(IGP) IAS Pre: GS - Gist of Indian Year Book - Defence
Gist of Indian Year Book
Defence
Defence
-
The Supreme command of the Armed forces vests in the President of India. The responsibility for national defence, however, rests with the Cabinet. The Defence Minister (Raksha Mantri) is responsible to Parliament. for all matters concerning defence of the country. Administrative and operational control of the armed forces is exercised by the Ministry of Defence and the three Service Headquarters.
Organisation
-
Tie principal task of the Ministry is to frame policy directions on Defence and security related matters and communicate them for implementation to the Services Headquarters, Inter- Service Organisations, Production Establishments and Research & Development Organisations.
-
The principal functions of the Departments are as follows:
-
After Independence, Ministry of Defence was created under the charge of a Cabinet Minister and each service was placed under its own Commander-in -chief, (tn 1955, the Commanders- in-chief were renamed as the Chief of the Army Staff, the Chief of the Nval Staff and Chief of the Air Staff, in November, 1962 a Department of Defence Supplies was created for planning and execution of schemes for import substitution of defence requirements! In 2004, the name of the Department of Defence Production and Supplies was changed to Department of Defence Production. In 1980, the Department of Ex- ervicemen Welfare was-created
-
The Department of Defence deals with the Integrated Defence Staff (IDS) and three Services and various Inter-Service Organisations. It is also responsible for the Defence Budget, establishment matters, Defence policy, matters relating to Parliament.
-
The Department of Defence Production deals with matters pertaining to defence production, indigenisation of imported stores, equipment and spares, planning and control of departmental production units of the Ordnance Factory Board.
-
The Department of Defence Research and Development is headed by a Secretary, who is - the Scientific Adviser to the Raksha Mantri. Its function is on advise the Government on scientific aspects of military equipment and logistics and the formulation of research, design and development plans for equipment required by the Services.
-
The Department of Ex-Servicemen Welfare, deals with all resettlement, welfare and pensionary matters of Ex-Servicemen.
-
Integrated Defence Staff (IDS) was created on October 1,2001. Since then, HQ IDS has been- acting as the single point organisation f6rincülcatingjdmtness and synergy between the Armed Forces, by way of integrating policy, doctrine, war fighting and procurement.
-
The three Services Headquarters, viz., the Army Headquarters, the Naval Headquarters and the Air Headquarters function under the Chief of the Army Staff (COAS), the Chief of the Naval Staff (CNS) and the Chief of the Air Staff (CAS) respectively. The Inter- Service Organisations, under the Department of Defence are responsible for carrying out tasks related to common needs of the three Services such as medical care, public relations and ersonnel management of civilian staff in the Defence Headquarters.
Army
-
It is organized into operational commands, each under a General Officer of the rank of Lieutenant General
-
The field formations in army are Corps, Division, and Brigade commanded by a General Commanding Officer and his rank is as follows:
- Corps - Lieutenant General.
- Division - Major General
- Brigade - Brigadier Towards the modernization of the Mechanised Infantry, contracts for procurement of Environmental Control System and Instant Fire Detection and Suppression System tbr BMP-2/2K, Battle Field Surveillance Radar (Medium Range on TATRA8x8 and Thermal Imaging Sight to replace Mia Infra Red have been included during the year. A proposal for procurement of Brahmos Supersonic Cruise Missle System for two regiments of the Indian Army has been approved. The contract has been concluded in March 2010.
Territorial Army
- The Tejtprja1 Army was established in 1948.
- The Territorial Army is a voluntary, part-time citizen’s Army.
- In recent times, a maximum of 22 units were embodied in Operational Rakshak, Operation Vijay and Operation Parakram.
Navy
- Around 97 per cent of India’s trade amounting to 273 million tonnes and valued at $83 billion annually comes from the seas.
- The entire import of more than 50 million tonnes of oil and gas comes by the sea. The air squadrons INAS311 and IN AS 350 were commissioned on 24th March, 2009. Indian Naval Air Station Parundu was commissioned on26th March, 2009 a Uchipull in Ramnad District Tamil Nadu. INS Airavat, The fifth LST (L) Class Ship was Commissioned on 19th May, 2009 at Visakhapatnam.’INS Chetlat and Car Nicobar were commissioned on 16th February, 2009. ENS Cheriyarn and Cora Divh were Commissioned on 10th September, 2009. INS Shivalik was commissioned on 29th April, 2010
- INS Shardul, landing ship tank (large), was commissioned at Naval base, Karwar on January 4, 2007. INS Jalashwa acquired from US was commissioned at Norfolk (USA) on June. 22, 20O7. The ship is the first Landing, Platform Dock (LDP) in the Indian Navy.
- The Indian Navy (IN), by virtue of its capability, strategic positioning and robust presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), has been a catalyst for peace, tranquility and stability in the IOR.
- The firing of Beyond Visual Range (BVR) Derby Missile has been conducted successfully. Six UH3H Utility helicopters have been inducted in the service.
- In continuation with the policy of enhancing cooperation with foreign navies, a series of exercises were conducted. This included Indra 01/09, Konkan O9, Malabar 10, Varuna 10 and SIMBEK 10.
- Intensive Flying Training Unit (IFTU) for UH3H helicopters has been set up. The unit was commissioned as Indian Naval Air Squadron (INAS) 350 on March 23, 2009.
- Indigenously built INS Kesari was commissioned into the Indian Navy in April 2008. Two Water Jet- Fast Attack Crafts Chetlat and Car Nicobar were commissioned into the Indian Navy in February 2009.
Coastguard
-
The Coast Guard was established as an independent service on August 19, I978as per the Coast Guard Act, 1978. Since its inception, the Coast Guard has acquired-a wide range of platforms both surface and airborne to undertake the assigned tasks during peace time and to supplement the efforts of Indian Navy during war.
-
The command and control of the Coast Guard - rests with the Director General of Indian Coast Guard at New Delhi. The Organisation has four Regional Headquarters i.e. Mumbai, Chennai, Gandhinagar and Port Blair. The Coast Guard is mandated to keep India’s EEZ measuring over 2.02 million Sq Km.
-
Safety and protection of artificial islands and offshore terminals, installations and devices in Maritime Zones.
-
Protection and “assistance to fishermen at sea while in distress.
-
Preservation and protection of marine environment.
-
Prevention and control of marine pollution.
-
Other matters, including measures for the safety of life and property at sea and collection of scientific data. In addition to the mandate laid down under section 14 of Coast Guard Act, 1975, the Indian Coast Guard has also been entrusted the following lead roles:-
-
Offshore Security Co-ordination Committee.
-
National Maritime Search and Rescue Co-ordinating Authority.
-
Lead Intelligence Agency for Coastal and Sea Border.
-
Coastal Security in territorial waters.
-
11 Coast Guard District Headquarters located along the coastal States of India
Air Force
-
It was formed on October 8, 1932.
-
The Chief of Air Staff at Air Headquarters in New Delhi is assisted by the Vice-Chief of Air Staff. The Vice Chief of Air Staff is responsible for operations whereas the Deputy Chief of Air Staff is responsible for acquisition and planning. The Inspector General looks after the operational readiness, flight safety and inspection.
-
The IAF has inducted state-of-the-art Su- 3OMKI aircraft in operational squadrons. Twenty Hawk AJT aircraft have also been inducted’ procurement contract of C-130-30 aircraft for special operations from US Government has been signed.
-
A contract has been signed with M/s Rosonboron Export Russia for delivery of Mi-17V5 helicopters.
-
Airborne Warning and Control System (AWACS) are being procured to significantly enhance the effectiveness of both Offensive and Defensive operations of the IAF.
-
Contract for MiG-29 mid life upgrade and extension of total technical life was signed with RAC MIG, Russia. IAF is also processing upgradation of the Mirage-2000 and Jaguar aircrafts and Mi- 17 helicopters in order to optimise their utilization. To keep the DO-228 aircraft abreast with the latest technology, all the existing aircrafts are being upgraded with the latest avionics.
-
The upgrade of DARIN-I Jaguar aircraft to DARIN-III standard has been approved and is planned to be completed by 2017-2018.
AIR FORCE |
||
|
The Air Force is organized into the following five (operation and two (functional) command; |
||
| S.No. |
Command |
Headquarters |
| 1 | Western Air Command | Delhi |
| 2 | South-Western Air Command | Gandhi Nagar |
| 3 | Central Air Command | Allahabad |
| 4 | Eastern Air Command | Shillong |
| 5 | Southern Air Command | Thiruvanan thapuram |
II. Functional Commands |
||
| 1 | Training Command | Bengaluru |
| 2 | Maintenance Command | Nagpur |
AIR FORCE TRAINING INSTITUTIONS |
||
| S.No. | Name | Located at |
| 1 | Air Force Administrative College | Coimbatore |
| 2 | Air Force Academy | Hyderabad |
| 3 | Air Force Technical College | Jalahalli |
| 4 | Air Force School | Sambra (Belgaum) |
| 5 | Flying Instructors’ School | Tambaram |
| 6 | Ground Training School | Avadi |
| 7 | Navigation and Signals School | Hyderabad |
| 8 | College of Air Welfare | Secunderbad |
Commissioned Ranks
The following are the commissioned ranks in the three Services; each rank is shown opposite its equivalent in the other Service:
| Army | Navy | Air Force |
| General | Admiral | Air Chief Marshal |
| Lieutenant General | Vice-Admiral | Air Marshal |
| Major General | Rear Admiral | Air Vice-Marshal |
| Brigadier | Commodore | Air Commodore |
| Colonel | Captain | Group Captain |
| Lieutenant Colonel | Commander | Wing Commander |
| Major | Lieutenant Commander | Squadron Leader |
| Captain | Lieutenant | Flight Lieutenant |
| Lieutenant | Sub-Lieutenant | Flying Officer |
Recruitment
Recruitment of Commissioned Officers in
Armed Forces through UPSC: Commissioned Officers in the Armed Forces are
recruited mainly through the UPSC which conducts the following two All
India Competitive Examinations:
|
 |
Training for Defence Services
|
SUBMARINES
WARSHIPS
MISSILE BOATS
|
Defence Production
The Department of Defence Production deals with the
indigenization, development and production of defence equipment both in the
public and private
sectors.
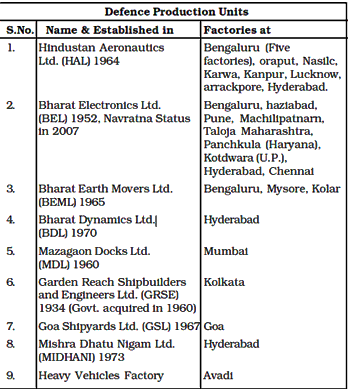
Ordnance Factories
Defence Undertakings
|
Products and Systems Developed by DRDO
|
Bharat Earth Movers Ltd.
-
(BEML Ltd.) is engaged in the design, manufacturing, marketing and fter sales support of a wide range of Mining & Construction equipment, Defence products and Railway Metro products. BEML was established in 1965 and commenced operations from January 1965.
-
Mazagair Dock Limited (MDL) is a Premier Ship Builder of the Nation. MDL is engaged in construction of warships including Destroyers, Corvettes, Submarines, New Generation Stealth Frigates, Offshore Patrol Vessels; construction of various types of merchant ships and repairs/ modernization of warships, submarines and merchant ships.
-
Goa Shipyard Ltd (GSL) is one of the leading shipyards, building medium- sized sophisticated vessels for Indian Navy, Indian Coast Guard and others. It commenced functioning with its own Board of Directors since September 29, 1967. Government of India has conferred the status of Mini Ratna, Category-I in March 2007. Goa Shipyard Limited is an ISO- 9001 certified company.
-
Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE) has kept pace withthe expanding maritime interests of India. The Company has been granted the Category-i Mini Ratna status. The main business activity of GRSE is shipbuilding and ship repair for the Indian Navy and Coast Guard.
-
Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) was established in 1970 for manufacture of Guided Missiles. It is one of the few strategic industries in the world that possesses the capability to produce state-of-theart missiles. BDL is engaged in the production of Konkurs-M and Invar (3UBK-20) Anti Guided Missiles in collaboration with Russian developed CMDS (Counter Measures Dispensing System) has been accepted by the Indian Air Force. BDL is working in close association with DRDO for technology absorption/assimilation and extending support by providing missile subsystems integration of missiles for conducting trials of missiles like Akash, Nag, Article K-15 and Agni Variants (Al, A2 and A3). Advanced Light Weight Tropedo (TAL); Heavy Weight Rorpedo (Varunastra) anI Light Weight Mines in Concurrent Engineering mode in association with NSTL, Visakhapatanam
-
Mishra Dhatu Nigam Limited (MIDHANI) was incorporated as a Public Sector Undertaking under the Administrative Control of Department of Defence Production & Supplies, Ministry of Defence in 1973.
Defence Research and Development Organisation
-
DRDO, came into existence in 1958 with the amalgamation of Technical ‘Development Establishment (TDES) of Indian Army and Directorate of Technical Development & Production (DTD&P) with Defence Science Organisation (DSO).
-
DRDO is headed by the Scientific Advisor to Raksha Mantri, who is also the Secretary,
-
Department of Defence R&D and Director General R&D. Dr. DS Kothari, the eminent scientist and educationist was the first to head the organisation. The corporate headquarter of DRDO-is at DRDO Bhawan, an environment friendly building located at Rajaji Marg, New Delhi.
-
“Balasya mulam vi am” i.e. “The source of strength is Science” is the tag line of DRDO. It is Science that drives the nation in war and peace. The Organisation has two tier structure, viz, the Corporate Hqrs at New Delhi; and laboratories establishments, regional centres, field stations, etc. across the length and breadth of the country. DRDO Hqrs, under the Department of Defence Research and Development, is organized into two sets of Directorates i.e. the Corporate Directorates and the Technical Directorates. The laboratories, based on their core-competence, are classified into to nine clusters namely, Aeronautics, Armaments, Combat Vehicles and Engineering, Electronics and Computer Sciences, Materials, Missiles and Strategic Systems, Micro Electronics and Devices, Naval Research and Development, and Life Sciences.
Resettlement of Ex-Servicemen
-
The Department of Ex-servicemen Welfare (ESW) formulates various policies and programmes for the welfare and resettlement of Ex-servicemen (ESM) in the country.
Entrepreneur Schemes
-
The schemes in operation at present are SEMFEX-II and SEMFEX-III comprising ventures in rural areas in agriculture, industry and service sectors. The lending institutions are Nationalised Banks, Cooperative Banks, Regional/Rural Banks etc. Subsidy of 25%-30% is available for these schemes. Application ‘for loan is submitted by ex-servicemen directly to the Bank through concerned Zila Sainik Boards.
-
SEMFEX-II Scheme : The Scheme was started in 1988 with the assistance of National Bank for Agriculture and (NABARD) for funding the entrepreneurship in agriculture, industry and service sectors in rural areas. Subsidy upto 25% of project cost is provided.
-
SE1PEX-III : The scheme was started in 1992 with the assistance of Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) for setting up of textile, village, cottage, tiny and small scale industries in rural areas. Loan up to Rs. 25 lakhs and subsidy upto 30% is provided under the scheme.
© UPSCPORTAL.COM

