(IGP) IAS Pre: GS - Geography - World Geography General: Africa
World Geography General
Africa
Introduction
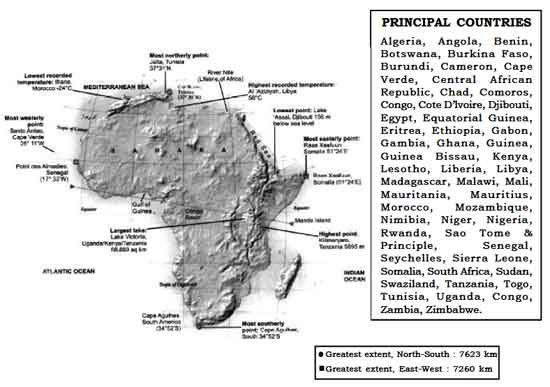
Area: 3,03,35,000 sq. km (20.4% of total area Madagascar and other islands of Africa)
Population : 778.5 million
Latitude : 37031'N to 34052'S Longitude : 25011'W to 51024'E
Size : Second largest continent after Asia and nine times the size of India.
Situation : Situated to the south of Europe and south west of Asia. It is bound by the Meditarranean Sea in the north, the Atlantic Ocean in the west and southwest, the Indian Ocean in the east and the Red Sea in the northeast. Africa belongs to all the four hemispheres and bulk of the continent lies in tropics. It is joined to Asia by the narrow isthmus of Suez and separated from Eurasia at three diffirent points (Strait of Gibraltar, Suez Canal and Strait of Bab-el-Mandeb). The only continent which is crossed by Tropic of Cancer, Equator and Tropic of Capricorn.
Important Seas / Ocean Channels around Africa:
| Name | Location | African Countries Along the Sea |
Mediterranean Sea
|
North of Africa | Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt. |
Red Sea
|
North East of Africa | Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea and Djibouti. |
| Indian Ocean | East of Africa | Somalia, Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambiquei and South Africa |
| Atlantic ocean | West of Africa | Morocco, Western Sahara, Mauritania, Senegal, Gambia, Guinea Bissau, Guinea, Sierra Leone, and Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Togo, Benin, Nigeria, Camernoon, Equatorial Guniea, Gabon, Congo, Zaire, Angola, Namibia, South Africa. |
| Mozambique Channel | East of Mozambique | Mozambique (West) and Madagascar (East). |
Important Gulfs and Bays
| Name | Location |
| Gulf of Guinea | South of Ivory coast, Ghana, Togo, Benin, Nigeria, Cameroon and Equatorial Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean. |
| Walvis Bay | West of Namibia, Atlantic Ocean |
| Maputo Bay | South East of Mozambique, Indian Ocean. |
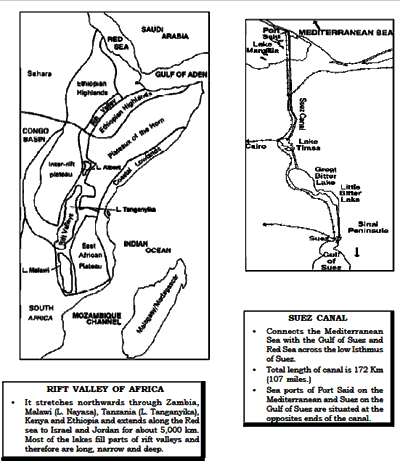
Important Straits
| Name | Separates | Connects |
| Strait of Gibraltar | Europe from Africa | Mediterranean Sea with Atlantic Ocean. |
| Strait of Bab-el-Mandeb | Djibouti (Africa) from Yemen (Asia) | Red Sea with Gulf of Aden. |
| Coasts of Africa | Countries | |
| Grain Coast | Sierra Leone and Liberia | |
| Ivory Coast | Ivory Coast | |
| Gold Coast | Ghana | |
| Slave Coast | Togo, Benin and Nigeria. |
Important Lakes
| Name | Information |
| Lakes from South to North | |
| LakeKariba |
|
| Lake Nayasa (Lake Malawi) |
|
| Lake Mweru |
|
| Lake Tanganyika |
|
| Lake Edward |
|
| Lake Victoria
Area : 68,880 sq. km. |
|
| Lake Turkana (Lak Rudolf) |
|
| Lake Tana |
|
| Lake Nasser |
|
| Lake Chad |
|
| Lake Volta |
|
| Lake Assal |
|
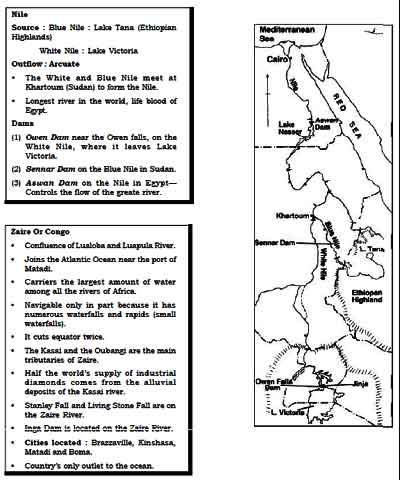
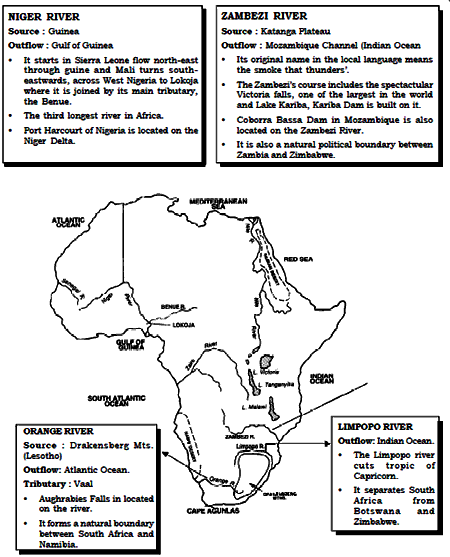
Important Rivers
Important Mountains and Plateaus:
| Name | Information |
| Atlas Mountains
Divided into five separate running to each other-
|
|
| Ethiopian Highlands
Highest peak : Ras Dashan (4,620 m) is the Africa’s third highest peak. |
|
| Mt. Kenya (5,200 m) |
|
| Mt. Elgon (4,210 m) |
|
| Mt. Kilimanjaro (5,895 m) |
|
| Drakensberg Scarpland |
|
| Mount Rouwenzori (5,109 m) |
|
| Mount Cameroon (4,070 m) |
|
| Tibesti Massif (3,400 m) |
|
| Ahaggar Massif |
|
| Bomi and Nibas hills |
|
| Katanga Plateau |
|
| Jos Plateau |
|
| Mount Sinai |
|
| Sahara desert |
|
| Libyan desert |
|
| Arabian desert |
|
| Nubian desert |
|
| Namib desert |
|
| Kalahari desert |
|
Click Here to Download full Chapter
Click Here for Africa MCQ
© UPSCPORTAL.COM


