UPSC Geo-Scientist and Geologist Exam Papers 2018 : Geo-Physics Paper - III

(Download) UPSC: Geologist Examination Papers-2018
Exam Name : UPSC Geo-Scientist and Geologist Exam 2018
Subject : Geophysics Paper - III
Year : 2018
GEOPHYSICS
Paper III
ITime Allowed : Three Hours
Maximum Marks : 200
QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS
Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
There are TEN questions divided under TWO Sections.
Candidate has to attempt SIX questions in all.
Questions No. 1 and 6 are compulsory.
Out of the remaining EIGHT questions, FOUR questions are to be attempted choosing TWO from each Section.
The number of marks carried by a question / part is indicated against it.
Attempts of questions shall be counted in sequential order. Unless struck off, attempt of a question shall be counted even if attempted partly.
Any page or portion of the page left blank in the answer-book must be clearly struck off. Answers must be written in ENGLISH only.
Neat sketches may be drawn to illustrate answers, wherever required.
Unless otherwise mentioned, symbols and notations have their usual standard meanings. Assume suitable data, if necessary and indicate the same clearly.
Constants which may be needed :
Kepler's constant = 3.986004418 105 km3s-2
Mean radius of Earth = 6378 km
Mass of electron (me) = 9.11 x 10-31 kg
Charge of electron (e) = 1-602 x 10-19 C
Planck's constant (h) = 6.62 x 10-34 J-sec
Boltzmann's constant (k) = 1-38 x 10-23 J/K
SECTION A
Q1. (a) Explain electromagnetic energy and its two units in which electromagnetic wavelength is measured.
(b) (i) Describe three principal applications of the seismic method.
(ii) What is a notch filter and what is its application ?
(c). Explain passive and active remote sensing with suitable examples.
(d). Calculate seismic data fold, if number of channels in a streamer is
120, shot and group interval is 25 m.
(e). Describe reflectance, absorbance and transmittance with balance
equation.
(f) Describe satellite orbit and swath in detail. On which factors does
orbit selection depend ?
(g) What do you mean by deconvolution ? Find out the convolution of two
signals given below :
x1 (n) = [0, 1, 2, 3]
x2 (n) = [-1,-1, 3, 4]
(h) What is Radioactive series ? How many steps (a
and b) emission take place from parent 92/233
U to stable daughter product 82Pb ?
Q2. (a) (i) What is the energy of a photon with a wavelength of 400 nm
?
(ii) List out four weather satellites.
(iii) Explain the Stefan-Boltzmann law of radiation.
(b). Describe ghost and peg-leg in seismic data with neat sketch
diagram.
(ii) Explain the principle of seismic reflection data acquisition in
marine environment with neat sketch diagram.
(c) (i) Discuss ocean basin, ocean ridge and ocean trench with
suitable examples.
(ii) What is radiometric age dating ? How can you calculate the absolute age of
a rock ?
Q3. (a) (i) Distinguish between satellite image and map.
(ii) What are the percentages of incoming natural radiation reflected back,
absorbed by the atmosphere, and absorbed by the Earth's surface ?
(iii) Give the values of emissivity of polished metal surface, granite, basalt
(rough) and water (pure).
(b) (i) Describe the reflection coefficient. Explain the cases if reflection
coefficient is zero, less than zero and one.
(ii) List vibrator sources used in marine survey. (iii) Explain dynamic
correction with appropriate equation.
(c) (i) What is nuclear logging ? Name three nuclear logs.
(ii) Draw gamma ray log curve for shale-sand-shale formation. (iii) In a rock
formation, the geothermal gradient is 0.022°C/m and the mean annual surface
temperature is 20°С. Find out the formation temperature at the formation depth
2440 m.
Q4. (a) (i) Explain interaction mechanism of electromagnetic
radiation.
(ii)What are LiDAR and RADAR ? Which type of remote sensing is performed by
LiDAR and RADAR ?
(b) Differentiate between CDP and CMP with neat sketch diagram.
(ii) Discuss the common offset gather and the common receiver gather with neat
sketch diagram.
(c) Explain how shale volume can be calculated from natural gamma ray log.
(ii) Discuss principle of ringing which occurs in time domain when sharp
boundaries are present in the frequency domain.
Q5. (a) (i) Explain geostationary satellite orbits and the
sun-synchronous satellite orbits and their applications in remote sensing.
(ii) Which are the sensors used for land use and land cover studies ?
(b) Describe marine seismic data processing flow chart.
(ii) Discuss applications of magnetic method.
(c) Explain induced magnetization and remanent magnetization with examples.
(ii) Explain how and where Eötvös correction applies.
SECTION B
Q6. (a) An X-ray beam of wavelength 0.71 Å is diffracted by a cubic
KCl crystal of density 1.99 x 103 kg m-3. Calculate the interplanar spacing for
(200) planes and the glancing angle for the second order reflection from these
planes. The molecular weight of KCl is 74.6 amu and Avogadro's number is 6.023 x
1026 kg-1 mole-1.
(b) Derive the conditions for light amplification using Einstein's coefficients.
(c) Determine the transition temperature, and the critical field at 4.2 K for a
given specimen of a superconductor if the critical fields are 1.41 x 105 and
4.205 x 105 Am-1 at 14.1 K and 12.9 K, respectively.
(d) Calculate the ratio of the current for a forward bias of 0.6 V to the
current for the same value of reverse bias applied to a Ge p-n diode at 27°C.
(e) Discuss the working of a satellite communication system with block diagrams.
(f) Obtain the Boolean expression for the output Y in the logic circuit shown in
the figure. Simplify the expression and show that the circuit is equivalent to
an AND gate with inputs A and B.
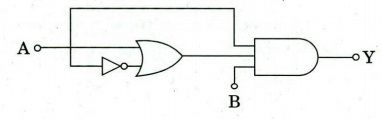
(g) If the uncertainty in the position of a moving particle is equal to the
wavelength associated with it, show that the uncertainty in its velocity is
equal to () times its velocity.
(h) Explain the role of an earth station in satellite communication set-up.
Q7. (a) (i) Differentiate between crystalline and amorphous solids.
(ii) Distinguish between orthorhombic and triclinic crystal systems.
(iii) Calculate the surface density of atoms in the (111) plane of a
body-centered cubic structure. Assume that the lattice constant a = 5 Å. In
addition, assume the atoms to be hard spheres, with the closest atoms touching
each other.
(b) Derive expressions for the voltage gain and the input resistance of an
inverting amplifier using an Op-Amp.
(c) Apply Heisenberg's uncertainty principle to explain the following:
(i) Non-existence of electrons within the nucleus.
(ii) Existence of finite zero-point energy.
Q8. (a) What is the mode locking technique of generating short laser
pulses ? Discuss its types with diagrams.
(b) Compare the characteristics of CO2 gas laser and Nd-YAG laser with energy
level diagrams.
(i) A material has energy levels separated by 1.95 eV. Calculate the temperature
at which the population inversion of two levels will be one half. (Given k =
1.38 x 10-23 J/K).
(ii) A particle limited to z-axis has the wave function y(x) = bz between o Szs
2; the wave function y(z) = 0 elsewhere. Find the probability that the particle
can be found between z = 0 and z = 0·5. Also find the expectation value <z> of
the position of the particle.
Q9. (a) Describe the changes that occur in electrical, magnetic and
thermal properties of substances when they change from normal state to
superconducting state.
(b) (i) An FET amplifier in the common-source configuration uses a load
resistance of 250 k 2. The ac drain resistance of the device is 100 k 2 and the
transconductance is 0.5 mA/V. What is the voltage gain of the amplifier ?
Calculate the voltage V, in the circuit shown in the figure.
(ii) Discuss quantum mechanically, the problem of one-dimensional linear
harmonic oscillator and obtain its eigenvalues. Also write the significance of
zero-point energy.
.jpg)
Q10. (a) (i) Discuss the longitudinal mode of resonators.
(ii) If a radar of 1 MW peak power and antenna gain of 1000 irradiates a 1 m2
target with a 10 usec pulse at 1000 km range, what energy density arrives back
at the radar and in how much elapsed time? 4+1
(b) (i) Distinguish between active and passive satellites.
(ii) What do you understand by orbit, apogee and perigee of a satellite ?
(c) Explain the design and working principle of an optical fibre.
(ii) A communication system uses 10 km of optical fibre having a loss of 2-3
dB/km. Calculate the out power at the receiving end if the power at input is 400
uW.
Click Here to Download PDF Geo-Physics Paper- III
<< Go Back To Main Page
Courtesy: UPSC

