Draft Labour Code: Mind Map for UPSC Exam
Draft Labour Code: Mind Map for UPSC Exam
Click Here to Download Full MAP in PDF
Study Material for IAS Prelims: GS Paper -1 + CSAT Paper-2
Online Crash Course for UPSC PRE Exam
Mind Map Important Topics:
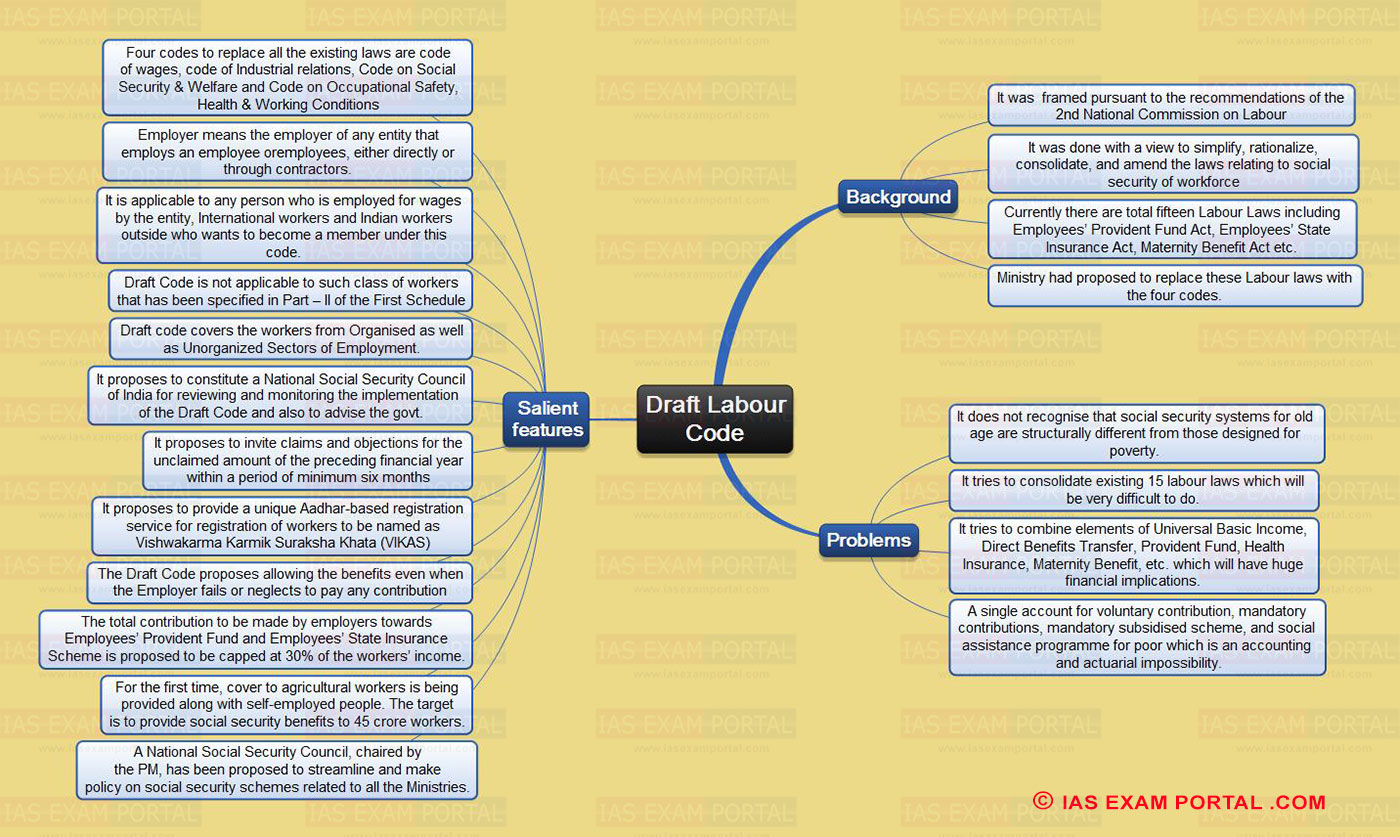
Draft Labour Code
Background
- It was framed pursuant to the recommendations of the 2nd National Commission on Labour
- It was done with a view to simplify, rationalize, consolidate, and amend the laws relating to social security of workforce
- Currently there are total fifteen Labour Laws including Employees’ Provident Fund Act, Employees’ State Insurance Act, Maternity Benefit Act etc.
- Ministry had proposed to replace these Labour laws with the four codes.
Problems
- It does not recognise that social security systems for old age are structurally different from those designed for poverty.
- It tries to consolidate existing 15 labour laws which will be very difficult to do.
- It tries to combine elements of Universal Basic Income, Direct Benefits Transfer, Provident Fund, Health Insurance, Maternity Benefit, etc. which will have huge financial implications.
- A single account for voluntary contribution, mandatory contributions, mandatory subsidised scheme, and social assistance programme for poor which is an accounting and actuarial impossibility.
Salient features
- Four codes to replace all the existing laws are codeof wages, code of Industrial relations, Code on Social Security & Welfare and Code on Occupational Safety, Health & Working Conditions
- Employer means the employer of any entity that employs an employee oremployees, either directly or through contractors.
- It is applicable to any person who is employed for wages by the entity, International workers and Indian workers outside who wants to become a member under this code.
- Draft Code is not applicable to such class of workers that has been specified in Part – II of the First Schedule
- Draft code covers the workers from Organised as well as Unorganized Sectors of Employment.
- It proposes to constitute a National Social Security Council of India for reviewing and monitoring the implementation of the Draft Code and also to advise the govt.
- It proposes to invite claims and objections for the unclaimed amount of the preceding financial year within a period of minimum six months
- It proposes to provide a unique Aadhar-based registration service for registration of workers to be named as Vishwakarma Karmik Suraksha Khata (VIKAS)
- The Draft Code proposes allowing the benefits even when the Employer fails or neglects to pay any contribution
- The total contribution to be made by employers towards Employees’ Provident Fund and Employees’ State Insurance Scheme is proposed to be capped at 30% of the workers’ income.
- For the first time, cover to agricultural workers is being provided along with self-employed people. The target is to provide social security benefits to 45 crore workers.
- A National Social Security Council, chaired by the PM, has been proposed to streamline and make policy on social security schemes related to all the Ministries.