Open Course on Environment for IAS Pre. "Biosphere Reserves, National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries of India"
Biosphere Reserves, National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries of India

BIOSPHERE RESERVES: A biosphere reserve is a voluntary, cooperative, conservation reserve in order to protect the biological and cultural diversity of a region while promoting sustainable economic development. It is a place of cooperation, education and experimentation. The origin of Biosphere Reserves goes back to the “Biosphere Conference” organized by UNESCO in 1968. This was the first intergovernmental conference examining how to reconcile the conservation and use of natural resources. This Conference resulted in the launching of the UNESCO “Man and the Biosphere” (MAB) Program in 1970. One of the original MAB projects was designed to establish a coordinated World Network of sites representing the main ecosystems of the planet in which genetic resources would be protected, and where research on ecosystems as well as monitoring and training work could be carried out. These sites were named as “Biosphere Reserves”.
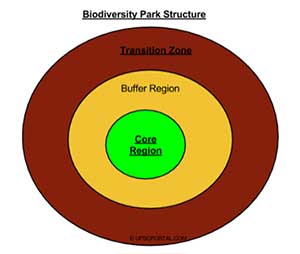
To be a biosphere reserve, an ecosystem must be nominated by a national government and approved by MAB Program of UNESCO. Ideally, biosphere reserve must contain three elements:
-
Core Areas: These areas are securely protected sites for conserving biological diversity, monitoring minimally disturbed ecosystems, and undertaking non-destructive research and other low-impact uses like education.
-
Buffer Zones: Buffer Zones may be used for cooperative activities compatible with sound ecological practices, including environmental education, recreation, ecotourism and applied and basic research and are located nearby core areas.
-
Transition, or Cooperation, Zones: These areas may contain farms, towns, fisheries, and are the areas where local communities, management agencies, scientists, non-governmental organizations, cultural groups, economic interests, and other stakeholders work together to manage and sustainably develop the area's resources.
There are 18 Biosphere Reserves in India, and often include one or more National Parks along buffer zones that are open to some economic uses. But interestingly, nine of the eighteen biosphere reserves are a part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves. These are : Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve(2001), Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve(2001), Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve(2001), Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve(2004), Nokrek Biosphere Reserve(2009), Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve(2009), Simlipal Biosphere Reserve(2008), Achanakmar-Amarkantak Biosphere Reserve (2012) and Nicobar Islands(2013).
Biosphere reserves of India :
- Great Rann of Kutch (Gujrat) : 2008 Gulf of Mannar (Tamil Nadu) : 1989
- Sundarbans (West Bengal ) :1989
- Cold Desert (Himachal Pradesh) 2009
- Nanda Devi National Park (Uttarakhand): 1988
- Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka): 1986
- Dihang-Dibang ( Arunachal Pradesh): 1988
- Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve ( Madhya Pradesh) : 1999
- Seshachalam Hills (Andhra Pradesh) : 2010
- Simlipal (Odisha) : 1994
- Achanakamar – Amarkantak (Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh) 2005
- Manas (Assam) : 1989
- Khangchendzonga (Sikkim) : 2000
- Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve ( Kerala, Tamil Nadu) : 2001
- Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve (Andaman and Nicobar Islands) 1989
- Nokrek (Meghalaya) 1988
- Dibru-Saikhowa ( Assam ) 1997
- Panna (Madhya Pradesh ) 2011
NATIONAL PARKS : First National Park of India was established in 1936 as Hailey National Park, now known as Jim Corbett National Park. In 1972, India enacted the Wildlife Protection Act and Project Tiger . So far, a total of 166 national parks have been authorized.
A national park is a reserve of natural or semi-natural land, owned by the government, and set aside for human recreation and enjoyment, animal and environmental protection and restricted from most development. The first National Park of the world , was the United States' Yellowstone National Park established, in 1872.
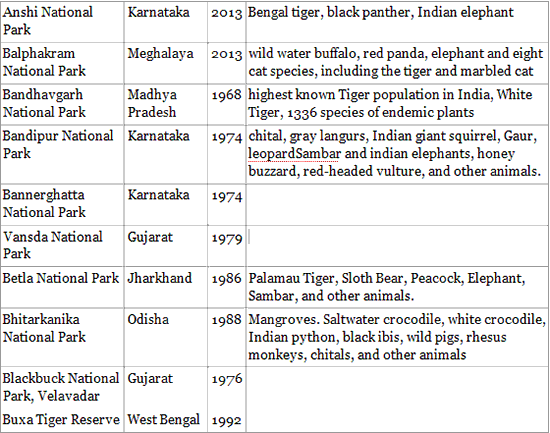
List of national parks in India are as follows:
Click Here to See Full List
WILDLIFE SANCTUARIES : India has over 500 wildlife sanctuaries among whom there are 28 Tiger Reserves are governed by Project Tiger, and are of special significance in the conservation of the tiger. Many National Parks were initially wildlife sanctuaries for instance, Keoladeo National Park . Wildlife sanctuaries which are of national importance in order to conservation, because of some flagship faunal species, are named National Wildlife Sanctuary.National Chambal (Gharial) Wildlife Sanctuary established in 1978 serves the perfect example. Following are Wildlife sanctuaries located in different states of India.
It has taken long enough for mankind to realize the importance of nature in day to day lives and most importantly ,the sustenance of eco-system. Let’s respect the setting up of reserved areas to protect precious animals, birds and other species and protect the laws along with the consideration that they are binding. As a fledgling step , that would be more than enough. Because what is otherwise seen most commonly is the dreaded misfortunes caused by poachers and hunters who do not care that they are neglecting the law when they are killing rhinos for their horn or elephants for ivory. We must not longer let that happen.
UPSCPORTAL will soon come up with more articles and study material on Environment section.
We wish the Candidates All the Best for their Preparations.
Team UPSCPORTAL