(IGP) IAS Pre: GS - Geography - World Geography General: Australia
World Geography General
Australia
Introduction
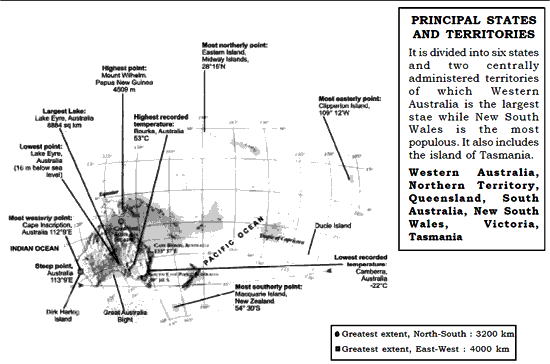
Latitude : 28015'N 54030'S Longitude : 112009'E 109012'W
Area: 76,86,850 sq. km Population : 18.7 million
Capital : Canberra
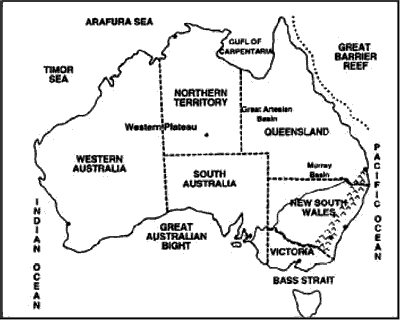
Situation : Australia, the only ontinent that is also a country. It liest between the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is surrounded by Timor Sea in the northwest, Arafura Sea dn Gulf of Carpentaria in the north, Great Barrier Reef in the northeast and Great Australian Bright in the south. To the south east of mainland lies the mountainous island of Tasmania.
Australia—Physical
- Major Physiographic Regions of Australia is—The Great Dividing Range, Central Lowlands and Western Plateau.
THE GREAT DIVIDING RANGE
|
|
CENTRAL LOWLANDS
|
THE WESTERN PLATEAU REGION
|
AUSTRALIA—WEST
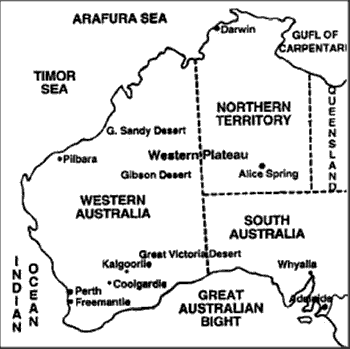
Western Australia
Major Physiographic Regions
Desert Landscape : Great Sandy desert in the north west, Gibson desert in the central part lying to the south of Lake Disappointment and Great Victoria desert extending into South Australia.
Highlands and Mountains
Darling Range
- Running in north-south direction in the south west of Western Australia.
- Kimberley Plateau-lies to the north of Great Sandy Desert.
- Mount Gold Worthy, Mount Whaleback and Mount Tom Price : Major region of iron ore reserves in Western Australia.
Cities of Western AustraliaPERTH
FREMANTLE
KALGOORLIE, COOLGARDIE
PILBARA
|
Northern TerritoryMajor Physiographic Regions Desert Landscape : Tanani desert in the north, Simpson Desert, in the south east of Alice Springs. HIGHLANDS AND PLATEAUS
DARWIN
ALICE SPRING
|
South AustraliaMajor Physiographic Regions Great Victoria Desert
Flinders Range
Lake Eyre
Important CitiesADELAIDE
WHYALLA
|
|
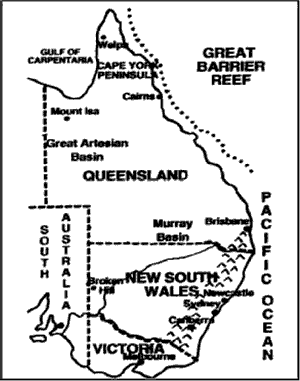
AUSTRALIA—EAST
Major Physiographic RegionsGreat Dividing Range
Australian Alps
|
Murray Darling Basin
|
New South WalesSYDNEY
NEW CASTLE
BROKEN HILL
|
 |
Major Physiographic Regions |
|
BRISBANE
IPSWICH
|
MOUNT ISA
WEIPA
|
Victoria
This state is situated in the south east of Australia, and the Murray River divides it from New South Wales.
MELBORNE
- The capital of Victoria.
- Country’s second largest city and also former capital of Australia.
- Centre of major industries based on Gippsland’s lignite coal and hydel power from the Snowy river scheme.
- Chemicals, ship-building, aircraft, engineering, railway equipments and motor vehicles are the major industries.
GIPPSLAND
- Centre of lignite and sub bituminous coal mining.
- Australian Capital Territory.
CANBERRA
- Nation’s capital, situated to the south of Sydney.
- It is mainly administrative city.
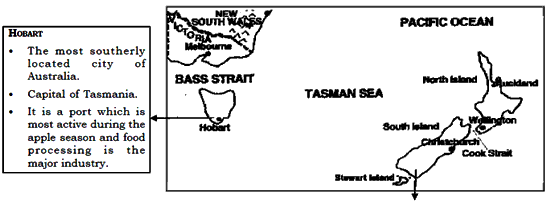
NEW ZEALAND
Area: 2,69,057 sq. km (excluding dependencies)
Population : 3.8 million Latitude : 34005'-47020'S
Capital : Wellington Longitude : 166010'-178020'E
Situation : The three main island of New Zealand are situated to the south east of Australia and 10,000 km west of Chile in the South Pacific Ocean. The two larger islands, North and South Islands are long and narrow and the third, Stewart Island, is the smaller one.
Physical features
Southern Alps
The mountains of the South Island, includes the country’s highest peak, Mount Cook (3,764 m).
Canterbury Plains
- The most extensive plains, an example of Piedmont Alluvial plain crossed by rivers cover 12,500 km of the South Island’s east coast.
- The chief farming region in New Zealand.
MOUNT EGMONT
- An extinct volcano in south-west of North Island.
- Situated to the north of central volcanic plateau of North Island.
WELLINGTON
- Situated on the southern tip of the North Island.
- Country’s capital and also the southernmost capital city of the world.
- An important sea port on the Cook Strait.
- Cattle rearing and dairy is the main economic activity around this city.
AUCKLAND
- Biggest city of the country and also the largst port on the coast of North Island.
CHRISTCHURCH
- Major industrial centre of the South Island.
THE PACIFIC ISLANDS
Scattered across the Pacific Ocean, between 1300W at a distance of 11,265 km are thousands of islands with a total land area of 2,60,0001 sq. km excluding New Zealand and New Guinea. They are made up of three main groups: Melanesia, Micronesia and Polynesia.
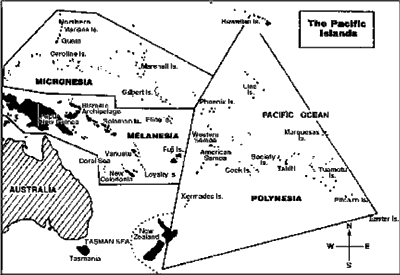
Important Independent Islands
Micronesia (Tiny Islands) |
Polynesia (Many Islands) |
Federal states of Micronesia Area : 702 sq. km. Population: 1,31,500 Capital : Palikir
Kiribati (Gilbert and Ocean Island) Area : 861 sq. km. Population : 85,501 Capital : Tarawa
Nauru Area : 21.1 sq. km. Population : 10,605 Capital: Yaren district
|
TUVALU Area : 26 sq. km. Population: 10,588 Capital : Funafuti
Melanesia (Black Islands)
|
Important Islands of Melanesia
PAPUA NEW GUINEA
Area : 4,62,840 sq. km.
Population : 4.8 million
Capital : Port Moresby
- The largest island of Melanesia.
- Consists of eastern part of New Guinea and adjacent islands.
FIJI
Area : 18,270 sq. km.
Population : 812,918
Capital : Suva
- Fiji’s largest island Viti Levu constituting more than half of the land area of the country.
SUVA
- It is located in the southeast coast of Viti Levu.
- It is the country’s capital and the largest city of Melanesia.
- Country’s light industrial centre and leading port.
SOLOMON ISLANDS
Area : 2,89,000 sq. km.
Population : 4,55,429
Capital : Honiara
- Situated to the east of Papua New Guinea in the Southwest Pacific Ocean.
NEW CALEDONIA
Capital : Noumea
- Minerally very rich, having deposits of nickel, chrome, cobalt, iron, gold, silver and copper.
Capital : Port-Vila
- It is a tourist destination offering unspoilt beaches and peaceful environment.
Click Here to Download full Chapter
Click Here for Australia MCQ
© UPSCPORTAL.COM