(HOT) UPSC Current Affairs 2025 PDF
NEW! The Gist (NOV-2025) | E-BOOKS
The Gist of Press Information Bureau: April 2013
The Gist of Press Information Bureau: April 2013
Content
-
Potential of Livestock and Fisheries Sector
-
Advance Estimates of National Income, 2012-13
-
Private Final Consumption Expenditure
-
Gross Fixed Capital Formation
-
New Bank Licences
-
Gender Budgeting
‘ONE STOP CRISIS CENTRE’ FOR WOMEN:
Ministry of Women and Child Development has formulated a scheme for operationalization of minimum 100 pilot projects of One Stop Crisis Centres (OSCCs), a specialized facility for providing all necessary services for women victims/ survivors of violence, in urban areas having population of more than 5 lakh, identified by the States for implementation during the remaining years of the 12th Plan. These Centres will be attached to the District Hospitals of the State Governments.
An outlay of Rs. 10.00 crores has been kept for the year 2013-14 for implementation of the Scheme.
This was stated by Smt. Krishna Tirath, Minister for Women and Child Development, in a written reply to the Lok Sabha today.
2013-14 Declared the Year for Skill Development of the Youth Parliamentary Consultative Committee Attached to Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports Meets
A meeting of the Consultative Committee chaired by Shri Jitendra Singh, Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Youth Affairs & Sports, was held here today to discuss the National Youth Policy-2012. Addressing the meeting, Shri Jitendra Singh said that this is of extreme relevance as the current year is being observed as the 150th Birth Anniversary of Swami Vivekananda, who is the youth icon of the Country. This will be a befitting tribute by declaring the Youth Policy of the Country. The goal of the Youth Policy is to empower the youth of the Nation by bringing a holistic development, whereby every youth should be able to grow to their potential, fulfill their aspirations and remain healthy and active and participative. As skill development is the thrust of the Nation and following the national objectives, Ministry of Youth Affairs is proposing to declare 2013-14 as the Year for Skill Development of the Youth. The Minister said that Youth are not a homogenous group.
The Youth Policy proposes to follow the age group of the UN and Commonwealth youth age criteria of 16-30 years. The target groups are Student Youth, Urban Youth, Rural Youth, Tribal Youth, Youth at risk, Youth in conflict, Youth out of school, Youth with Social stigma and Youth in Institutional Care. The priority groups are young women, socially and economically disadvantaged Youth and differentlyabled Youth. Shri Jitendra Singh said that the unique feature of the Youth Policy is monitorable indicators under 5 domains. They are Youth Health Index, Youth Education Index, Youth Amenities Index and Youth Participation Index. These constitute the Youth Development Index. The Youth Policy advocates establishment of strong coordination mechanism between the Centre and the States. Youth being a State Subject, there is an urgent need for evolving a youth Policy at the State level in consonance with National Youth Policy. The National Youth Policy will be reviewed after every census.
MAHARATNA STATUS TO BHEL AND GAIL
Government has approved the grant of Maharatna status to Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) and Gas Authority of India Ltd.(GAIL). This decision was communicated on 1st February, 2013. The delegation of powers, exercise of delegated powers, review of their performance and continuation/divestment of Maharatna status of the above listed CPSEs will be governed as per guidelines laid down by the Department of PublicEnterprises(DPE), Government of India which provides that the exercise of delegated Maharatna powers is subject to appointment of requisite number of non-official Directors as per SEBI guidelines. The concerned administrative Ministries of the two CPSEs have been asked to take immediate steps to appoint requisite number of non-official Directors on the Boards of BHEL and GAIL so that the boards could exercise delegatedMaharatna powers.
POTENTIAL OF LIVESTOCK AND FISHERIES SECTOR
Speaking of the importance of this sector, the Minister said, “…with 128 million tonnes of milk production we are the largest producers of milk in the world. With 8.6 million tonnes of fish production, we are the second largest producer of fish in the world. We have world’s largest livestock population accounting for about half the population of buffalos and 1/6th of the goat population.
Last year we achieved a phenomenal growth of over 13% in the meat production. Overall the sector contributes to more than 32% of agricultural GDP and has potential to grow faster in view of growing demand for animal protein from the consumers. The livestock sector acts as insurance in stabilising the farm income in the event of a natural calamity like drought.”
Shri Pawar also gave details about the strategy to be adopted in the XII Plan to increase production of dairy, animal and fisheries products. These would include implementing the National Dairy Plan, with aim to increase the annual milk production to the level of about 180 million tonnes by 2021-22. This will be achieved by increasing milch animal productivity by scientific breeding and nutrition programme supported by effective control of animal diseases. “In order to meet the growing demand for milk, the incremental annual production will now have to rise annually to an average of 6 million tonnes per year over the next 10-12 years, as against an average increase of about 3.5 million tonnes per year over the last 10 years. Of course, in last five years we have been achieving per year increase of 5 to 5.5 million tons per year and thus the target in front of us is definitely achievable,” the Minister said. Introduction of high yielding as well as hardy breeds, expansion of artificial insemination of milch animals, prevention and control of animal diseases, making fodder and feed available in sufficient quantities, and providing credit and fish-seed to fishermen are some of the planks of the strategy mentioned by the Minister.
Special Focus on the North East
Stating that tapping rich potential of North East should be our foremost priority, the Minister said, “It is disheartening to note that with such huge water bodies in this area, the fish are brought there all the way from Andhra Pradesh. The hills of North East can offer excellent climate for the cold water fisheries. We must also concentrate on indigenous varieties of livestock like Yak, Mithun etc available in these areas. Pig rearing is integral part of the household in many of the North East communities. However, these need to be organised in more scientific manner. I would ask the Secretary ADF to have a special session on North Eastern issues in Guwahati or any other suitable location.” The Conference of State Ministers of Animal Husbandry, Dairying and Fisheries was also addressed by Ministers of State, Shri Tariq Anwar and Shri Charan Das Mahant. Shri Tariq Anwar said that fisheries has been recognized as a powerful income and employment generator for economically backward population of the country. Besides, it is a source of cheap and nutritious food. Dr. Charan Das Mahant said that there is a need to develop grazing land as there is a shortage of feed and fodder. This is posing a major challenge in attaining higher growth in the livestock sector. Besides Ministers, those participating in the Conference include secretaries of the three departments of the Agriculture Ministry (Animal Husbandry, Dairying and Fisheries, Agriculture and Cooperation and DG, ICAR), MD, NDDB, State secretaries and experts.
Formation of SPV (TAPI Limited) for the TAPI Pipeline Project and to permit GAIL India Ltd. to join the SPV
The Union Cabinet today gave its approval for formation of the Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) for the Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India(TAPI) Pipeline Project and to permit GAIL India Ltd. to join the SPV. The four countries involved in the TAPI Gas pipeline project, signed an Inter-Governmental Agreement along with a Gas Pipeline Framework Agreement(GPFA). To accelerate the project, parties have formed the Minister Level Steering Committee and Technical Working Group (TWO). Suitable provisions for security & safety of the pipeline have been made in the Inter-Governmental Agreement (IGA) and Gas Pipeline Framework Agreement (GPFA). In the meeting of the 16th Steering Committee held on 23rd September, 2012, all parties reaffirmed their commitment and intention to fast track this important regional co-operation project. As a way forward, Turkmenistan suggested the formation of a SPV by the TAPl members. The SPV would take up the Feasibility Study and Design work of the TAPl pipeline to meet the agreed timelines for the project, as well as search for a consortium lead. Turkmenistan and Pakistan agreed to the formation of TAPl Ltd. considering it to be in consonance with the GPFA.
Afghanistan also agreed to the formation of TAPl Ltd. so long as there was consensus amongst the Parties. TAPl Ltd. is required to have an initial contribution of USD 20 million that is USD 5 million from an identified entity from each of the four participating countries. GAIL, being a Navratna Company, is empowered to make an investment of this level for India. GAIL has agreed to make an investment upto USD 5 million in the proposed SPV that is TAPI Ltd. An active interest in the project by all the partner countries at this stage would sustain the credibility of the project, and generate interest in the international market and could eventually pave the way for selection of an appropriate consortium leader in the future.
Background
Based on an ‘in-principle‘ approval of the Cabinet on 18th May, 2006, India joined the Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan (TAP) Project in April, 2008 and thereafter, the name of the project stood amended to Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India (TAPl) Gas Pipeline Project.
Merger of National Lake Conservation Plan and National Wetlands Conservation Programme into a new scheme. The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs today approved the proposal for the merger of National Lake Conservation Plan (NLCP) and National Wetlands Conservation Programme (NWCP) into a new scheme called the ‘National Plan for Conservation of Aquatic Eco-systems‘ (NPCA). The merged scheme shall be operational during the XII Plan Period at an estimated cost of Rs.900 crore on 70:30 cost sharing between the Central Government and respective State Governments (90:10 for North-East States).
For conservation of lakes and wetlands, the Ministry of Environment and Forests is presently, implementing two separate Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS), namely the NWCP and the NLCP. To avoid overlap, promote better synergies and to ensure conservation and management works, an integrated scheme, NPCA is proposed, with the objective of conserving aquatic ecosystems (lakes and wetlands), through implementation of sustainable conservation plans and governed with application of uniform policy and guidelines.
The principal objectives of the new scheme will be holistic conservation and restoration of lakes and wetlands for achieving desired water quality enhancement, besides improvement in biodiversity and the ecosystem, through an integrated and multidisciplinary approach with a common regulatory framework, The scheme would contribute to reduction of pollution loads and improvement in goods and services provided by these water bodies to stakeholders.
The new scheme will have conservation and management of lakes and wetlands in the country within its scope, to include inventory and information system on lakes and wetlands national level directive on criteria for lakes and wetlands, regulatory framework, capacity building at state government and local body levels, evaluation etc.
Advance Estimates of National Income, 2012-13
The Central Statistics Office (CSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation has released the advance estimates of national income at constant (2004-05) and current prices, for the financial year 2012-13. These advance estimates are based on anticipated level of agricultural and industrial production, analysis of budget estimates of government expenditure and performance of key sectors like, railways, transport other than railways, communication, banking and insurance, available so far. The advance estimates at current prices are derived by estimating the implicit price deflators (IPDs) at sectoral level from the relevant price indices. The salient features of these estimates are detailed below:
I. ADVANCE ESTIMATES OF NATIONAL INCOME, 2012-13
Estimates at Constant (2004-05) Prices Gross Domestic Product
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at factor cost at constant (2004-05) prices in the year 2012-13 is likely to attain a level of Rs.55,03,476 crore, as against the First Revised Estimate of GDP for the year 2011-12 of Rs. 52,43,582 crore, released on 31st January 2013. The growth in GDP during 2012-13 is estimated at 5.0 per cent as compared to the growth rate of 6.2 per cent in 2011-12.
-
The sectors which registered growth rate of over 5 percent are ‘Construction’, ‘trade, hotels, transport and communication`, `financing, insurance, real estate and business services`, and `community, social and personal services`. There may be slow growth in the sectors of ‘agriculture, forestry and fishing’ (1.8%), manufacturing (1.9%) and electricity, gas & water supply (4.9%). The growth in the mining and quarrying sector is estimated to be (0.4%).
Agriculture
The ‘agriculture, forestry and fishing’ sector is likely to show a growth of 1.8 per cent in its GDP during 2012-13, as against the previous year’s growth rate of 3.6 per cent. According to the information furnished by the Department of Agriculture and Cooperation (DAC), which has been used in compiling the estimate of GDP from agriculture in 2012-13, production of foodgrains is expected to decline by 2.8 per cent as compared to growth of 5.2 per cent in the previous agriculture year. The production of cotton and sugarcane is also expected to decline by 4.0 per cent and 6.5 per cent, respectively, in 2012-13. Among the horticultural crops, production of fruits and vegetables is expected to increase by 3.5 per cent during the year 2012-13 as against 5.1 percent in the previous year.
Industry
The manufacturing sector is likely to show a growth of 1.9 per cent in GDP during 2012-13. According to the latest estimates available on the Index of Industrial Production (IIP), the index of manufacturing and electricity registered growth rates of 1.0 per cent and 4.4 per cent, respectively during April-November, 2012-13, as compared to the growth rates of 4.2 per cent and 9.5 per cent in these sectors during April-November, 2011-12. The mining sector is likely to show a growth of 0.4 per cent in 2012-13 as against negative growth of 0.6 per cent during 2011-12. The construction sector is likely to show a growth rate of 5.9 per cent during 2012-13 as against growth of 5.6 per cent in the previous year. The key indicators of construction sector, namely, cement production and steel consumption have registered growth rates of 6.1 per cent and 3.9 per cent, respectively during April-December, 2012-13.
Services
The estimated growth in GDP for the trade, hotels, transport and communication sectors during 2012-13 is placed at 5.2 per cent as against growth of 7.0 percent in the previous year. This is mainly on account of decline of 3.4per cent and 4.8 per cent respectively in passengers and cargo handled in civil aviation and decline of 3.1 per cent in cargo handled at major sea ports during April-November, 2012-13. There has been an increase of 4.3 per cent in stock of telephone connections as on November 2012. The sales of commercial vehicles witnessed an increase of 0.74 per cent per cent in April-December 2012. The sector, `financing, insurance, real estate and business services`, is expected to show a growth rate of 8.6 per cent during 2012-13, on account of 11.1 per cent growth in aggregate deposits and 15.2 per cent growth in bank credit as on December 2012 (against the respective growth rates of 17.2 per cent and 16.0 per cent in the corresponding period of previous year). The growth rate of `community, social and personal services` during 2012-13 is estimated to be 6.8 per cent.
National Income
The net national income (NNI) at factor cost, also known as national income, at 2004-05 prices is likely to be Rs.47,64,819 crore during 2012-13, as against the previous year`s First Revised Estimate of Rs. 45,72,075 crore. In terms of growth rates, the national income registered a growth rate of 4.2 per cent in 2012-13 as against the previous year’s growth rate of 6.1 per cent.
Per Capita Income
The per capita income in real terms (at 2004-05 prices) during 2012-13 is likely to attain a level of Rs.39,143 as compared to the First Revised Estimate for the year 2011-12 of Rs. 38,037. The growth rate in per capita income is estimated at 2.9 per cent during 2012-13, as against the previous year`s estimate of 4.7 per cent.
Estimates at Current Prices Gross Domestic Product
GDP at factor cost at current prices in the year 2012-13 is likely to attain a level of Rs. 94,61,979 crore, showing a growth rate of 13.3 per cent over the First Revised Estimate of GDP for the year 2011-12 of Rs. 83,53,495 crore.
National Income
The NNI at factor cost at current prices is anticipated to be Rs. 83,68,571 crore during 2012-13, as compared to Rs. 73,99,934 crore during 2011-12, showing a rise of 13.1 per cent.
Per Capita Income
The per capita income at current prices during 2012-13 is estimated to be Rs. 68,747 as compared to Rs. 61,564 during 2011-12, showing a rise of 11.7 per cent.
II. ESTIMATES OF EXPENDITURES ON GDP, 2012-1313
Alongwith the Advance Estimates of GDP by economic activity, the CSO is also releasing the Advance Estimates of expenditures of the GDP at current and constant (2004-05) prices. These estimates have been compiled using the data on indicators available from the same sources as those used for compiling GDP estimates by economic activity, detailed data available on merchandise trade in respect of imports and exports, balance of payments, and monthly accounts of central government. As various components of expenditure on gross domestic product, namely, consumption expenditure and capital formation, are normally measured at market prices, the discussion in the following paragraphs is in terms of market prices only.
Private Final Consumption Expenditure
Private Final Consumption Expenditure (PFCE) at current prices is estimated at Rs. 57,05,857 crore in 2012-13 as against Rs. 50,56,219 crore in 2011-12. At constant (2004-05) prices, the PFCE is estimated at Rs. 34, 72,980 crore in 2012-13 as against Rs. 33,34,900 crore in 2011-12. In terms of GDP at market prices, the rates of PFCE at current and constant (2004-05) prices during 2012-13 are estimated at 56.9 per cent and 59.7 per cent, respectively, as against the corresponding rates of 56.3 per cent and 59.2 per cent, respectively in 2011-12.
Government Final Consumption Expenditure
Government Final Consumption Expenditure (GFCE) at current prices is estimated at Rs. 11,86,726 crore in 2012-13 as against Rs 10,42,677 crore in 2011-12. At constant (2004-05) prices, the GFCE is estimated at Rs. 6,60,630 crore in 2012-13 as against Rs. 6,34,559 crore in 2011-12. In terms of GDP at market prices, the rates of GFCE at current and constant (2004-05) prices during 2012-13 are estimated at 11.8 per cent and 11.4 per cent, respectively, as against the corresponding rates of 11.6 per cent and 11.3 per cent, respectively in 2011-12.
Gross Fixed Capital Formation
Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) at current prices is estimated at Rs. 29,93,873 crore in 2012-13 as against Rs. 27,49,072 crore in 2011-12. At constant (2004-05) prices, the GFCF is estimated at Rs. 19,44,279 crore in 2012-13 as against Rs.18,97,309 crore in 2011-12. In terms of GDP at market prices, the rates of GFCF at current and constant (2004-05) prices during 2012-13 are estimated at 29.9 per cent and 33.4 per cent, respectively, as against the corresponding rates of 30.6 per cent and 33.7 per cent, respectively in 2011-12. The rates of Change in Stocks and Valuables at current prices during 2012-13 are estimated at 3.0 per cent and 2.4 per cent, respectively.Estimates of gross/net national product, gross/net domestic product and per capita income, alongwith GDP at factor cost by kind of economic activity and the Expenditures on GDP for the years 2010-11 and 2011-12 and 2012-13, at constant (2004-05) and current prices are given in Statements 1 to 6.
Merger of National Lake Conservation Plan and National Wetlands Conservation Programme into a New scheme
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs today approved the proposal for the merger of National Lake Conservation Plan (NLCP) and National Wetlands Conservation Programme (NWCP) into a new scheme called the National Plan for Conservation of Aquatic Eco-systems (NPCA). The merged scheme shall be operational during the XII Plan Period at an estimated cost of Rs.900 crore on 70:30 cost sharing between the Central Government and respective State Governments (90:10 for North-East States).
For conservation of lakes and wetlands, the Ministry of Environment and Forests is presently, implementing two separate Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS), namely the NWCP and the NLCP. To avoid overlap, promote better synergies and to ensure conservation and management works, an integrated scheme, NPCA is proposed, with the objective of conserving aquatic ecosystems (lakes and wetlands), through implementation of sustainable conservation plans and governed with application of uniform policy and guidelines. The principal objectives of the new scheme will be holistic conservation and restoration of lakes and wetlands for achieving desired water quality enhancement, besides improvement in biodiversity and the ecosystem, through an integrated and multidisciplinary approach with a common regulatory framework, The scheme would contribute to reduction of pollution loads and improvement in goods and services provided by these water bodies to stakeholders.The new scheme will have conservation and management of lakes and wetlands in the country within its scope, to include inventory and information system on lakes and wetlands national level directive on criteria for lakes and wetlands, regulatory framework, capacity building at state government and local body levels, evaluation etc.
Currency Note Press, Nashik has Highest Ever Monthly Production of 451.5 Million Pieces (MPCS) of Banknotes during January, 2013 Currency Note Press (CNP), Nashik (a unit of SPMCIL) which is engaged in production of Bank Notes using state of the art technology, has produced 451.5 million pieces (mpcs) of Banknotes during January, 2013.This is the highest ever monthly production in the history of CNP. The previous highest was 442.65 mpcs in August 2012. It is more than double the average monthly production achieved (217.1 mpcs) during 2006-07, the first year after corporatization. The Productivity per Employee per Annum of CNP, Nashik has substantially increased to above 2.4 times before corporatisation. In the current year, the production target for CNP is 4,800 mpcs which is 85% more than that of 2006- 07.
Currency Note Press, Nashik (a unit of SPMCIL) is equipped with designing, engraving, complete Pre-printing and Offset Printing facilities, Intaglio Printing machines, Numbering & Finishing machines etc. It is ISO 9001:2000 & ISO 14001:2004 certified unit, having fool-proof accounting of security items, stringent security systems. It has history of export of manufacturing and supply of Bank Notes of many countries in the past. After corporatisation, Currency Note Press, Nashik (CNP) has significantly improved its production with the existing machinery even after reduction of about 27% of manpower. During 2006-07 with 3510 nos. of employees, CNP, Nashik had produced 2605 million pieces of banknotes. In 2011-12 CNP, Nashik has produced 4428 million pieces of Banknotes with 2682 nos. of employees. The above achievement has been the result of all round improvements including process re-engineering, redeployment of manpower, motivation of the employees and better Industrial relation.
New Bank Licences
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is in the process of finalizing the guidelines for licencing of new banks. The Government has not received any such suggestion from the International Monetary Fund (IMF). However, in its report on “India: Financial System Stability Assessment Update” of January, 2013 IMF has, in the context of the current bank licensing policy of RBI, indicated that the international experience supported the prudent policy position of disallowing industrial houses from promoting and owning banks. The policy of RBI aims to address the concerns of “under the radar” risk transfer, concentration risk, across the group contagion risk, etc.; through appropriate prudential means.
The IMF Report lists out such prudential measures as setting-up of a non-operative financial holding company (NOFHC) to hold all the financial sector entities in the group and to be supervised by RBI as a Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC); requirement of 50 percent of directors (increased to a majority in some cases) to be independent of the promoter; and the bank, group entities, non-operative holding company, and the promoter being subject to RBI’s consolidated supervision, etc. This was stated by the Minister of State for Finance, Shri Namo Narian Meena in a written reply to a question in the Lok Sabha today.
High Level Committee on Status of Women
The Government has set up a High Level Committee (HLC) on the status of women to undertake comprehensive study to understand the status of women since 1989 as well as to evolve appropriate policy interventions based on a contemporary assessment of women’s needs.
The composition of the Committee is as under:-
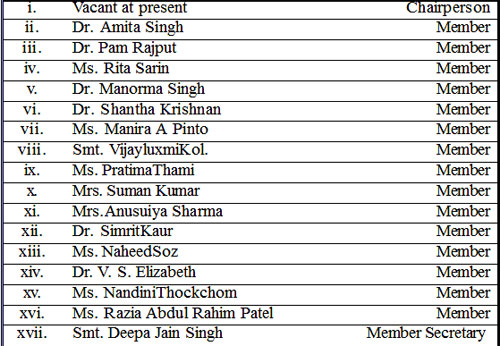
The Terms of Reference of the above High Level Committee (HLC) includes, among others, the following:
I. The HLC will conduct an intensive literature survey to take stock of published data, reports, articles and research from about 1989 onwards, on the status of women in India.
II. The HLC will prepare a Report on the current socio-economic, political and legal status of women in India. The Report will also bring out the interconnectedness of these aspects in terms of their impact on women and recommend measures for holistic empowerment of women.
III. The HLC will examine the overall status of women including, inter-alia, the socio-economic, health and nutritional, legal and political status, disaggregated by rural/urban, economic and social position (e.g. APL/BPL, SC/ST, single women, disabled women, migrant women) and wherever possible by minority status (e.g. Muslims/others). The analysis would take account of cross-regional differences and focus on inequalities both within and outside the household. It would also assess the impact made by existing policies and legislative changes on equality, security and holistic empowerment of women, and will identify inequalities in policy and legislation as well as gaps in implementation.
The High Level Committee has invited suggestions from NGOs/social activists and individual experts working in the field of welfare of women. The High Level Committee was constituted vide Resolution dated the 27th February, 2012 and it is required to present its report within 2 years from the date of its first meeting, which was held on 24th July, 2012. This was stated by Smt. Krishna Tirath, Minister for Women and Child Development, in a written reply to the Lok Sabhatoday.
Gender Budgeting
The Government has adopted Gender Budgeting based on the recommendations of the Expert Group on classification system of Government transactions constituted by the Ministry of Finance under the Chairmanship of the Chief Economic Advisor to Government of India. An Inter-Departmental Committee was constituted in November 2004 under the chairmanship of Secretary, Expenditure, Ministry of Finance. Following which, instructions were issued by the Ministry of Finance, to all Ministries/ Departments in December, 2004 to establish a ‘Gender Budgeting Cell (GBC)’. The GBCs have been formed with the objective of influencing and effecting a change in the Ministry’s policies, programmes in a way that could tackle gender imbalances, promote gender equality and development. On 8th March 2007, the Ministry of Finance also issued a Charter for Gender Budget Cells (GBCs) outlining the composition of GBCs and their functions. The following steps are being taken by the Government in the sphere of Gender Budgeting:
i. Since 2005, the Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD)
along with the Ministry of Finance has been pursuing with various Ministries/
Departments for setting up of GBC As per information available, so far 56
Central Ministries/Departments set up GBCs.
ii. As part of the Union Budget, every year, since 2005-06, a Gender Budget
Statement 20 is prepared by the Ministry of Finance, which reflects 30% and
above allocations made for women by different Ministries / Departments. In
2012-13, an allocation of Rs. 88,142.80 crores in relation to 29 Ministries/
Departments was reported in the GB Statement.
iii. Further in order to strengthen the process of gender budgeting, the
Ministry of Women and Child Development has been undertaking various capacity
building measures for officials of Central, State Governments and various
stakeholders. A Gender Budgeting Plan Scheme was launched during 2007-08 to this
effect. The Ministry has also developed a Gender Budgeting Handbook for
Government of India Ministries & Departments and a Gender Budgeting Manual for
Trainers. The Ministry has also undertaken one-to-one sessions with several
departments to promote Gender Budgeting.
This was stated by Smt. Krishna Tirath, Minister for Women and Child Development, in a written reply to the Lok Sabha today.

