(HOT) UPSC Current Affairs 2025 PDF
NEW! The Gist (NOV-2025) | E-BOOKS
(IGP) IAS Pre Paper - 2: GS - General Mental Ability - Series
General Mental Ability
Series
NUMBER SERIES
Prime Number Series
Example 1. 4, 9, 25, 49, 121, 169,…
(a) 324
(b) 289
(c) 225
(d) 196
Solution. (b) The given series is a consecutive square of prime number
series. The next prime number is 289.
Example 2. 5, 7, 13, 23, …
(a) 25
(b) 27
(c) 29
(d) 41
Solution. (d) The difference between prime numbers is increasing.
7 is next prime to 5; 13 is second to next prime to 7; 23 is third to next to
13. Hence, next should be fourth to next prime to 23. Hence, required number is
41.
Multiplication Series
Example 3. 4, 8, 16, 32, 64… 256
(a) 96
(b) 98
(c) 86
(d) 106
Solution. (a) The numbers are multiplied by 2 to get the next number. 64
× 2 = 128
Example 4. 5, 20, 80, 320, … 1280
(a) 5120
(b) 5220
(c) 4860
(d) 3642
Solution. (a) The numbers are multiplied by 4 to get the next number.
1280 × 4 = 5120
Difference Series
Example 5. 3,6,9,12,15,…. 21
(a) 16
(b) 17
(c) 20
(d) 18
Solution. (d) The difference between the numbers is 3. 15 + 3 = 18
Example 6. 55, 50, 45, 40,….30
(a) 33
(b) 34
(c) 35
(d) 36
Solution. (c) The difference between the numbers is -5. 40 – 5 = 35
Division Series
Example 7. 5040, 720, 120, 24, ….2,1
(a) 8
(b) 7
(c) 6
(d) 5
Solution. (c)

Example 8. 16, 24, 36,… 81
(a) 52
(b) 54
(c) 56
(d) 58
Solution. (b) Previous number × 3/2 = Next number


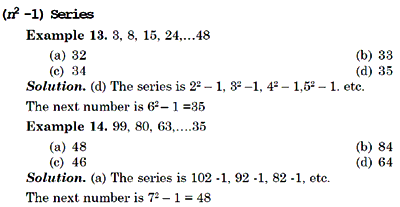

(n2 – n) Series
Example 17. 0, 2, 6, 12, 20,….42
(a) 25
(b) 30
(c) 32 (
d) 40
Solution. (b) The series is 12 – 1 = 0, 22 – 2 = 2,
32 – 3 = 6, etc.
The next number is 62 – 6 = 30
Example 18. 90, 380, 870, 1560,…..
(a) 2405
(b) 2450
(a) 2400
(d) 2455
Solution. (b) The series is 102 – 10, 202 – 20, 302 – 30, etc.
The next number is 502 – 50 = 2450
n3 Series
Example 19. 1, 8, 27, 64,…. 216
(a) 125
(b) 512
(c) 215
(d) 122
Solution. (a) The series is 13, 23, 33 ,
43, etc.
The next number is 53 = 125
Example 20. 1000, 8000, 27000, 64000,….
(a) 21600
(b) 125000
(c) 152000
(d) 261000
Solution. (b) The series is 103 , 203, 303,
403, etc.
The next number is 503 = 125000
(n3 + 1) Series
Example 21. 2, 9, 28, 65,…217
(a) 123
(b) 124
(c) 125
(d) 126
Solution. (d) The series is 13 +1, 23 + 1, 33
+ 1, etc.
The next number is 53 + 1 = 126
Example 22. 1001, 8001, 27001, 64001, 125001,….
(a) 261001
(b) 216001
(c) 200116
(d) 210016
Solution. (b) The series is 103 + 1, 203 + 1, 303
+ 1, etc.
The next number is 603 + 1 = 216001
(n3 -1) Series
Example 23. 0, 7, 26, 63, 124,…
(a) 251
(b) 125
(c) 215
(d) 512
Solution. (c) The series is 13 – 1, 23 – 1, 33
– 1, etc.
The next number is 63 – 1 = 215
Example 24. 999, 7999, 26999, 63999,….
(a) 199924
(b) 124999
(c) 129994
(d) 999124
Solution. (b) The series is 103 – 1, 203 – 1, 303
– 1, etc.
The next number is 503 – 1 = 124999
(n3 + n) Series
Example 25. 2, 10, 30, 68,….222
(a) 130
(b) 120
(c) 110
(d) 100
Solution. (a) The series is 13 + 1, 23 + 2, 33
+ 3, etc.
The next number is 53 + 5 = 130
Example 26. 1010, 8020, 27030, 64040,….
(a) 125500
(b) 125050
(c) 100255
(d) 120055
Solution. (b) The series is 103 + 10 = 1010, 203
+ 20 = 8020, etc.
The next number is 503 + 50 = 125050
(n3 – n) Series
Example 27. 0, 6, 24, 60,…. 210
(a) 012
(b) 210
(c) 201
(d) 120
Solution. (d) The series is 13 – 1 = 0, 23 – 2 = 6,
33 – 3 = 24, etc.
The next number is 53 – 5 = 120
Example 28. 990, 7980, 26970, 63960,….
(a) 124500
(b) 124005
(c) 120045
(d) 124950
Solution. (d) The series is 103 – 10, 203 – 20, 303
– 30 etc.
The next number is 503 – 50 = 124950
LETTER SERIES
Type 1
One Letter Series Such series consists of one letter in each term and this series is based on increasing or decreasing positions of corresponding letters according to English alphabet.
Example 1: B, C, A, D, Z, E, … F, X, G
(a) U
(b) Y
(c) W
(d) V
Solution. (b) The sequence consists of two series B, A, Z, Y, X and C, D, E, F,
G. The missing letter is Y.
Example 2: P, U, Z, … J, 0, T
(a) E
(b) U
(c) S
(d) P
Solution. (a) The sequence is P+ 5, U+ 5,Z+ 5. The missing letter is Z +
5 = E
Example 3: B, D, G, I, … N, Q, S
(a) I
(b) J
(c) L
(d) K
Solution. (c) The sequence is B + 2, D+ 3, G + 2, I + 3 and so on.
Type 2
Two Letter Series The first letters of the series follow one logic and the second letters follow another logic.
Example 4: EZ, DX, CV,..., AR, ZP
(a) CS
(b) AM
(c) BT
(d) TG
Solution. (c) First and second letters follow a sequence of-1 and -2
respectively.
Example 5: DG, HK, LO, PS, TW,…
(a) XA
(b) ZA
(c) XB
(d) None of these
Solution. (a) First and second letters follow a sequence of + 4.
Example 6: DX, EY FV, ... : ; HT, IU
(a) HV
(b) IX
(c) GW
(d) BZ
Solution. (c) First, -third and fifth terms follow a sequencee and
second, fourth and sixth terms follow another sequence. (DX, FV, HT, etc) and (EY,
GW, IU, etc).
Type 3
Three Letter Series: :Such series consist of three letters in each term. The first letters follow one logic, the second letters follow another logic and the third letters follow some other logic.
Example 7: DIE, XCY, RWS, ...
(a) LQN
(b) QMP
(c) LMS
(d) LQM
Solution. (d) First, second and third letters of each group follow a
sequence of -6 series.
Example 8: VPG, UQF, ..., SSD, RTC
(a) SQD
(b) TRE
(c) TRS
(d) QDT
Solution. (b) First, second and third letters follow a sequence of –1, +
1, –1 series respectively.
Example 9: DJS, HNW, LRA, PVE, ..., XDM
(a) TZI
(b) SAF
(c) UXH
(d) None of these
Solution. (a) First, second and third letters follow a sequence of + 4
series.
Type 4
A series of letters is given with one or more missing letters. Fromthe choices, the choice that gives the letters that go into the blanks has to be selected as answer.
Example 10: In the following series some letters are missing. From the
choices, select the choice that gives that letters that can fill the blanks in
the given sequence. a_ c_ b_ab_a_ca_c
(a) abaccb
(b) accbab
(c) aabbcc
(d) baccbb
Solution. (d) First of all, notice that there are 6 blanks in the given
sequence and each choice gives six letters to fill the six blank in order. Now,
we have to select an alternative which if placed in the blanks of the series in
order, we get a complete series of letters which follow some particular pattern.
The best way is to try with each option. Inserting the letters of option (d) in place of the blanks, we get a series like “abc abc abc abc abc” which is a repetition of the group of letters “abc”.
Type 5
Here, students are asked to count how many times a particular letter or group of letters satisfying some conditions occurs and mark that number as the answer choice.
Example 11: In the following sequence of letters, in howmany instances the
letters n is immediately preceded by the letter t ?
snruatnnghjtknstndgclntttnnntntntsmvbtngcxdptnklstnt
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 8
Solution. (d) On counting, we find that the letter n occurs 8 times,
where n is immediately preceded by the letter t.
© UPSCPORTAL.COM

