(HOT) UPSC Current Affairs 2025 PDF
NEW! The Gist (NOV-2025) | E-BOOKS
(IGP) IAS Pre: GS - Geography - World Geography General: Asia
World Geography General
Asia
Introduction
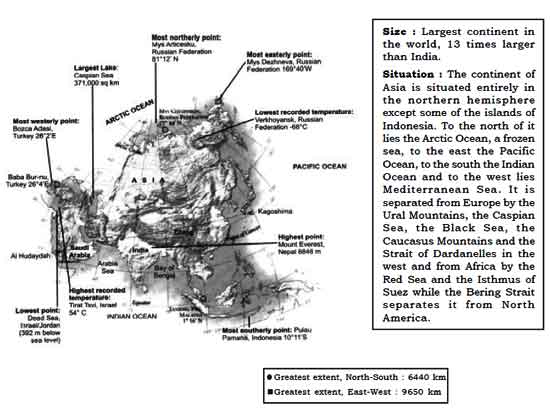
Area: 43,608,000 million sq. km (30% of total land surface of the earth.)
Population : 3588.9 million
Latitudes : 10011'S to 81012'N
Only some of the Indonesian group of Islands is located to the south of equator in the Southern Hemisphere.
Longitude : 2602'E to 169040'W in the east crossing 1800 longitude.
North-South Extent : 6,440 km East-West Extent : 9,650 km
Asia—Physical
Important Seas
| Name | Location | Part of Ocean |
| Kara Sea, Laptev Sea, and East Siberian Sea | North of Russia | Arctic Ocean |
| Bering Sea | Northerst of Russia | Pacific Ocean |
| Sea of Okhotsk | East of Russia | Pacific Ocean |
| Sea of Japan | West of Japan | Pacific Ocean |
| Yellow Sea | West of Korea | Pacific Ocean |
| East China Sea | East of China | Pacific Ocean |
| South China Sea | South of China | Pacific Ocean |
| Sulu Sea | West of the Philippines Island | Pacific Ocean |
| Celebes Sea | North of Celebes Island | Pacific Ocean |
| Banda Sea | East of Celebes Island | Pacific Ocean |
| Flores Sea | South of Celebes Sea | Pacific Ocean |
| Molucca Sea | East of Celebes Island | Pacific Ocean |
| Java Sea | North of Java | Pacific Ocean |
| Timor Sea | Northwest of Australia | Pacific Ocean |
| Arafura Sea | North of Australia | South Pacific Ocean |
| Bay of Bengal | East of the Indian Peninsula | Indian Ocean |
| Arabian Sea | West of the Indian Peninsula | Indian Ocean |
| Red Sea | Separates Asia from Africa | Indian Ocean |
Important Gulfs
| Name | Location | Part of Ocean |
| Gulf of Ob | Between Yamal Peninsula and Gyda Peninsula | Arctic Ocean |
| Gulf of Chihli | East of China | Yellow Sea (Pacific Ocean) |
| Gulf of Tonkin | Eastof Vietnam | South China Sea (Pacific Ocean) |
| Gulf of Thailand | South of Thailand | South China Sea |
| Persian Gulf | Separates Arabian Peninsula from the Plateau of Iran | Indian Ocean |
| Gulf of Oman | Between Iranian Plateau and Oman | Indian Ocean |
| Gulf of Aden | Between Somalia and Yemen | Indian Ocean |
| Gulf of Aquaba | Between Aquaba (Jordan) and Sinai Peninsula (Egypt). | Red Sea |
| Severnaya Islands | North of Russia | Arctic Ocean |
| New Siberian Islands | North of Russia | Between Laptev Sea and East Siberian Sea, Arctic Ocean |
| Wrangel Islands | North of Russia | East Siberian Sea, Arctic Ocean |
Kurile Islands
|
Between Kamchatka Peninsula and Hokkaido Island | Pacific Ocean |
Ryukyu Island
|
Between Kyushu and Taiwan | Pasific Ocean |
| Bonin Island | East of Ryuky Island | Pasific Ocean |
| Babuyan Islands | Between Taiwan and Luzon (Philippines) | Pasific Ocean |
| Spartly and Parcel Islands |
A group of atolls in South China Sea | Pasific Ocean |
|
||
| The Philippines archipelago | Lying 1200 km east of Vietnam and 150 north of the equator.
Luzon.
|
Pasific Ocean |
Important Straits
| Name | Separates | Connects |
| Bering Strait | Asia and North America | East Siberian Sea with Bering Sea |
| La Parouse Strait | Sakhalin Island and Hokkaido Island | Sea of Okhotsk with Sea of Japan |
| Tata Strait | Eastern Russia and Sakhalin | Sea of Okhotsk with Sea of Japan |
| Korea Strait | South Korea and Kyushu (Japan) | Yellow Sea with Sea of Japan |
| Formosa Strait (Taiwan Strait) | Taiwan and China | East China Sea with South China Sea |
| Luzon Strait | Taiwan and Luzon (Philippines) | South China Sea with Pacific Ocean. |
| Makassar Strait | Borneo (Kalimantan) and Celebes Island | Celebes Sea with Java Sea. |
| Sundra Strait | Java and Sumatra | Java Sea with India Ocean |
Malacca Strait
|
Malaya Peninsula and Sumatra | Java Sea with Bay of Bengal |
| Strait of Jahore | Singapore and Malaysia | South China Sea with strait of Malacca |
| Strait of Hormuz | UAE and Iran | Persian Gulf with Gulf of Oman. |
| Strait of Bosporus | Asia and Europe | Black Sea with Sea of Marmara. |
| Strait of Dardanelles | Asia and Europe | Sea of Marmara with Mediterranean Sea |
Important Mountains
| The Himalayan Mountain Range |
|
| Karakoram Range |
|
| Kailash Range |
|
| Kunlun Shan Range |
|
| Tienshan |
|
| Great Khingan Mountain |
|
| Altai Mountain
Hangay Mountain Sayan Mountain |
|
| Yablonovy Range, Stanovoy Range, Dzhugzur Range and Kolyama Range |
|
| Verkhoyansk Range |
|
| Pegu Yoma |
|
| Arakan Yoma |
|
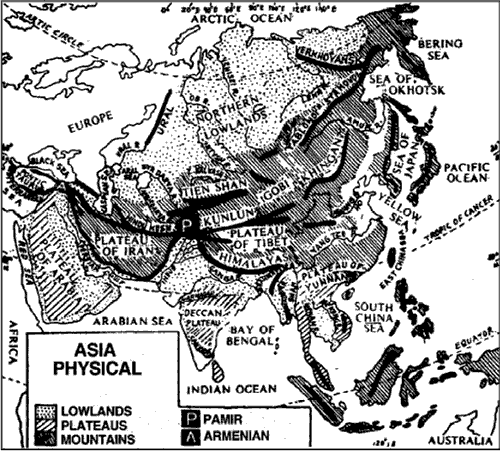
The Mountain Regions to the West of the Pamir
| Hindukush Mountains |
|
| Elburz Mountains |
|
| Sulaiman Range |
|
| Kirthar Range |
|
| Makran Range |
|
| Zagros |
|
| Pontic Mountain Range |
|
| Taurus Mountain Range |
|
Important Plateaus and Basins
| NAME | INFORMATION |
| Ladakh Plateau (Inter- montane Plateau) |
|
| Tibet Plateau (Inter- montane Plateau) |
|
| Yunan Plateau |
|
| Takla Makan Desert Plateau and Tarim Basin |
|
| Pamir Plateau |
|
| Armenian Plateau |
|
| Iranian Plateau |
|
| Mongolian Plateau |
|
| Urfan Basin |
|
| Aldan Plateau |
|
| Indo-China Plateau |
|
| Shan Plateau |
|
| Deccan Plateau |
|
| Baluchistan Plateau |
|
| Arabian Plateau |
|
| Plateau of Antolia of Asia Minor or Turkey |
|
| Loess Plateau |
|
| Dzungarian Basin |
|
| Mesopotamian Plain |
|
| Gobi Desert |
|
Important Land Regions
| Manchurian Plain |
|
| Great Plain of China |
|
| Turanian Plain |
|
| West Siberian Plain |
|
| Taaidam Basin |
|
| Szechuan Basin |
|
|
THE DESERT LANDSCAPE OF SAUDI ARABIA |
|
| Rub-al-Khali |
|
| Al Nafud Desert |
|
|
THE DESERT LANDSCAPE OF IRAN |
|
| Dash-I-Kavir |
|
| Dasht-I-Lut |
|
Important Lakes
| NAME | INFORMATION |
| Lake Baikal |
|
| Lake Balkash |
|
| Aral Sea |
|
| Lake Van Golu |
|
| Lake Turnool |
|
| Lake Asad |
|
| Dead Sea |
|
| Sea of Gallilee |
|
| Lake Tonle Sap |
|
| Lake Toba |
|
| Lop Nor |
|
| Caspian Sea |
|
Important Rivers
| NAME | SOURCE | OUTFLOW |
|
NORTH FLOWING RIVERS FROM WEST TO EAST IN RUSSIA |
||
| Ob
Tributaries : Irtysh, Tobolsk |
Altai Mountain | Gulf of Ob |
| Yenisey | Tannuala Mountain | Arctic Ocean |
| Lena | Lake Baikal | Arctic Ocean |
| Kolyma | Kolyma Range | East Siberain Sea |
| EAST FLOWING RIVERS (FROM NORTH TO SOUTH) | ||
| Amur
Tributary : Sungari River. |
Confluence of Shika Argun River. | Tatar Strait |
Yalu
|
Korea Bay (Yellow Sea) | |
| Hwang Ho | Tibetan Plateau | The river’s course was diverted away into the Gulf of Pohai instead of the Yellow Sea. |
Yangtse Kiang
|
Tibetan Plateau | East China Sea. |
Si Kiang
|
Eastern Yunan (China) | South China Sea. |
| EAST FLOWING RIVERS (FROM NORTH TO SOUTH) | ||
|
||
| SOUTH FLOWING RIVERS | ||
Mekong
|
Tibetan highlands | South China Sea |
Chao Phraya
|
Gulf of Thailand | |
Salween
|
Tibetian highlands | Gulf of Martaban |
| Irrawaddy
Tributary : Chindwin City located : Mandalay
|
North Myanmar | Bay of Bengal |
Brahmaputra
|
Rises in galcier about 100 km south east of Mansarovar Lake |
Bay of Bengal |
| SOUTH FLOWING RIVERS | ||
|
||
Ganga
|
Gangotri Glacier | Bay of Bengal |
Indus
|
Mansarovar lake | Arabian Sea |
Tigris and Eupharates
|
Persian Gulf | |
Amu Darya and Syr Darya
|
||
Click Here to Download full Chapter
Click Here for Asia MCQ
© UPSCPORTAL.COM


