(Paper) C-SAT Sample Test Paper-3 : Logical Reasoning and Analytical Ability
C-SAT Sample Test Paper- 3
Logical Reasoning and Analytical Ability
1. How many meaningful words can be made from the letters ‘AINTS’ using
each letter only once ?
(a) None
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Three
(e) More than three
2. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and so from
group. Which is the one that does not belong ?
(a) Tree
(b) Plant
(c) Shrub
(d) Creeper
(e) Farm
3. In a certain code BANK is written as 5796 and FIRE is written as 3146.
How is FEAR written in that code ?
(a) 3564
(b) 3674
(c) 3574
(d) 3654
(e) None of these
4. If it is possible to make only one meaning word from the second, the
sixth, the seventh, the eight and the tenth letters of the word PERFORMANCE,
using each letters only, first letter of the word is your answer. If no such
word can be formed your answer is X and if more than one such word can be formed
your answer is Y.
(a) C
(b) R
(c) M
(d) X
(e) Y
5. If the first and second digits are interchanged in each number from the
following set of numbers, and then the numbers are arranged in descending order,
which number will be second ?
376 438 476 389 567
(a) 376
(b) 438
(c) 476
(d) 389
(e) 567
6. How many such pairs of letters are there in the word EDUCATION, each of
which has as many letters between them in the word, as have in the English
alphabet ?
(a) None
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Three
(e) More than three
7. Five friends P, Q, R, S and T went to college independently. Each one
of them reached at a different time. If only Q reached after R and S, who last
person to reach ?
(a) P
(b) T
(c) Q
(d) Cannot be determined
(e) None of these
8. If ‘+’ means ‘-’, ‘-’ means ‘×’, ‘×’ means ‘÷’, and ‘÷’ means ‘+’, then
what is the value of :
40÷ 360× 24 - 4 + 18 = ?
(a) 118
(b) 82
(c) 72
(d) 90
(e) None of these
9. If in the word PROJECTING, all the vowel are first arranged
alphabetically and then all the consonants are arranged alphabetically, which
letter will be fifth from the left ?
(a) C
(b) N
(c) J
(d) G
(e) None of these
10. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and so form a
group. Which is the one that does not belong to the group ?
(a) Sharpener
(b) Calculator
(c) Eraser
(d) Pencil
(e) Stapler
11. If the digits of the number 375486 are arranged in ascending order,
how many digits will remain at the same position ?
(a) None
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Three
(e) More then three
12. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way three so form a
group. Which is the one that does not belong to the group ?
(a) 17
(b) 19
(c) 23
(d) 27
(e) 29
13. If in the word LUBRICATOR the positions of the first and the sixth
letters are interchanged, similarly the positions of the second and the seventh
letters are interchanged, and so on, which letter will be second to the right of
sixth letter from the right ?
(a) B
(b) T
(c) A
(d) O
(e) None of there
14. In a certain code DURATION is written as VEBSJUP, how is FORECAST
written in that code ?
(a) PGSFBDTU
(b) PGFSUTBD
(c) PGSFUTBD
(d) PGFSBDUT
(e) None of these
15. If ‘A $ B’, means ‘A is father of B’, ‘A # B’ means ‘A is daughter of
B’, ‘A @ B’ means ‘A is sister of B’, then how is K related to M in H @ K $ L #
M ?
(a) Husband
(b) Uncle
(c) Father
(d) Cannot be determined
(e) None of these
Direction (Q. 16-22): Study the following
arrangement carefully to answer these questions.
5 H I 7 $ K J 4 % L A T 3 8 @ F 6 U # V P 1 E * 9 D 2
16. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way on the basis of
their position in the above arrangement and so form a group. Which is the one
that dose not belong to the group ?
(a) J% 4
(b) H 7 I
(c) T 3 8
(d) E 9 *
(e) F U 6
17. What will come in place of the Question mark (?) in the following
series based on the above arrangement?
H7$ K4% LT3 ?
(a) F 6 #
(b) 8@ 6
(c) 8 F 6
(d) F U #
(e) None of these
18. How many such vowels are there in the above arrangement, each of which
is immediately following by a symbol ?
(a) None
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Three
(e) Four
19. Which element is sixth to the right of fourteenth from the right end ?
(a) #
(b) P
(c) U
(d) 1
(e) None of these
20. If from the above arrangement, all the digits are dropped which
element will be tenth from the left end ?
(a) F
(b) @
(c) T
(d) U
(e) None of these
21. How many such digits are there in the above arrangement each of which
is immediately followed by a symbol which is immediately followed by a consonant
?
(a) None
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Three
(e) More than three
22. How many such consonants are there in the above arrangement each of
which is immediately followed by a vowel but not immediately preceded by a
symbol ?
(a) None
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Three
(e) Four
Directions (Q. 23-30) : In each of the
questions below are given three statements followed by two conclusions numbered
I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to
be at variance with commonly know facts. Read all the conclusions and then
decide which of the given conclusions and then decide which of the given
disregarding logically follow from the given statement disregarding commonly
known facts.
Give answer (a) : if only Conclusion I follows.
Give answer (b) : if only Conclusion II follows.
Give answer (c) : if either Conclusion I or II follows.
Give answer (d) : if neither Conclusion I or II follows.
Give answer (e) : if both Conclusion I or II follows.
23. Statement :
All books are magazines.
Some magazines are notebooks.
Some notebooks are papers.
Conclusions :
I. Some books are notebooks.
II. Some magazines are papers.
24. Statement :
Some pearls are stones.
All stones are bricks.
All bricks are walls.
Conclusions :
I. Some pearls are bricks.
II. Some pearls are walls.
25. Statement :
Some apples are oranges.
Some oranges are grapes.
All grapes are bananas.
Conclusions :
I. Some apples are bananas.
II. Some oranges are bananas.
C-SAT Sample Test Paper- 3
Logical Reasoning and Analytical Ability
26. Statement :
All mobiles are phones.
All phones are computers.
All computers are scanners.
Conclusions :
I. All mobiles are computers.
II. All phones are scanners.
27. Statement :
Some boxes are bags.
All bags are trunks.
All trunks are drawers.
Conclusions :
I. All bags are drawers.
II. All trunks are bags.
28. Statement :
All cars are buses.
Some buses are scooters.
No scooter is a train.
Conclusions :
I. No bus is a train.
II. Some buses are train.
29. Statement :
Some chairs are wheel.
Some wheels are sofa sets.
All sofa sets are cupboards.
Conclusions :
I. Some wheels are cupboards.
II. Some chairs are sofa sets.
30. Statement :
Some coins are notes.
All notes are cards.
All cards are plastics.
Conclusions :
I. Some coins are cards.
II. All notes are plastics.
Directions (Q. 31-35) : These
questions are based on the following information :
Eight persons L, M, N, P, Q, R, S and T are sitting around a circular table
facing the centre. Q is not the neighbour of P or R. M is second to the left of
T and third to the right of P. R is third to the left of N, who is to the
immediate left of T. L is second to the right of P.
31. Which of the following pairs of person represents the neighbours of T
?
(a) MN
(b) QS
(c) RP
(d) ML
(e) None of these
32. Which of the following is definitely true ?
(a) Q is to the immediate right of S.
(b) R is to the immediate right of P.
(c) M is between N and Q.
(d) R is between P and S.
(e) None of these.
33. Who is to the immediate right of T ?
(a) R
(b) S
(c) N
(d) Q
(e) None of these
34. Who is to the immediate left of P ?
(a) S
(b) R
(c) Q
(d) L
(e) None of these
35. In which of the following pairs of persons the second person is to the
immediate left of the first person ?
(a) QS
(b) NT
(c) ML
(d) RL
(e) None of these
Direction (Q. 36-40) : In these
question symbols @, #, $, % and © are used with different meaning as following :
< ‘A @ B’ means ‘A is smaller than B’.
> ‘A # B’ means ‘A is greater than B’.
< ‘A $ B’ means ‘A is either smaller than or equal to B’.
> ‘A % B’ means ‘A is either greater than or equal to B’.
= ‘A © B’ means ‘A is neither greater then nor smaller than B.’
In each question, three statements showing relationships have been given, which
are followed by two conclusions I & II. Assuming that the given statements are
true, find out which conclusion (s) is/are definitely true.
Mark answer (a), if only conclusion I is true; mark answer (b), if only
conclusion II is true; mark answer (c), if either conclusion I or II is true;
mark answer (d), if neither I nor II is true and mark answer (e), if both
conclusion I and II are true.
36. Statement :
L$K, K@M, J%M
Conclusions :
I. L @ M
II. K @ J
37. Statement :
E $ W, W @ Q, Q % H
Conclusions :
I. E $ Q,
II. E©H
38. Statement :
J © T, T # W, W % R
Conclusions :
I. J # R
II. T % R
39. Statement :
T # R, R % H, H @ F
Conclusions :
I. H @ T
II. F © T
40. Statement :
F © D, D # V V @ P
Conclusions :
I. F © P
II. V # F
Direction (Q. 41-45) : In each of these
questions a group of digits is given followed by four combinations of
letter/symbol codes numbers (a), (b), (c) & (d). The group of digits is to be
coded as per the following scheme and conditions. The serial number of the
combination that represents the group of digits is your answer. If none of the
combinations is correct, your answer is (e), i.e. ‘None of these’.
Digit : 5 1 4 8 9 3 6 2 7 0
Letter/Symbol : Q T % # E F $ L W @
Conditions :
(i) If the first digit is odd and the last digit is even, their codes are to be
swapped.
(ii) If the first as well as the last digit is even both are to be coded by the
code for first digit.
(iii) If the first digit is even and the last digit is odd, both are to be coded
by code for odd digit.
41. 431068
(a) %FT@$#
(b) %FT$@#
(c) %FT@$%
(d) #FT@$#
(e) None of these
42. 803279
(a) E@FLWE
(b) #@FLWE
(c) #@FLW#
(d) E@FLW#
(e) None of these
43. 765984
(a) W$QE#%
(b) W$QE#W
(c) %$QE#%
(d) %$QE#L
(e) None of these
44. 584632
(a) Q#%$FL
(b) L#$%FQ
(c) L#%$QF
(d) L#%$FQ
(e) None of these
45. 384695
(a) F#%$EF
(b) F#%$EQ
(c) Q#%$EQ
(d) Q#%$EF
(e) None of these
Directions (Q. 46-50) : Study the
following information carefully to answer these questions.
Seven friends H, I, J, K, V, W and X study different disciplines, viz Arts,
Commerce, Science, Engineering, Architecture, Management and Pharmacy, not
necessarily in the same order. Each of them belongs to a different state, viz
Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh
and Punjab, but not necessarily in the same order.
J studies Engineering and does not belong to either Uttar Pradesh and Punjab. The one who belongs to Madhya Pradesh does not study Architecture or Pharmacy. H belongs to Maharashtra. V belongs to Kerala and studies Science. The one who belong to Andhra Pradesh studies Commerce. K studies Management and X studies Arts. I belongs to Karnataka and does not study Architecture. The one who studies Arts does not belong to Punjab.
46. Who studies Architecture ?
(a) V
(b) X
(c) W
(d) Cannot be determined
(e) None of these
47. Which of the following combination of state and subject is correct ?
(a) Uttar Pradesh - Arts
(b) Uttar Pradesh - Science
(c) Kerala - Management
(d) Punjab - Science
(e) None of these
48. Which subject is studies by I ?
(a) Arts
(b) Commerce
(c) Pharmacy
(d) Management
(e) None of these
49. Who belongs to Madhya Pradesh ?
(a) W
(b) J
(c) X
(d) X
(e) None of these
50. W belongs to which state ?
(a) Kerala
(b) Madhya Pradesh
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) Andhra Pradesh
(e) None of these
C-SAT Sample Test Paper- 3
Logical Reasoning and Analytical Ability
Directions (Q. 51-55) : Below in each
question are given two statements (A) (B). These statements may either
independent causes or may be effects of independent causes or a common cause.
One of these statements may be the effect of the statement. Read both the
statements and decide which of the following answer choices correctly depicts
the relationship between these two statements.
Mark answer (a) if statement (A) is the cause and statement (B) is its effect.
Mark answer (b) if statement (B) is the cause and statement (A) is its effect.
Mark answer (c) if both the statement (A) and (B) are independent causes.
Mark answer (d) if both the statement (A) and (B) are effects of independent
causes.
Mark answer (e) if both the statement (A) and (B) are effects of some common
causes.
51. A. The State Education Board has decided to do away with preparing
merit lists for SSC and HSC examinations.
B. A large number of students scored very high marks in the recently help SSC
examinations.
52. A. The State Government decided to grant permission for opening
more junior colleges in the state.
B. Percentage of qualified students in SSC examinations was higher this year
compared to the past few years.
53. A. Increase in rainfall and rising flood situations are regular
phenomena for past few years.
B. People avoid going out in heavy rains.
54. A. The health department has advised people to drink boiled and
filtered water and maintain hygiene during the monsoon.
B. The health department has instructed the civic hospitals to equip themselves
with adequate stock of medicines during monsoon.
55. A. The Government has made it compulsory to wear a helmet for the
riders of two-wheelers.
B. The number of cases of accident involving two-wheelers has been increasing
every year.
Directions (Q. 56-60) : In making
decisions about important questions, it is desirable to be able to distinguish
between “strong” arguments and “weak” arguments. “Strong” arguments must be
important and directly related to the question. “Weak” arguments may not be
directly related to the question and may be of minor importance or may be
related to the trivial aspects of the question.
Each question below is followed by two arguments number I and II. You have to
decide which of the arguments is a “strong” argument and which is a “weak”
argument.
Give answer (a) : if only argument I is strong.
Give answer (b) : if only argument II is strong.
Give answer (c) : if either argument I or II is strong.
Give answer (d) : if neither argument I or II is strong.
Give answer (e) : if both argument I or II are strong.
56. Should the major part of school examinations be made objective-type?
Arguments :
I. No, objective-type examination does not test the students’ ability to
express.
II. Yes, this is the best method of assessing one’s ability and
knowledge.
57. Should the Government service in rural areas at least for two years
after completion of graduation be made compulsory for the students of medicine?
Arguments :
I. Yes, it is everyone’s duty to serve the people in rural and contribute
to their upliftment.
II. No, it cannot be applied only to the medicine students since anyways
they are contributing during their studies and particularly in the period of
internship.
58. Should all the factories in the cities be shifted to the outskirts,
far away from the main city?
Arguments :
I. Yes, this is an essential step for controlling pollution in the city.
II. No, such a step will lead to lot of inconvenience to the employees of
the factories and their families as well.
60. Should there be a total ban on use of plastic bags?
Arguments :
I. No, instead the thickness of plastic bags, which can be used without
much damage to the environment, should be specified.
II. Yes, use of plastic bags causes various problems like water pollution
and water-logging and hence it is necessary t ban it.
Directions (Q. 61-70) : For recruiting
Management Trainees in an organisation, the following criteria have been laid
down. The candidate must:
(a) be a first-class graduate in Commerce with at least 65% marks.
(b) have secured at least 70% marks in SSC.
(c) be not more than 26 years and not less than 21 years of age as on 1.8.2007.
(d) have secured at least 60% marks in selection test.
(e) have secured at least 50% marks in selection interview.
However, if a candidate fulfils all the above-mentioned criteria except
(i) at (a) above but is an Economics graduate with at least 70% marks, the case
may be referred to GM of the organisation.
(ii) at (e) above but has secured at least 40% marks in selecting interview and
at least 70% marks in selection test, the case may be referred to the President
of the organisation.
In each of the questions below, information of one candidate is given. You have
to take one of the following five decisions based on the information provided
and the criteria and conditions given above. You are not to assume anything
other than the information provided in each question. All these cases are given
to you as on 1.08.2007. You have to indicate your decision by marking answers to
each question as following:
Give answer (a) : If the candidate is to be selected.
Give answer (b) : If the candidate is not to be selected.
Give answer (c) : If the case is to be referred to GM.
Give answer (d) : If the case is to be referred to president.
Give answer (e) : If the data is inadequate to decide the course of
action.
61. Abhishek has passed degree examination in Commerce with Economics one of the subjects in first class with 68% marks in 2006 at the age of 22 years. His marks in SSC was 73%. He has cleared the selection test with 64% marks and selection interview with 62% marks.
62. Sharad Bhatia has passed B Com in first class with 69% marks and SSC with 78% marks. He joined a private organisation as an Officer in Jun 2005 immediately after completing 23years of age. He has scored 65% marks in selection test 48% marks in selection interview.
63. Priyanka Ghate has passed graduation in Arts with specialisation in Economics in first class with 75% marks. Her data of birth is 08.07.1985. She had scored 89% marks in SSC, 63% in selection interview and 61% marks in selection test.
64. Rakesh has passed SSC with 85% marks and graduation in Art with specialisation in Economics with 72% marks. His data of birth is 12.06.1985. He has scored 65% marks in selection test as well as in interview.
65. Sarita Dere is a postgraduate in Commerce passed in first class with 62% marks. Her score in SSC was 75%. She completed 23 years of age on 23rd December, 2006. She has scored 64% marks in selection test and 55% marks in selection interview.
66. Ashish Gharpure is a Commerce graduate passed out in Jun 2006, at the age of 21 years with 72% marks and first class. Presently he is pursuing his post graduation in Economics. He had scored 82% marks in SSC. He has cleared the selection test with 67% marks and selection interview with 56% marks.
67. Radhika has passed BA examination with specialisation in Economics securing 76% marks and first class. She topped her class in SSC examination with 82% marks. She has completed 24 years of age on 25th may, 2007. She cleared the selection test with 66% marks and the selection interview with 54% marks.
68. Ashwini is a B.Com passed in first class with 68% marks. She had scored 75% marks in SSC. Her data of birth is 14.09.1984. She had cleared the selection test with 74% marks and selection interview with 45% marks.
69. Rajesh is a graduate and postgraduate in Commerce and has passed both these examinations in first class. He had scored 75% marks in SSC. He completed 23 years of age on 23rd Jun 2007. He has scored 65% marks in interview as well as selection test.
70. Rashmi is B Com in First class with 62% marks and M.Com also in first class with 67% marks. He marks in SSC were 85%. She completed 24 years of age on 3rd October 2006. She has scored 66% marks in selection test and 56% marks in interview.
C-SAT Sample Test Paper- 3
Logical Reasoning and Analytical Ability
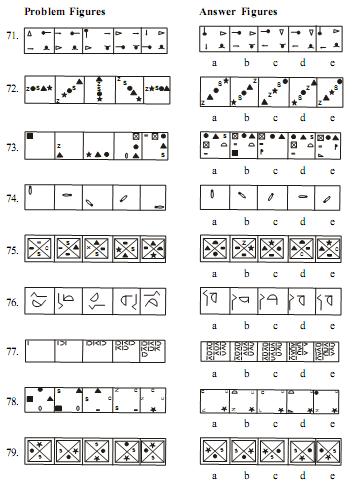
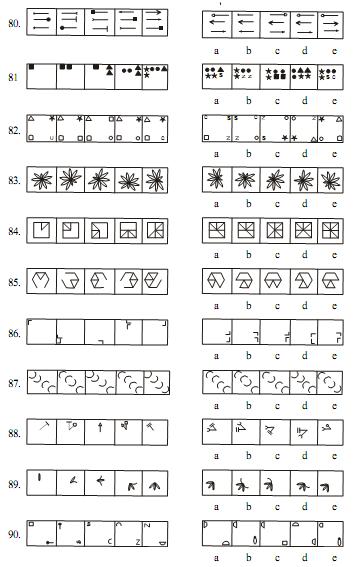
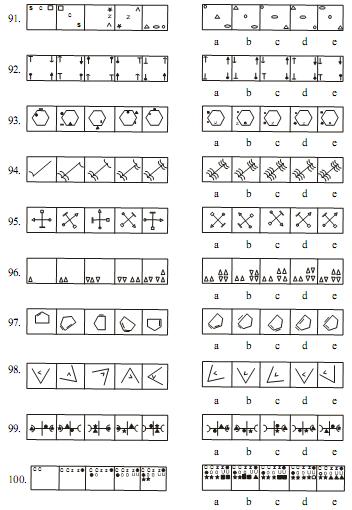
Direction (Q. 71-100) : In each of the questions given below which one the five answer figures on the right should come after the problem figures on the left, if the sequence were continued ?