Mind Map for UPSC Exam (Judicial Appointment and Vacancies)
Mind Map for UPSC Exam (Judicial Appointment and Vacancies)
Click Here to Download Full MAP in PDF
Study Material for IAS Prelims: GS Paper -1 + CSAT Paper-2
Online Crash Course for UPSC PRE Exam
Mind Map Important Topics:
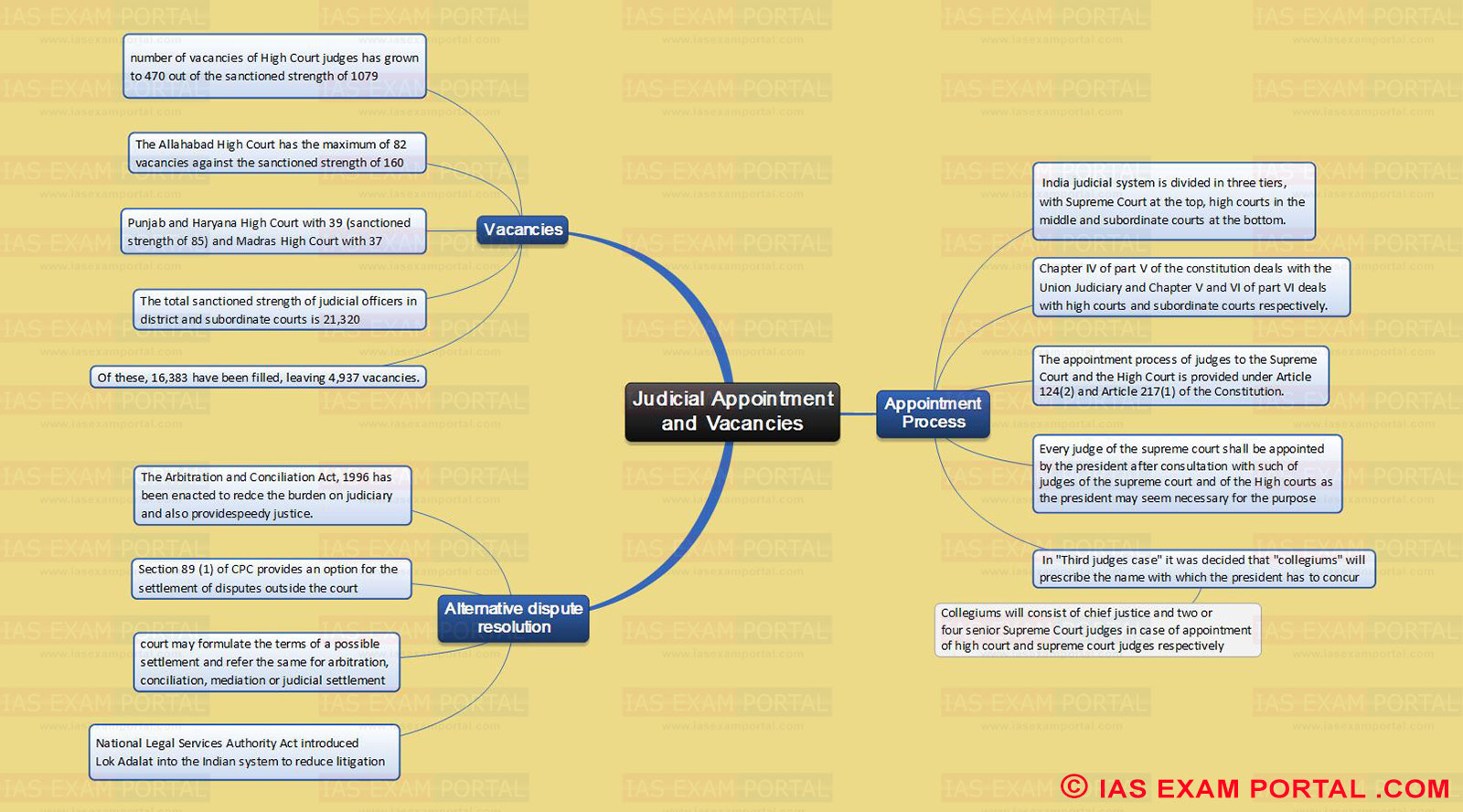
Judicial Appointment and Vacancies
Vacancies
- Number of vacancies of High Court judges has grown to 470 out of the sanctioned strength of 1079
- The Allahabad High Court has the maximum of 82 vacancies against the sanctioned strength of 160
- Punjab and Haryana High Court with 39 (sanctioned strength of 85) and Madras High Court with 37
- The total sanctioned strength of judicial officers in district and subordinate courts is 21,320
- Of these, 16,383 have been filled, leaving 4,937 vacancies.
Alternative dispute resolution
- The Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 has been enacted to redce the burden on judiciary and also provide speedy justice.
- Section 89 (1) of CPC provides an option for the settlement of disputes outside the court
- Court may formulate the terms of a possible settlement and refer the same for arbitration, conciliation, mediation or judicial settlement
- National Legal Services Authority Act introduced Lok Adalat into the Indian system to reduce litigation
Appointment Process
- India judicial system is divided in three tiers, with Supreme Court at the top, high courts in the middle and subordinate courts at the bottom.
- Chapter IV of part V of the constitution deals with the Union Judiciary and Chapter V and VI of part VI deals with high courts and subordinate courts respectively.
- The appointment process of judges to the Supreme Court and the High Court is provided under Article 124(2) and Article 217(1) of the Constitution.
- Every judge of the supreme court shall be appointed by the president after consultation with such of judges of the supreme court and of the High courts as the president may seem necessary for the purpose
- In "Third judges case" it was decided that "collegiums" will prescribe the name with which the president has to concur
- Collegiums will consist of chief justice and two or four senior Supreme Court judges in case of appointment of high court and supreme court judges respectively