NEW! The Gist (FREE) | E-BOOKS |
India and WTO : Important Topics for UPSC Exams

India and WTO : Important Topics for UPSC Exams
Mandate of WTO:
WTO came into existence after the conclusion of the Uruguay round in 1995 replacing the post WWII General Agreement on trade and tariff (GATT). It was an improvement over GATT in the following ways:
-
Providing an institutional backbone to GATT
-
Provision of a dispute settlement body
-
Representation to the developing nations in its formation and negotiations
-
Covering other trade related aspects such as services, IPR, investments etc.
-
It included safeguards against non-tariff barriers as well
The objective of WTO is to establish a rule based global trade regime providing equitable opportunity to every nation for reaping the benefits of globalization. WTO works on the following principles:
-
Non Discrimination
-
Most Favored Nation: No special favors can be granted to any trading partner
-
National Treatment : No discrimination between the imported and domestic products once they enter the market (which allows imposition of custom duty)
-
-
Freer Trade: removal of the tariff and non-tariff barriers gradually through negotiations
-
Predictability: providing predictability in the trade policy through binding rules and transparency
-
Promoting fair competition: providing a system of rules dedicated to open, fair and undistorted competition such as allowing for imposition of anti-dumping duty
-
Encouraging Development and Economic Reforms: nudging the countries towards an open market and allow for special assistance and trade concessions for developing countries
Buy Printed Complete Study Materials for UPSC IAS PRELIMS Exam
Online Crash Course for UPSC PRE Exam
Why WTO is important for India:
-
Free and Fair trade
India has visibly benefitted from the open market reforms that it embraced in the early 1990s. It could sustain its higher growth rates only because of globalization. But at the same time it requires protection for its industry from the cheaper products from the developed nations with superior tech and higher capital. Through WTO India can ensure and rule based global trade regime.
-
Globalization:
WTO has played an instrumental role in the success of globalization with its various agreements such as TRIPS, TRIMS, GATS etc. that have created a fine balance between the interest of developing and developed nations. India has been a major beneficiary of the globalization in terms of economic growth, employment, poverty number, standards of living etc. Expansion in the footprints of globalization will open up new markets for India further boosting the investments and employment opportunities
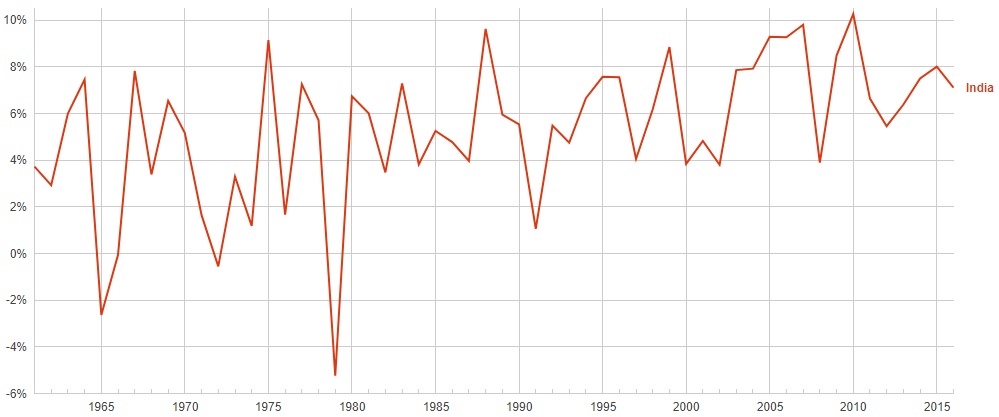
-
Leadership role:
India harbors the ambition of becoming superpower and therefore need more and more foras to take up the leadership roles as it has been doing at WTO. In the recently concluded ministerial conference at Buenos Aires, it successfully defended the interests of developing nations against the attempts of developed nations to subvert the agenda as agreed to under DDA
-
Global inequality:
The share of the developing nations in world GDP has been rising steadily since the advent of globalization which is evident from the increased prominence of G20 over G7. For the trend of shrinking gap between the GDP of developing and developed nations WTO will be playing a crucial role in the future. It is also essential to realize SDG goal 10 which seeks to reduce inequalities
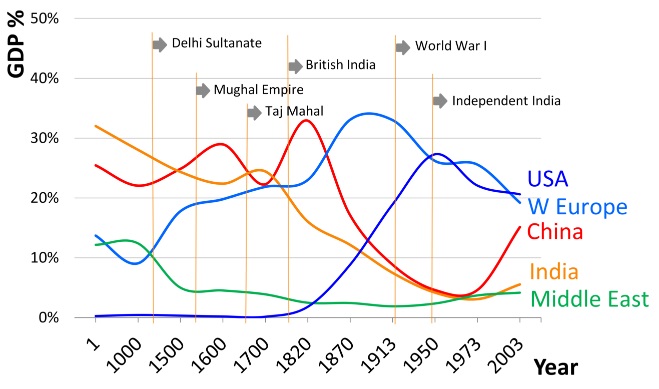
-
Bulwark against protectionism
WTO can be an insurance against the rising tide of protectionism which has the potential of halt the successful streak of globalization. Rise of protectionist tendencies in USA and Europe have the potential to reverse the trend of global growth and benefits accruing from it especially for India with a sizable diaspora and being the largest recipient of remittances
-
Fair mechanism for dispute settlement
One of the factors behind the increasing relevance of WTO in the recent times is its free and fair dispute settlement mechanism. The US-Brazil cotton dispute which became a landmark case has assured the developing nations that their interest can be protected by WTO
-
TFA for services
For India service sector continues to be its major strength and will be the major beneficiary upon the conclusion of the Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) in services as proposed by India
Challenges India faces at WTO
-
Conflicting interests of developing and developed nations:
The conflict became more pronounced during the recent ministerial conference at Buenos Aires. While developing nation were pushing for concluding the agreements on Doha Development Agenda (DDA), developed countries like USA, Japan and other clubbed together to include issues like e-commerce, investment etc. into the negotiations without a final agreement on DDA
-
Agricultural subsidies:
Since India is an agrarian economy based on employment heavily subsidized agricultural products of developed nations have always been a cause of concern for agri-exports from India. The present quota of subsidies is based on the price levels of 1986-88 allowing developed countries to take away a major chunk of trade distorting subsidies quota
-
Issue of public stockholding
The minimum support price (MSP) provided to farmers in India falls under the Amber box category of subsidies under WTO which have to be removed. However, it directly affects India’s food security and income of farmers. Though a ‘peace clause’ agreed to during Bali conference allows India to carry on with its PDS program as of now, developed countries are hindering the realization of a permanent solution to the problem
-
Divisions within developing nations
There are divergence with the developing nations such as India and china on various trade related issues. In the recent conference while many developing nations supported the issues like E-commerce propose by developed nations, those lead by India staunchly opposed it
-
Attempts to derail the judicial body
USA under the new administration has been blocking the appointment to WTO’s appellate body which could erode the credibility of WTO as an effective arbitrator in future (1)
-
Lack of alternatives
There are only few other multilateral bodies that deal with issue of global trade. Though UNCTAD does concern itself with the issues of global trade, its work is mostly advisory in nature and is not binding upon the nations as in case of WTO agreements
-
Special and differential treatment (SDT):
In Doha round, member agreed to provide a favorable treatment to developing and least developed nations who have asymmetric capabilities in terms of resources. However, developed countries have been calling emerging economies such as India and China as unworthy of SDT
-
Issues related to intellectual property rights:
Though the issues related to compulsory licensing of medicines has been resolved by renegotiating the language of TRIPS, developed nations have been trying to push TRIPS+ commitments through WTO
-
Threats to existence of WTO
WTO itself faces the following threats which have the potential to turn it into a redundant and ineffective bodies.
-
-
Rising protectionism: The rising wave of protectionism across the developed world (USA, Brexit in UK) threatens the derailment of the ongoing as well as previous agreements of WTO. Developed nations are the primary markets for developing nations’ industries and are therefore a crucial link for success of globalization
-
Mega free trade agreements: Increasing number of free trade agreements such as RCEP, TPP etc. are an indication of WTO’s failure as well a major threat to its existence. FTAs distort the global market and are therefore need to be contained by providing fairer terms to nations in WTO agreements.
-
Way forward:
India has been leading the front for developing nations to secure their interests in the global trade rules. In doing so, it must continue to stick to the fundamental principle of equity and non-discrimination. First of all it must reach a consensus with all the other developing nations (among the G33 group) to create a united front against the developed nations. The recently held mini-ministerial conference can be used to reach such a consensus in the run up to the next ministerial conference. At the same time India must invest in its domestic industry and improving connectivity with other nations to increase its competitiveness in the global market.
Major agreements of WTO:
-
General Agreement on Trade in Services – GATS
-
Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS)
-
Trade-Related Investment Measures (TRIMS)
-
Agreement on Agriculture (AOA)
-
Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
-
Trade Facilitation Agreement for goods (TFA)
Previous year mains questions:
-
“The broader aims and objectives of WTO are to manage and promote international trade in the era of globalization. But the Doha round of negotiations seem doomed due to differences between the developed and the developing countries.” Discuss (2016)
-
WTO is an important international institution where decisions taken affect countries in profound manner. What is the mandate of WTO and how binding are their decisions? Critically analyze India’s stand on the latest round of talks on Food security. (2014)
-
WTO is an important international institution where decisions taken affect countries in profound manner. What is the mandate of WTO and how binding are their decisions? Critically analyse India’s stand on the latest round of talks on Food security. (2014)
-
Food security bill is expected to eliminate hunger and malnutrition in India. Critically discuss various apprehensions in its effective implementation along with the concerns it has generated in WTO. (2013)
UPSC prelims questions:
In the context of which of the following do you sometimes find the terms `amber box, blue box and green box’ in the news?
(a) WTO affairs
(b) SAARC affairs
(c) UNFCCC affairs
(d) India-EU negotiations on FTA
The term ‘Domestic Content Requirement’ is sometimes seen in the news with reference to
(a) Developing solar power production in our country
(b) Granting licenses to foreign T.V. channels in our country
(c) Exporting our food products to other countries
(d) Permitting foreign educational institutions to set up their campuses in our country
Consider the following statements:
1. India has ratified the Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) of WTO.
2. TFA is a part of WTO’s Bali Ministerial Package of 2013.
3. TFA came into force in January 2016.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
The terms ‘Agreement on Agriculture’, ‘Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures’ and Peace Clause’ appear in the news frequently in the context of the affairs of the:
a) Food and Agriculture Organization
b) United Nations Framework Conference on Climate Change
c) World Trade Organization
d) United Nations Environment Programme

