niggantha Nathputta - (He was Bhagvan Mahavir
Charvak
This school of philosophy is also known as Lokayat. According to this philosophy there is no Law of Karman and no rebirth. There is no conscious entity like soul. It also promulgated that death is the only end.
Jainism
This school of philosophy is based on the teachings of Parsvanath and Mahavira. The doctrine of Jainism is known as Anekantvad. Jaina doctrine is also called Syadvad. This school of thought recognises five sources and kinds of knowledge. These are Mati (sense-perception), Sruti (intelligible symbols), Awadhi (knowledge acquired through supernormal means), Manahprayay (telepathy) and Kevalya (Omniscience). Jainas also believe that Jivas are infinite in number.
Bhagvatism
Chandogya upanishad depicts about Lord Krishna.
- Sutra of Panini speaks of Lord Krishna and Krishna was disciple of Ghora Angirasa.
- Bhagvatisrn is known as Satvat, Eknatika Dharma;
- This believes in the worship of Panchavrishni Veers named Bairama, Krishan, Pradyaman, Samb and Anirudha.
- Samb introduced Sun worship in India.
- Nagri, Ghosundi and Besa nagar inscriptions depict about this cult.
- Later on it was known as Vaishnavism.
- The philosophy of this cult is called Bhakti that means complete surrenderence to God.
- Follower of Krishna were known as Bhagwat.
- Follower of Narayan were known.as Vaishnav his cult.
In South India this cult was promulgated by Vaishnav saints called Alvars. There were eleven great Alvars. There devotional anthologies are of great fame. The best one is known as Halaroyam Which was composed by Wamalvar.
Buddhism
Buddha’s four noble truths are called Aryasatya. These are
(1) Dukha - (World is full of miseries).
(2) Sukha Smudya - (Causes of miseries).
(3) Dukh Nirodh - (Miseries can be checked).
(4) Dukh Nirodha Gamini Pratipada - (Eight fold path).
Eight Fold Path (Astangik Marg)
Right Faith (Samyak Dristi)
Right Resolve (Samyak Sankalp)
Right Speech (Samyak Vak)
| EVENT | SYMBOL |
| Birth | Lotus and Bull |
| Great renunciation | Horse |
| First Sermon | Dharmachakra or wheel |
| Nirvana | Bodhi tree |
| Pararinivana or Death | Stupa. |
| Three Ratna | Budha Dhaxnma, Sangha. |
Right Action (Samyak Action)
Right Living (Samyak Ajiv)
Right Effort (Samyak Vyayam)
Right Thought (Samyak Smriti)
Right Concentration (Samyak Concentration)
Buddhism believes in Law of Karman operating in this life and next. In this regard Buddha also talked about twelve-linked chain of causation. (Dvadas Nidan).
Other schools of Buddhist Thought
1. Vaibhasik of Vijanvada — Entire world is mental in structure. Ideas of the mind are the stuff of the world and the entire world originates from Alyavijana (Cosmic-consciousness) Asvaghosh was the most renowned leader of this school.
2. Madhyamika (Sunyavad) — There is nothing real in this world Ngaup was the chief exponent of this school.
Astika
1. Sankhya: It is a kind of dualistic ontology. It believes in two ultimate realities Prakrit and Purusa. Prakrit is made of a triad of fundamental attributes (Gunas) called Sattva, Rayas and Tamas. Purusa is pure consciousness.
2. Yoga System : It is applied Samkhya. It has devised a systematic method of bringing about the release of Purusa from Prakriti through mental mechanism.
3. Nyaya : It considers God as the creator who is free from Law of Karman. God is a soul and his wisdom, desire and effort are unbounded. Nyaya makes a detailed study of the sources of knowledge (Praman)
4. Valsesika : When the atoms of five basic elements begin to combine the creation of the world begins. Creation and dissolution of the world go on in cycles.
5. Mimansa : It is a philosophy of interpretation, application, and use of truths of Samhita and Brahmanas portions of the vedas. It has devised certain principles according to which the vedic mantras and their application in the field of sacrifies could be understood.
6. Vedant : According to this philosophy Atman and Parmatman are same. Partmatman is the ultimate reality and the whole world is an illusion (Maya). The whole philosophical thinking of this school is based on Upthiisahd, Bhagwatgeeta and Brahamsastra of Bhadrayan, called Prasthantrayi.
Buddhism
- Buddha was born at Lumbanivan in 563 B.C.
- His father was the king of Kapilvastu.
- He belonged to the clan of Sakyas, so he is called Sakyamuni and also Sirnha Sakya.
- Yasodhara was his wife and Rahul was his son.
- Buddha renunciated the wordly life when he was 29 years old.
- He meditated at Uruvela. There he got Nirvan. This place was later on known as Bodh Gaya.
- Buddha gave his first sermon at lsipatan, i.e. modern Sarnath.
- Bimbisar and Ajatsatru were his contemporary ruler of Magadh.
- Prasenjit of Khosla was also his contemporary.
- Bimbisar donated him Venuvan at Rajgriha.
- Anath Pindak donated him jetvan at Sravasti.
- Gautami was the first woman who joined the Sangha.
- Anand and Upali were his twomost eminent disciples.
- Buddha got his Mahaparinirvan at Kusinara.
Important Seats of Buddhism
- Sthavirvadi — Only ten people can get Buddhahood.
- Mahasanghika — Every one can get Buddhahood.
- Sautantrik — They wrote their texts in Sanskrit language.
- Sammitiyas — They believed in Atma (Soul)
- Hinyana — Buddha was only a great saint.
- Mahayana— Buddha was a great incarnation.
- Yogachar (Vijanvad) —They believed in Yoga and called it vijan.
- Sunyavad — There is nothing real in this world. It was also known as Madhyamika sect.
- Vajrayan — It believed in Tantra.
SECTSFOUNDERS
- Theravada - Mahakatyayam
- Mahasanghika - Mahakashyapa
- Sarvastivadin - Rahul bhadra
- Mahayan - Vasumitra
- Yogachar - Asang / Varusandhu
- Sunyavad - Nagarjuna
BUDDHIST TEXTS
Pitak-
(1) Sut Teachings of Buddha
(2) Vinay Discipline and order
(3) Abhidhamma Esoteric Philosophy
(1) Khuddak Nikaya of Sut Pikak has 15 tents.
- Dhammapad It is known as Bhagvatgita of Buddhism.
- Jatak This is collection of 550 stories of the previous births of Buddha.
(2) Vinay Pitak has three parts known as Parivar, Khandak and Vibhanga.
(3) Mahavibhasa sutra was written by Vammitra.
(4) Guhya Samaj Tantra and Manju Sn Miii Kalpa are the texts of Vajrayan.
Jainism
- According to Jainism there were 24 Trithankaras (Enlightened Monks).
- 23 Trithankar was Parsavanath. He was the son of the king of Kasi. He was a historical figure.
- Mahavira was born in the family of Jantrika.
- Yasodawas his wife and Priyadarsa was his daughter.
- Herennounced the family life when he was 30 years old.
- He got Kaivalya at Jrimbhakgram.
- His disciples were called Ganadhara.
- Sudharman became the head of the Jam sangha after him.
JAIN TEXTS
- 12 Angas
- 12 Upanga
- 10 Prakrinaka
- 6 Bhedsutra
- 4Sutra
- Churnika was commentary
- Way to Nirvana (Three Ratna)
- Right faith (Samyak Vishwas)
- Right knowledge (Samyak Gyan)
- Right conduct (Samyak Karma) Various Heterodox Philosophies
NIYATIVADA
- Third religious chief was Makhkhali Putta Gosal (supposed to be the real founder who popularised it).
- Followers are known as Ajivikas.
- Main profession was fortune telling and Astrology.
- Philosophy is based on Niyati (Destiny) which means everything in the world is predetermined.
- Makhkhali Gosala was a companion of Mahavira and this sect had a lot in common with Jainism.
- Bindusar was disciple of Ajivikas.
- Practised complete nudity and rigorous practices.
- Ashoka donated Barabar cvend king Dhasarath donated Nagarjuni cave to Ajivikas.
Click here to download full Chapter
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS HISTORY 11 YEARS SOLVED PAPERS PDF
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS HISTORY 10 Years Categorised PAPERS
Study Noted for UPSC MAINS HISTORY Optional
Materialism
- Developed by_Brihpor Charvaka.
- Followers are known as Charvakas or Lokyatas.
- Believed that nothing existed which could not be understood by five senses.
- Believed that earth, water, fire and air are the only elements.
- Believed that death was ultimate and everything ended after death.
- Believed that there was no soul, no god, no rebirth, no karm—’
Akriyavad/Antinomism
- Founder was Purana Kasyapa (a brahmin of Kasyapa gotra).
- Believed in the doctrine or non-action.
- Believed that action did not lead to either merit or demerit.
Akrittavada /Aagasvatavad/Anunada
- Founder was Pakuda Katyayana.
Unhchedavada /Jarvada /Annihilationism
- Founder Ajita Keshakamblin (meaning with the hair blanket)
- Believed in materialistic philosophy.
- Ajita was the earliest propounder of materialism
Bhagvatism
Facts about Bhagvatism
- Religion based on the idea of a supreme God Han or Narayan or Vishnu (later known as Vaishvanism).
- Main philosophy is Bhakti, complete surrender of self to God and salvation through his prasada.
- Did not believe in sacrifice and slaughter of animals.
- Rise in west among the tribe satvatas (a branch of yadavas) in Mathura region.
- Vasudeva-Krishna of Vrishni race was the chief God who discussed its philosophy in Bhagvad — Gita
- Vasudeva— Krishna was the disciple of Ghora Agnirasa.
- Bhagvat—Gita gives amphasis on one’s wordly duties as dharma.
- Magasthenes refers to Krishna as Herakies of Sourseni tribe.
- Ten awatares
- Matsya (Fish)
- Kurma (Tortoise)
- Varaha (Bear)
- Narsimha (man-lion)
- Vamana (Dwarf)
- Parasurama (Rama with the axe)
- Rama
- Krishna
- Buddha
- Kalkin (As a man on a white horse with a sword in his hand, the awatara yet to come in Kaliyuga).
10. The earliest reference to Krishna is found in Chhandogya Upanishad. Here he is represented as pupil of Ghora Angirasa and son of Deviki.
11. The reference of Vasu4eva is found in Panini’s Astyaohyagi and Patanjali’s Mahabhashya.
12. The Besnagar Pillar inscription is associated with Heliodorus son of Dion and a native of Taxila, and ambassador from the court of the Indo-Greek king Antialkidas to King Bhagabhadra (Sungas) who erected a garduadhwaj at Besnagar and claimed himself a Param-Bhagvata.
13. Pancharatra (of five nights), a vaishnavite school gave the doctrine of Vyuha (emanations) according to which Sankarsana (aftother name of Bulrama) Pradyumna (Krishna’s Son) and Aniruddha (Krishna’s grand son) emerged out of Vasudeva.
14. Developed and popularised in South by twelve saints known as Alvars.
15. Total No. of Nayanar saints was 63 and they were shaiv.
- Tirumurai which is consider as fifth veda in which the preaching of Aiwar and Naynar saint were compiled in 11 volumes.
Saivism
Facts about Saivism
- Developed around the concept of Siva associated with the vedic god Rudra.
- Wema Kadphises, the Kushana king adopted salvism and depicted ‘he figure of siva with trident and Nandi on the reverse of his coins.
- Developed and popularised in south India around 500 A.D. by the saints Nayanars, 63 in number.
- The sacred literature of the Saivas is known as Saivagama.
- The God Shiva ismentioned by different names namely Ishwara, Mahadev, Mahesvara, Shankara, Bholenath.
- The collection of the songs of 63 Nayanars is knows as Tevaram stotras and is in Tamil. It is also known as Dravida - veda.
- Agmas, 18 in number and said to have been composed by the various aspects of Siva himself are the greatest work in salvism.
- Various forms of siva:
- Nataraja — Lord of dance, invented 108 forms of dances, tandava, a fierce dance is one of them.
- Dakshinamurti — A God south-facing.
- Ardhanariswara — Haif-siva and haifparvati representing the union of God with his sakti.
9. In South India, daughter of a Pandayan king named Minakshi is associated with Siva as his spouse and the Minakshi temple of Madurai had been constructed to celebrate the event of marriage of Siva with Minakshi.
Various sects of Salvism
Pasupatas / Naku1isapasupatas
- Founded by Lakulisa / Nakulisa I Lakulin /Lakutin
Kalmukhas /Kapalikas
- Extreme forms of Saivism Mattamayuras
- Moderate form of Saivism
- Developed in central India.
Virasaivas /Lingayats
- Founded by Basava, the prime minister of
Bijjala, the Kalachuri king.
- Popular in Kamataka region.
Kashmir Saivism
Pratyabhijna
- Founder is Vasugupta (800-900 AD)
- Moderate form of Saivism.
Spanda — sastra
- Founders are Kallata and Somananda the two desciples of Vasugupta
- Moderate form of Saivism
- Believes in spitirual development
Agmantas
- Greatest exponent was Aghora Sivacharya (1200 AD).
Facts about Buddhism
Life of Siddhartha (Gautam Buddha)
| 1. Title | Buddha, Sakyarnuni, Tathagata |
| 2. Birth Place | Lumbini (Modern Rumindel /Rupan—Delhi) in Kapilvastu (Piparwaha) |
| 3. Birth Year | 563 BC |
| 4. Clan | Sakya |
| 5. Class Caste | Kshatriya |
| 6. Gotra Name | Gautama (Gotama in Pali) |
| 7. Foster Mother | Mahaprajapati Gautami |
| 8. Wife | Bhadda Kanchana, Subhadraka, Bimba, Gopa, Yasodhara |
| 9. Cousin | Devadutta |
| 10.Son | Rahul |
| 11.Horse | Kanthaka |
| 12.Charioteer | Channa |
| 13.Teachers under whose guidance Sidhartha remain for quite some time before he attained enlightenment |
Alara Kama & Ruddaka Ramaputta |
| 14. Got enlighten- ment at | Uruvela (modern Bodh Gaya) on thebank of the river Niranjana |
| 15.Got enlightenment under the tree | Pipal (known as Bodhitree) |
| 16.Delivered, first sermon at | Deer Park in Sarnath (Isipatna) |
| 17.Death (year | 483 BC at the age of 80 yrs |
| 18.Death (Place) | Kushinagar (Kushinara) in U.P., capital of the Mallas |
| 19. Birth, Enlightenment & Death | Vaishakha Purnima (Full Moon day |
| 20.Preached most of his sermons at Sravasti | |
FOUR NOBLE TRUTH / CATTARIARIYASACCANI
- Sorrow (dukkha) — The world is full of sorrow
- The cause of sorrow (dukkha samudaya) / is desire
- Cessation of sorrow (dukkha— nirodha)
- The path leading to the cessation of sorrow (dukkha — nirodhagamini pratipada) is Ashtangikamarga
Eight Fold Paths /Ashtangika Marg
- Right belief/observation /views (Samnia — Ditthi) — Understanding that desire is the cause of sorrow and the ending of it will lead to the liberation of the soul.
- Right thought / determination / resolve (Samma — Sankappa) — Avoiding the enjoyment of the senses and luxury & to love humanity & increase the happiness of others.
- Right speech (Samma — Vaka) — Always tell truth.
- Right action/effort (Samma — Kammanta) — Unselfish action.
- Right means of livelihood (Samma — Ajiva) — Man should live by honest means.
- Right endeavour/conduct (Samma — Vayamma) — Proper way of controlling senses for preventing bad thoughts through correct mental exercises that one can destroy desire & attachment.
- Right recollection /memory (Samma — Sati) — Emphasises the meditation for the removal of wordly evils.
- Rightmeditation (Samma— Samadhi)—leads to peace.
Buddhist order (Sangha)
1. Provisions of the membership
- No caste restriction
- Slaves, soldiers, debtors and other persons under obligation were not to enter it without the permission of their superior.
- Criminals, leapers and persons affected by infectious diseases were not given admission into it.
- On the repeated requests of the chief disciple of Buddha Ananda and his foster mother Mahaprajapatl Gotami, admitted the women in Sangha.
1. His foster mother Gautami became the first woman to join the Sangha.
2. During the four months of the rainy season the monks look up a fixed abode and meditated.
Three Jewels in Buddhism
- Buddha (Enlightened one)
- Dhamma (Doctrine)
- Sangha (Order)
Symbols Signifying Different Events of Buddha‘s Life
- Birth - Lotus & Bull
- Renunciation - Horse
- Enlightenment - Bodhi tree
- First Sermon - Wheel
- Death - Stupa
Four Great Events in the life of Buddha
- Mahabhiniskarman - Renunciation
- Nirvana - Enlightment
- Dhammachakaparivartan - First sermon
- Mahaparinirvana or Parinirvana - Death
Name of Famous Buddhist Scholars
Upali, Ananda, Vasumitra, Asvaghosha, Sabakamik, Moggaliputta Tissa, Nagarjuna, Buddhaghosha, Asanga, Buddhapalita, Bhavaviveka, Dinnaga, Chandrakirti, Sthrimati, Dhammapala, Aryadeva, Santideva, Santaraksita, Kamalasila. Dharmakirti.
Five Buddhas in Buddhist Tradition
Krakucchnada, Kanakamuni, Kasyapa, Sakyamuni And Maltreya (Yet to Come) Four Signs in Buddhism
- Oldman
- Sick man
- Corpse
- Saint
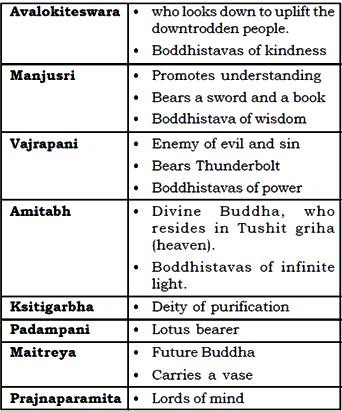
Various Boddhistavas In Buddhist Tradition
Buddhist Councils
I. First Council
- Year—483B.C.
- Place — Saptparni Cave (Near Rajagriha)
- Over By - Mahakassapa Upali
- Under - Ajatsatru
- Purpose — To compile the Buddhist scriptures
- Outcome
- All the teachings of Buddha were divided into two pitakas
- Vinaya Pitaka— established under the leadership of Upali
- Sutta Pitaka — settled under the leadership of Ananda
II. Second Council
- Year-383B.C.
- Place — Vaisali
- Presided over by— Saba Kami
- Under — Kalasoka / Kankavarmin
- Purpose — To settle down the dispute between the two opposing groups monks of Vaishali and Patliputra and monks of Kausambi and Avanti regarding the code of discipline.
- Outcome
- The council failed to brag about a compromise between the two opposing groups.
- The council ended in a permanent split of the Buddhist order into Sthaviravadins and Mahasangikas.
III. Third Council
- Year—237 Bc
- Place — Patliputra
- Presided Over By - Mogali Putta Tissa
- Under — Ashoka
- Purpose — To Revise the Scriptures
- Outcome
- The Philosophical interpretations of the doctrines of Buddha were collected into third Pitaka called Abhidhamma Pitaka.
- Heretical monks numbering sixty thousand were expelled from the order
IV Fourth Council
- Year-100A.D.
- Place — Kundalavana In Kashmir
- Presided over by — Vasumitra
- Under — Kanishica.
- Purpose — To settle the disputed doctrines
- Outcome —Rise of Mahayana and Hinanyana
- Compiled commentaries (Upadesa Sastras & Vibhasa Sastra) of the three pitakas.
- Decided certain controversial questions of differences that arose between the sarvastivada teacher of Kashmir and Gandhara.
Kings who gave Patronage To Buddhism
Bimbisara, Ajatastru (Magadha), Prasenjita (Kosala), Udayana (Kausambi), Ashoka, Menander, Kadphises, Harsha, Kanishka, Dharampala, Kujula. Famous Buddhist Centres (1) Bharhut (2) Sanchi (3) Sarnath (4) Bodhgaya (5) Nalanda (6) Purushapura (7)Taxila (8) Mathura (9) Amarvati (10) Karle (11) Kanheri (12) Nagarjunkonda (13) Odantpuri.
Schools of Buddhism
- Mahasanghikas
- Sthavlravadin / Theravada
- Sarvastivadin
- Mahayana
- Believed in the divinity of the Buddhas
- Worshipped the images of several Buddhas and Bodhistavas.
- “Sanskrit” became the language of preaching and teaching.
- It had two chief philosophical schools, the Madhyamika and the Yogachara.
- Prominent place given to the Bodhistavas — who were being of great kindness and helped the humanity through their own suffering.
- Teaches the salvation for all.
- Believed in the original teachings of the Buddha.
- Popular in Ceylon, Bunna, Thailand, Combodia, Loas etc. but lost its popularity in India.
- Teaches the attainment of salvation for oneself alone.
- Salvation through self-descipline and meditation.
- No belief in idol-worship. Worshiped Budha in form of the symbols.
- Adopted Pali as the language for teaching and texts.
6. Vajrayana / Vehlcle Of Thunder Bolt
- Salvation attained by acquiring the magical power.
- The chief divinities of this new sect were the Taras, wives of the Buddhas and Bodhisattavas.
- Yogic and megical in character.
7. Yogachara/Vinanayadin
- Founded by Miitreyanath around 400 AD.
- The only reality is tahatata/suchness/ thusness or Dharamadhatu which is equivalent to Sunyata of Madhyamika school.
8. Madhyamika
- Founded by Nagarjuna / Nagasena around 150 AD.
- Philosophy of Sunyavada/Sunyata/Void/ Emptiness according to which everything around us is emptiness and whatever we perceive is only illusion.
- Associated with theory of relativity.
Other Important seats of Buddhism
9. Sautrantikas
10. Samitlyas
11. Lokottaravadin
12. Pudgalavadin
13. Shahajnyana
14. Tantrayana
Buddhist Scriptures
- Buddshist Scriptures are Pitakas, which are written in Pall language.
- It consists of three sections called Tripitakas.
I. Sutta Pitaka
- Largest & most important of the Tripilakas. contains the teachings of Buddha.
- It is divided into five “Groups” (Nikayas)
- Digha (long) Nikaya — Collection of long sermons ascribed to the Buddha, with accounts of the circumstances in which he peached them.
- Majjhima (medium) Nikaya — Shorter sermons
- Samyutta (connected) Nikaya—Collections of brief pronouncements.
- Anguttara (Graduated) Nikaya—Collection of over 2,000 brief statements, arranged in eleven sections.
- Khuddaka (Minor) Nikaya
3. Contains miscellaneous works in prose and verse.
4. Among the contents of Khuddaka are Dhammapada (versus on virtue) is containing a summary of Buddha’s universal teachings. Tharagatha (Hymns of the elder monks) Therigatha (Hymns of the elder nuns) Jatakas (a collection of over 500 poems which describe the previous birth of Buddha, many of them being in the animal forms).
II. Vinava Pitaka
Contains moral code of conduct
III. Abhidhamma Pitaka
Consists of philosophy of Buddhism especiallymela physics.
Buddhist Works
1. Milinda-Panho (Questions of Menander) — An account of the discussion between Bacterian king Menandar or Milinda and the Buddhist monk Nagasena.
2. Ceylonese chronicles — The history of Buddhism in Ceylon and give valuable information on political and social history
Click here to download full Chapter
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS HISTORY 11 YEARS SOLVED PAPERS PDF
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS HISTORY 10 Years Categorised PAPERS
Study Noted for UPSC MAINS HISTORY Optional
© UPSCPORTAL.COM


