(Online Course) Pub Ad for IAS Mains: Chapter: 4 Organisation - Systems Approach and Contingency/Situational Theory (Paper -1)
Paper - 1
Chapter: 4 (Organisation)
SYSTEMS APPROACH
System is a set of characters which work together towards
organisation goal.
Every social science including physical science do have Systems Approach.
How they try to see the phenomena is referred to as Approach.
It is a viewpoint through which any phenomenon is seen to understand that
particular phenomenon.
Theory includes not only the viewpoint or the way any thing is looked into but
also derive conclusion out of it.
Approach by and large work through hypothesis.
After the viewpoints.
After verification these are established as principles.
Systems approach has had late emergence in Public Administration As compared to
other Social Sciences.
Main root, i.e. origin of this term and idea both lies in biology.
Biologist named Ludwig Von Bertalanffy, coined the term and gave meaning to it.
To understand certain phenomena different approaches were taken.
But it was felt that there should be single approach, a type of grand
methodology which would be used to solve & understand different problems without
referring to different types of methodology/approach/tools & teachings.
Culmination of Such urge of a grand methodology which would be used as one
station solution for all problems resulted into emergence of systems Approach.
Since previous approaches were partial in nature, they were like group of blind
men trying to define shape of elephant.
Their observation might be logical but their findings were not true.
System- refers to a complete or unified whole or
entity composed of two or more interrelated parts and delineated / separated
from the outside environmental supra system.
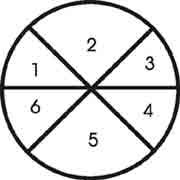
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 inter related parts / sub-systems. Separated from the area
which is outside the circle.
Area beyond circle is outside environmental supra -system.
Characteristics of a system
(1) Complete entity / whole:- everything in this world
is a system in its own right. Everything can be considered a unified entity.
(2) Inter dependent Sub-parts:- The two or more parts within a system
interact with each other and influence each other and they remain in a state of
equilibrium. Each of them are sustaining each other.
Eg: Politics and character of society Economics and Administration.
The very system flows from the dynamic interaction of these inter-related parts.
(3) the system remains in a interaction with the environment.
Systems Approach believes that system interacts with environment & environment
interacts with the system.
System itself is a Sub-System of the Environmental Supra System.
System remained in a state of interaction with Environmental Supra System.
There by environment influences system. Character of the system flows from his
things:
(1) Dynamic interaction of Sub-Systems.
(2) Dynamic interaction of system with the environmental Supra- System.
There are other characteristics which further explain:
Dynamic Equilibrium
System thrives through equilibrium. Systems will be
interacting with each other based on some basic values and Characteristics which
matches with each others. Thus they will Support each other and sustain each
other.
There should complement and supplement each other.
Systems approach has included in this idea two (Oxymoronic views).
Systems approach is more about Dynamic equilibrium / moving equilibrium than
mere equilibrium.
Every system strives to attain equilibrium.
It means systems approach also believes that change is the only unchanging
phenomena change.
Every system faces change.
Change might be.
Endo-genetic Change which emerges from within.
Exo-genetic Change which flow from outside.
Simultaneously System Approach says that changes whether
endogenatic or exogenetic it put pressure on the system and disturb the
equilibrium.
It has a tendency to reach equilibrium.
It has a spontaneous reaction or natural propensity to attain equilibrium.
It has a spontaneous reaction to reach by rectifying imbalance.
Entropy:-
Disintegration, Irrelevant):-
System Approach says that concept of Dynamic Equilibrium is to maintain a state
of Negative Entropy.
Positive Entropy- disintegration
Negative Entropy – Integration
]A system which is unable to reach to new state of
equilibrium when facing temporary equilibrium will result into positive Entropy.
Moves from a state of Old equilibrium through a temporary in equilibrium to a
new state of equilibrium through a process of adaptation and maintenance.
Homeo Stasis: The inherent tendency of a system to
reach a new state of equilibrium.
Not only adaptation but also Regulated adaptation is necessary for maintaining
equilibrium within the system to maintain negative Entropy.
Positive Entropy will also be there when there is unregulated adaptation.
Equifinality Systems Approach also believes in the
concept of Equifinality.
Depending on situation a solution is good or do not remain good.
Paradigm which in detail explained the systems approach is given by C. West
Churchman.
1950s,-1960s Systems Approach emerged in full-fledged member. But it was
very much visible during Behavioral era also.
Performance is dependent on satisfaction it is indirect.
Bernard’s idea of contribution- satisfaction equilibrium shows traits of systems
Approach.
Inducements:
Psychological power of choice of satisfaction – Throughout.
It results into output ® contribution.
Simon’s idea of Decision Making Stages.
Intelligence ® Input
Design ® Processing
Choice ® Output
Other theorists of system approach.
Negro & Negro Waldo Frederickson
Any problem could be understood through a single Approach i.e. System
Approach. Two things have to be analyzed:
-
Interactions within the system of different Sub-Systems.
-
Interactions of the system with environment.
Accuracy of the results depends on the accuracy at which these multiple interactions have been dealt with.
Huge unmanageable data.
Theorists subsequently from 1960s onwards started questioning the
feasibility of this approach.
This Approach will demand such ability and tools and techniques which were
beyond the capability of existing methods & methodology.
To make study manageable this Grand theory was negated for a Middle Range
Approaches. Which were known as Situational Theory of Administration Contingency
theories?
Basic ingredient
That the character / identity of the system was the result of dynamic
interaction. But at the same time it was considered that in order to make it
manageable. We have to study the dynamic into with limited perspective not from
all the perspectives. They in fact tried to understood one aspect of
environment and some of the aspects of organization/system.
They tried to final out, which type of organization for well with which type of
environment. They did not looked into every aspect of environment. Rather they
looked into one aspect of environment.
Contingency / Situational Theory
-
Burns & Stalkers
-
Lawrence & Lorsch
-
James Thompson
-
Perrow
-
Alvin Toffler
-
Warren Bemios (Post modern theorist)
They chose a middle range theory. Contingency / Situational
theory are maturation of the System Approach.
They had same character but with modifications.
(1) BURNS & STALKERS:
They considered 20 manufacturing units in Scotland & England.
They found that few are- very successful few not successful.
Among the successful units – there were mechanistic as well as organic /organismic
structures.
Organismic – they are open democratic.
Mechanistic – closed.
Later on found,
Whether successful or Unsuccessful there were both mechanistic as well as
organismic structure. Broadly there were two types of Environment. They were
operating under:-
-
Stable Environment.
-
Unstable Environment
Stable Environment
Rarely any change in terms of technology, competition, clients.
Unstable:- Changing technology, competition, clientele, Clients and their
preference is changing.
Conclusion
All those successful organization operating is an unstable environment were
Organizmic in terms of their structure.
All those successful organizations operating in Stable Environment were
Mechanistic is nature.
Study, analyses interaction of structure of the organization with one factor of
environment- Stability / Unstability of environment.
(2) LAWRENCE & LORSCH
They considered three categories of industry for their study.
-
Plastic Industries.
-
Packaged Food Industries
-
Container Industries.
In their study they tried to establish relationship between
Differentiation, Integration & Environment.
Differentiation:- (Needs specialization)
Differentiation mean the process through which an organization establishes separate Sub-parts to deal with different activities.
Integration: in process through which organization establish coordination among there different sub parts.
Environment- refers to the surrounding of the organization. Most unstable dynamic environment is Plastic Industry. Then Food – Packaging Industry. Then contains Industry. Successful Industries or by and large depends on specific relationship between Differentiation, Integration & Environment.
Dynamic Environment
Plastic Industry
Which were successful were more dynamic thus more differentiation more
specialization and more Integration. Those which were unsuccessful had gone for
less differentiation and less integration.
Container Industry
Stable Environment
Nature of interaction in container. Industry is different from that of
nature of integration in Plastic Industry.
| Plastic Industry |
|
Container Industry | |
|
Successful |
Unsuccessful |
Successful |
Unsuccessful |
| HD + H.I. Domestic (less standardized work) team orientation group formation. |
L.D. / L.I. | D + I Mechanistic (more standardized work) |
|
Same type of Integration do not operate is different types of
Environment.
Same type of differentiation do not operate in different types of environment.
Highly Polycentric type of Administration System is
successful in Plastic Industry is successful in Dynamic environment.
Hierarchic type of organization is successful in the context of container
Industry.
WARREN BENNINS
(Post Modern Theorist):- It is a Post-modern theorist. While explaining through empirical study found out inadequacy of Bureaucracy.
Bureaucracy has very Little validity when studied in reality.
Did not say it is invalid or has been invalid. Valid is context of particular environment & now since environment has changed it is no longer valid.
Evolutionary View point Situational:-
At the political of Evolution of society there was type of man Bureaucracy
was most sited. Now in Post Industrial era nature of man has changed thus
Bureaucracy has lost its relevance.
Bureaucracy Functions nicely in era of Industrialization (Stable Environment).
Man was ignorant, submissive and docile and in that background Bureaucracy was
most suited kind of Administration. It has changed from Stable to highly
unstable Society.
Choice of the people also changes. A new kind of man emerges. A new kind of man
is ambitious, demanding skilled. Mechanistic structure i.e. Bureaucracy has
become redundant.
Organic Adaptive Structure
All those societies which have organic adaptive structure are successful.
Relating to a type of situation a type of Administration was suitable but with
the change in situation that Administration no more remains suitable.
Theory of is becoming more and more relevant in today’s context.
JAMES THOMPSON
“He in his book, organization in Action”
Undertook a study- wanted to analyze relationship between type of technology on
work processes in from of interdependence among workers and units in workplace.
This study indicated towards three types of technology:-
-
Mediating Technology
-
Long-Linked Technology
-
Intensive Technology
Within organization these different technologies a specific type of interdependence match well with specific type of technologies.
-
Mediating Technology- Pooled Interdependence
-
Long-Linked Technology – Sequential Pattern of Interdependence
-
Intensive Technology- Reciprocal Interdependence
(1) MEDIATING TECHNOLOGY
Relate to an organization where workers are operating in a single place and
providing different types of services to no. of different clients. These
different employees, their Job is coordinated on the basis of standardization of
the Job. Organization undertakes multiple activities which are standardized /
routine in mature.
(2) Long Linked Technology
L.L.T. this refers to assembly line production, where each unit in terms of
its production is dependent on the other unit. Final product of the is byproduct
of all the units. Organization which are undertaking different activities. Final
product depends on all the activities of these units.
Mon of the units can operate in complete autonomy. Only it the proceeding unit
completed to its work the succeeding unit can start its work. Common thing in
both (1) & (2) is standardization of Job.
(3) INTENSIVE TECHNOLOGY
Is refers to organization which does Jobs which demands high level of
expertise and skill. There has to be constant interaction (reciprocal
interdependence) Study indicated that as per as -
Mediating Technology ® centralized structure is required.
Long Linked Technology ® centralized structure is required.
Intensive Technology ® decentralized structure is required.
PERROW
has evaluated work process across 2 dimensions.
-
Frequency with which there is exceptions to normal way of doing work.
-
Extent to which work is analyzable (Rational)
(1) Relating to work
there can be two characters-
-
Routine
-
Non-Routine
When frequency is low work is of routine category.
When frequency is high work is of Non-Routine Category.
Routine Job- More Rational, highly analyzable.
Non-Routine- Innovative approach.
Simon’s theory was referred to as- logical Positivism (fact
based theory) logical Positivistic Theory.
This theorist based on come out with four different types of organization
situation and in that context a different types of organizational structure.
4 Structures:-
(i) Routine Structure
(ii) Engineering Structure
(iii) Craft Structure
(iv) Non-routine Structure
-
Study of Per row establishment that organization where there is low exception those Jobs are highly analyzable, there Routine structure is more appropriate and highly successful.
-
High exception and Low analysis nature of Job is innovative and lowly analyzable. Non- Routine structure is more successful.
-
Low exception + Low analysis:- Craft structure
-
Budget Process closer to non-routine structure
(ii) ENGINEERING STRUCTURE:-
Eg: Audit / Tax Organization
High Exceotion + Highly Analyzable.
Exceptions are high but approach should not be innovation.
Problems or exceptions has to be dealt with already established principles. Thus
it is highly centralized in nature.
Routine – Centralized.
ALVIN TOFFLER
Famous author of two books
“Future Shock” and “Third Wave”.
- Analyzing the pace of change and its impact on the various aspects of society,
- Core theme of idea is that unless & until the change is adequately addressed
the system is about to enter into shock. (Disintegration)
Third Wave:-
Pace of change is so high these days that Previously Bureaucracy was
appropriate b/c it was dealing with stable society.
But with pace of changed being so fast these days it is not bureaucracy but days
it is which is more appropriate these days.
Similar to that of concept of “Organic Adaptive Structure” (Bennis)
As for as systems organization are concerned they are broadly conceived from two
broad perspectives:
-
Open Model
-
Closed Model
There are certain theorists
They perceive the organization from the perspective of closed model.
Certain theorists like Humanistic theorist, Human-Relations, Systems, contingency theories open model they perceive the organization from perspective of open model.
Closed Model
Differentiation can be brought about from five major perspective.
(1) Role of Organization
(2) Concept of Organizational man
(3) Concept of Organizational structure
(4) Concept of Organizational Order.
(5) Concept of Organizational Environment.
(1) Role of Organization
Closed Model- dichotomy between organization & society thereby establishing
dichotomy between bureaucracy and citizen.
Organization – Rational
Society – Irrational
Organization – Ordered
Society – Disordered
Bureaucracy Repository of Rationality & scienticism.
Citizen – Repository
Outside organization – there is chaos (Irrational)
Inside organization – Rational
Closed Model- Organization & Society Bureaucracy & citizen
Outside should be insulated to inside.
Maintain dichotomy- not only explain dichotomy but want to maintain dichotomy
OPEN MODEL
Bureaucracy is very much a social man. If Social man is rational / irrational.
Same will be bureaucrat.
(2) ORGANISATIONAL MAN
Closed Model : Man is lazy by; open model – man is industrious by nature.
(3) STRUCTURE
C.M. (CLOSED MODEL)
- Hierarchic
- Authoritarian
- Direction / Command.
O.M. (OPEN MODEL)
- Poly centric
- Decentralized multicratic
- free flow of command.
(4) ORDER
C.M. (CLOSED MODEL)
Discipline via coercion & force
O.M. (OPEN MODEL)
Self control / regulation
(5) ENVIRONMENT
C. M. (CLOSED MODEL)
Takes environment for granted believes environment is unchanging.
O.M. (OPEN MODEL) believes that organization
suitability lies in adapting to the changing nature of environment.
C. M. – responsibility is individually exercised.
O. M. – responsibility is jointly exercised in fact referred as (shedding of
responsibility)
C. M. – specialization is specific .
O. M. – preference towards multiple specific.
C. M. – Domination is towards.
O. M. – authority is exercised through function and through the concept of “Myth
of Peerage”
There is also a third view:
Nicholas Henry:
“Model Synthesis”
“Newer Tradition”
Simon, Thompson, March, Griys
Nicholas believes that these theorists view fall somewhere between closed model
and open model.
Analyzes has combined both C. M. and open Model.
Model Synthesis is characterized by:
3 characteristics:
-
Organization & their environment change.
-
Organization & people in them act to survive.
-
Organization & people in them learn from their mistake.
(Organization has a tendency towards closure) try to derive standardized response strategies towards the change, by closing the organization from outside impact, for a considerable period of time.
When there is huge change once again the organization open up.

