(Sample Material) Online Coaching for CAPF (AC): Geography - "Indian Geography (Part - 1)"
Online Coaching for UPSC Central Armed Police Forces (AC) Written Examination
Geography
Indian Geography (Part - 1)
Physiography
Location
- India lies in the northern and eastern hemispheres of the globe between 8° 4' N and 37°6' N latitudes and 68°7' E and 97°25’E longitudes.
- The southern extent actually goes upto 6°45' N latitude to cover the last island of the Nicobar group of islands. The southern extremity is called Pygmalion Point or Indira Point.
- The tropic of cancer passes through the middle part of India and crosses the states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Tripura and Mizoram.
- Its total land frontier of 15,200 kilometres passes through marshy lands, desert, level plains, rugged mountains, snow covered areas and thick forests.
- Besides there is a maritime boundary of 6,100 kilometres along the main land mass which increases to 7,516 kilometres if the coastlines of Andaman-Nicobar and Lakshadweep Islands are added to it.
- India-Afghanistan and Pakistan-Afghanistan international boundary is called the Durand Line, determined as a “militarily strategic border between British India and Afghanistan”.
- The India-China boundary (4,225 km) is a natural boundary running along the Himalayan ranges and is based on various treaties. Its eastern part (1,140 km) is called the Mc Mahon Line.
Length of India’s Border with its Neighbouring Countries
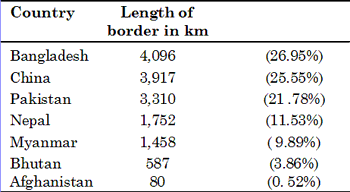
- The boundary with Pakistan and Bangladesh (the East Pakistan) was finalized at the time of partition in 1947 through the ‘RadCliffe Award’.
- India is the only country which has given its name to an ocean, i.e. Indian Ocean encircled by 46 countries (27 littoral including Australia, 7 island states and 12 land locked countries).
Size and Shape
- India commands a total geographical area of 32,87,263 sq. km which is roughly 0.57% of the area of the earth and 2.4% of the total area of the land hemisphere.
- After Russia, China, Canada, USA, Brazil and Australia, India is the seventh largest country of the world. Its area is almost equal to the area of Europe (excluding Russia), one-third of Canada, onefifth of Russia, eight times of Japan and twelve times of United Kingdom.
The states having common frontiers with neighbouring countries
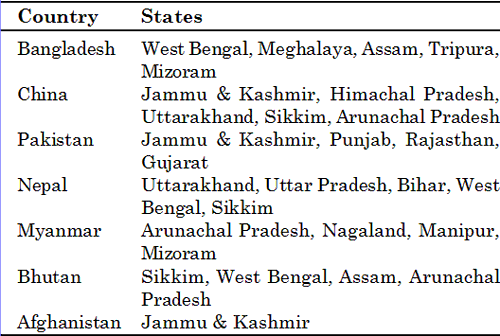
- In population-size, India (1027 million in 2001) is the second giant country in the world after China (1265 million in 2000).
- Its total population is more than - the combined population of USA, Russia, Australia, Canada and Japan.
- India has roughly a quadrangular shape. It measures about 3,214 km from north to south and about 2,933 km from east to west, the difference between the two being just 281 km.
India’s Frontiers
-
Its total land frontier of 15,200 kilometres passes through marshy lands, desert, level plains, rugged mountains, snow covered areas and thick forests.
-
The land frontier is provided by the high Himalayan Mountains, which are world’s most elevated ranges.
-
The Himalayan ranges form a natural frontier between India and China. In the northwest, India’s Jammu and Kashmir share the international border with Sinking and Tibet in China.
-
Towards its east, Himachal Pradesh and the mountain region of Uttarakhand have common frontier with Tibet.
-
Nepal has its border with Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
-
West Bengal and Sikkim also touch the Nepalese border for a small distance.
-
India-Afghanistan and Pakistan-Afghanistan international boundary is called the Durand Line, determined as a “militarily strategic border between British India and Afghanistan”.
-
The boundary with Pakistan and Bangladesh (the East Pakistan) was finalized at the time of partition in 1947 through the ‘Radcliffe Award’.
-
India’s frontiers with Pakistan are artificial and unsatisfactory except in some limited and uninhibited dry parts of the Thar Desert.
-
In Punjab, the frontier runs through a smooth and fertile plain, which is purely man made. The Indian frontier with Pakistan in Kashmir is still disputed and has led to strained relations between the two countries since partition in 1947.
-
The eastern boundaries of India are formed by a complex chain of the Himalayan offshoots consisting of the Mishmi, the Patkai, the Naga hills, the Barail range, the Mizo hills and finally the majestic Arakan Yama Mountains range.
-
The Arakan Yoma is submerged in the Bay of Bengal for sufficiently long stretch and emerges again in the form of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
-
Between the eastern states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram on one hand and West Bengal on the other hand, lies Bangladesh.
-
The boundary line between India and Bangladesh crisscrosses the vast Ganga - Brahmaputra delta. This boundary runs through an entirely flat country in which there is not even a small mount or hill which could be used for demarcating the boundary between the two countries.
-
Besides, there is a maritime boundary of 6,100 kilometres along the main land mass which increases to 7,516 kilometres if the coastlines of Andaman-Nicobar and Lakshadweep Islands are added to it.
-
The nearest neighbour in the south across the seas is Sri Lanka which is separated from India through the narrow channel of Palk Strait.
-
Similarly Eight Degree Channel forms the boundary between Lakshadweep and Maldive islands.
Nicknames of Indian cities

Important Facts
- Andaman and Nicobar islands are separated by 10 degree Channel
- Duncan passage is between South Andaman and Little Andaman.
- Water body between Indonesia and Andaman and Nicobar islands - Great Channel.
- Water body between Andaman and Nicobar islands and Thailand is Andaman sea.
- 2 Provinces of China that borders with India - Tibet and Sikiang.
- Boundary between India and China is divided into 3 parts
- J & K sector - Western sector
- H.P and Uttarakhand- Middle sector
- Arunachal Pradesh - Eastern sector
- Eastern sector - Mc Mahon line - demarcated in 1914 - according to Shimla Agreement between British India and Tibet.
- Boundary line between British India and Afghanistan - Durand line.
- Central Asian Republic very close to India - Tajikistan.
- Water Body separate India and Sri Lanka - Palk strait.
- Water body separate Lakshadweep from Maldives - 8 degree Channel.
- Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh are the states of India lying completely in the Himalayas.
- Uttarakhand lies partly in the Himalayas and partly in the northern plains.
- Coastal States of India: Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Orissa and West Bengal.
- States having international boundary and coastline; Gujarat, West Bengal.
- States having neither coastline nor international boundary 1. Madhya Pradesh 2. Haryana 3. Chhatisgarh 4. Jharkhand.
- Assam and UP share boundary with 8 other states.
- Assam shares 2 international boundaries and 8 states.
- UP has 8 state boundaries and 1 international boundary.
- Boundary line between India and Pakistan is known as RadCliffe line.
<< Go Back To Main Page
