LOKPAL: Mind Map for UPSC Exam
LOKPAL: Mind Map for UPSC Exam
Click Here to Download Full MAP in PDF
Study Material for IAS Prelims: GS Paper -1 + CSAT Paper-2
Online Crash Course for UPSC PRE Exam
Mind Map Important Topics:
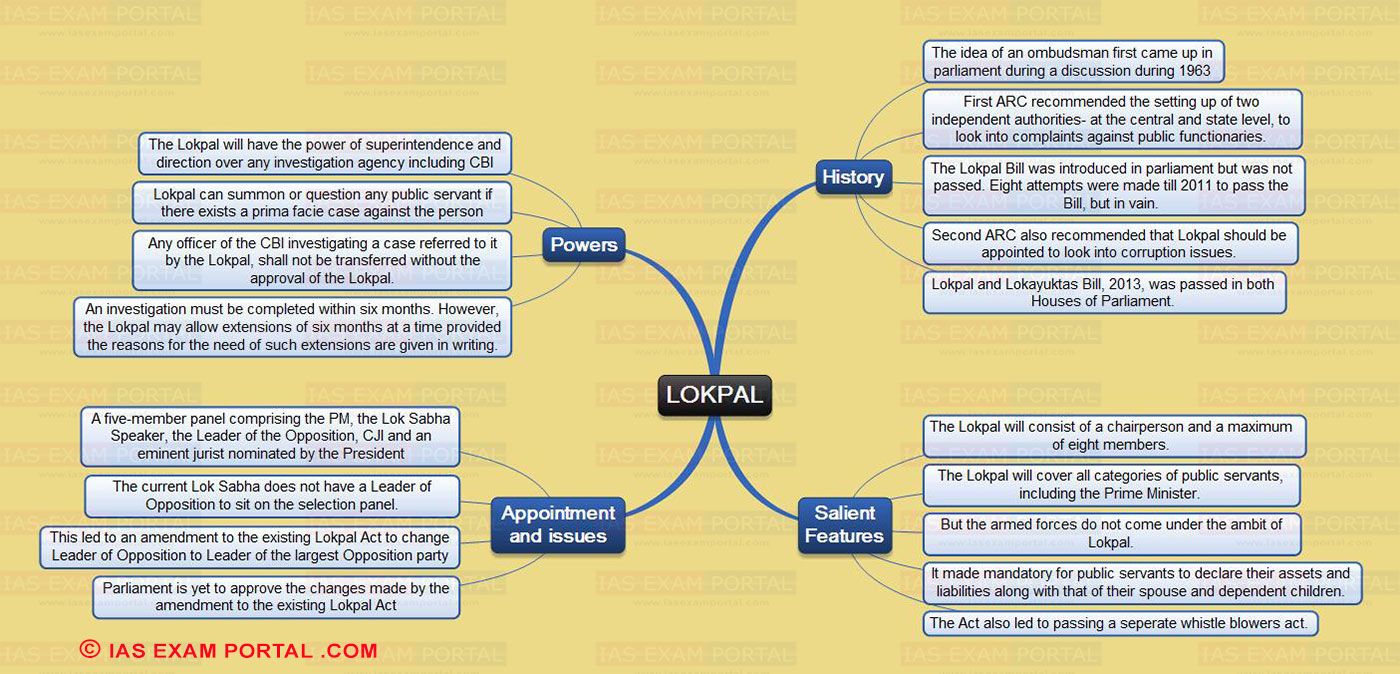
LOKPAL
History
- The idea of an ombudsman first came up in parliament during a discussion during 1963
- First ARC recommended the setting up of two independent authorities- at the central and state level, to look into complaints against public functionaries.
- The Lokpal Bill was introduced in parliament but was not passed. Eight attempts were made till 2011 to pass the Bill, but in vain.
- Second ARC also recommended that Lokpal should be appointed to look into corruption issues.
- Lokpal and Lokayuktas Bill, 2013, was passed in both Houses of Parliament.
Powers
- The Lokpal will have the power of superintendence and direction over any investigation agency including CBI
- Lokpal can summon or question any public servant if there exists a prima facie case against the person
- Any officer of the CBI investigating a case referred to it by the Lokpal, shall not be transferred without the approval of the Lokpal.
- An investigation must be completed within six months. However, the Lokpal may allow extensions of six months at a time provided the reasons for the need of such extensions are given in writing.
Appointment and issues
- A five-member panel comprising the PM, the Lok Sabha Speaker, the Leader of the Opposition, CJI and an eminent jurist nominated by the President
- The current Lok Sabha does not have a Leader of Opposition to sit on the selection panel.
- This led to an amendment to the existing Lokpal Act to change Leader of Opposition to Leader of the largest Opposition party
- Parliament is yet to approve the changes made by the amendment to the existing Lokpal Act
Salient Features
- The Lokpal will consist of a chairperson and a maximum of eight members.
- The Lokpal will cover all categories of public servants, including the Prime Minister.
- But the armed forces do not come under the ambit of Lokpal.
- It made mandatory for public servants to declare their assets and liabilities along with that of their spouse and dependent children.
- The Act also led to passing a seperate whistle blowers act.