The Gist of Press Information Bureau: July 2013
The Gist of Press Information Bureau: July 2013
Content
- Steps Taken for Protection of Endangered Species
- Environmental Taxes
- Amendment in Money Laundering Act
- E-Biz Portal to Ease G2B Services
- Success in the Skies!
First Ever Hackathon by the Planning Commission on the 12th Plan
The Planning Commission and the National Innovation Council are organising the first ever Hackathon on the 12th Five Year Plan (2012-17) on 6th – 7th April 2013. The Hackathon is being organised simultaneously in 11 locations across India and participants can also join virtually.
The event is taking place at University of Jammu, IIT Delhi,
Delhi University, Aligarh Muslim University, IIT Kanpur, IIT Kharagpur, TISS
Mumbai, IIIT Hyderabad, IISc Bangalore, IIT Madras and IIM Shillong.
Thousands of young creative designers, coders, film-makers along with policy and
development enthusiasts will visualise and narrate the 12th Plan through
infographics, short films, and support the initiatives proposed in the Plan by
developing software applications.
The Hackathon will last for thirty two hours during which participants will gather in teams across India to compete for interesting prizes in three categories - mobile/web applications, infographics and short films. More details about the hackathon are available on www.data.gov.in/hackathon.
The 12th Plan is the product of unprecedented participation from Indian citizens and civil society to set out a vision for India‘s progress over the next five years. The Planning Commission and the National Innovation Council now invite similar participation to visualise and articulate its rich and insightful content to India.
UNWTO Conference on Sustainable Tourism Development to be Held at Hyderabad from 12th to 14th April
United Nations World Tourism Organisation ( UNWTO) Commission’s Conference on Sustainable Tourism Development and 25th Joint Meeting of the UNWTO Commission for East Asia, Pacific and South Asia will be held at Hyderabad from 12th to 14th of this month. Announcing this in New Delhi today Union Tourism Minister Shri K. Chiranjeevi said the need of the hour is not the tourism growth alone but development of tourism in sustainable manner. He said in this meeting, International experts; delegates from the member countries of the UNWTO Commissions for South Asia and East Asia and Pacific, UNWTO, various state governments of India and tourism industry will participate. During the conference exchange of ideas will take place on the way forward to develop tourism in a sustainable manner. The Minister said “India has been working with UNWTO closely for the cause of developing nations. Our initiative at the international level to host the two events, no doubt, will go a long way in highlighting India’s role in promoting global and regional tourism in sustainable manner for the economic growth, employment generation and social integration”. The Tourism Minister said South Asian region has rich and varied tourism products to attract visitors from the world over – with heritage and culture dating back to thousands of years, architectural and natural marvels, an unmatched bio-diversity and home to almost all the world religions. He said “In spite of rich heritage, the market share of South Asia in World Tourist Arrivals is only 1.3% - which is a cause of concern. On a positive note the average annual growth in international tourist arrivals to the region during the period 2005 to 2011 has been 7.2% as compared to the world annual average growth of 3.5% during the same period”. Shri Chiranjeevi said the 25th meeting of the UNWTO Joint Commission will bring together tourism authorities from 27 member countries and two associate members and give them an opportunity to review the tourism performance of the two regions and deliberate upon measures and policies to be adopted for future. In this meeting, the best practices and policies adopted world over will also be shared. India is currently the chairperson of the UNWTO Regional Commission for South Asia and considering the fact that the 25th Joint Meeting is being held in India, we would be chairing this meeting with Malaysia as co-chair, the Minister added.
The Union Tourism Minister informed that till date 21 countries namely Bangladesh, Bhutan, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Fiji, Indonesia, Iran, Japan, LAO PDR, Macau, Malaysia, Maldives, Myanmar, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Timor Leste and Vietnam have confirmed their participation. He said the UNWTO will be represented by Mr. Taleb Rifai, Secetary General and his team. This meeting will also be attended by the Chief Executive Officer of the Pacific Asia Travel Association (PATA). The tourism Minister said that for the first time Ministry of Tourism will be sending an electronic invitation and itinerary in form of a short film to all delegates and invitees welcoming them to the city of Hyderabad. This film shows them in advance the venues of the meetings, dinners and tours. The film is being uploaded on the promotional website of the Ministry www.incredibleindia.org The Ministry of Tourism, Government of India, in collaboration with the Government of Andhra Pradesh is hosting the joint meeting and the conference.
The UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism. As the leading international organisation in the field of tourism, UNWTO promotes tourism as a driver of socio-economic growth and development and advocates its inclusion as a priority in national and international policies. India is currently the chairperson of the UNWTO Regional Commission for South Asia.
The UNWTO Joint Commission Meeting will bring together delegates from member countries and give them an opportunity to review the tourism performance of the region and deliberate on measures for further development. India accords great importance to the issue of Sustainable Tourism. As a commitment to Safe and Sustainable Tourism Development, India has developed a code for “Safe & Honorable Tourism” and Sustainable Tourism Criteria for the Accommodation and Tour Operators sectors. The UNWTO Conference on Sustainable Tourism Development will include a global review on sustainable tourism development and sustainable practices as well an industry and media perspective on sustainable criteria for tourism. Over 250 delegates are expected to participate in the Sustainable Tourism Conference.
National Regulatory Authority of India Meets International Standards for Vaccine Regulations: WHO
The National Regulatory Authority of India (NRA) and affiliated institutions meet WHO published indicators for a functional vaccine regulatory system. AWHO-led team of international experts from eight countries came to this conclusion at the end of a comprehensive review from 10-14 December 2012. ”The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization in collaboration with WHO, has made exemplary efforts towards this achievement. The Government of India has decided to further strengthen the Central as well as the State Drugs Regulatory Systems during the 12th Five Year Plan (2012-17) and looks forward to strengthening our collaboration with WHO towards this end,” said ShriGhulamNabi Azad, Union Minister for Health & Family Welfare, Government of India. ”We welcome this positive development. It reaffirms faith in India’s regulatory system and also reiterate country’s strength for pharmaceutical sector. The effective regulatory oversight of vaccines is especially crucial for India which is a major vaccine producer and also supplier across the globe,” said Mr KeshavDesiraju, Secretary, Health& Family Welfare, Government of India. India is a major vaccine producer that has 12 major vaccine manufacturing facilities.
These vaccines are used for the national and international market (150 countries), which makes India a major vaccine supplier across the globe. In 2012, India had seven vaccine manufacturers producing 67 prequalified vaccines (dosage forms). Currently 16 vaccines are prequalified by WHO and exported through United Nations agencies. More than 70% of all measles vaccines used globally are produced in India. “This is indeed a great achievement and we would like to congratulate the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare and its affiliated institutions- Central Drugs Standards Control Organization (CDSCO), Central Drugs Laboratory, Kasauli, Immunization Division of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, and other relevant institutions, engaged in the regulation, control and testing of vaccines,” said Dr Lahouari Belgharbi, WHO Team Leader for the NRA Assessment, Quality, Safety and Standards Team, Department of Immunization, Vaccines and Biologicals of the World Health Organization. ”WHO had scaled up its technical support to the Indian NRA over the past several months in the context of this assessment.
The recent success is a culmination of intensive effort by CDSCO, in collaboration with WHO, to implement a roadmap to strengthen capacity for regulation of vaccines. WHO will continue to support development of the NRA through technical advice, training and capacity building. We welcome this positive outcome. It shall go a long way in reaffirming the joint mutual strategic priority under the WHO’s new Country Cooperation Strategy with India (2012-17), of supporting an improved role of India in global health, including strengthening the pharmaceutical sector and drug regulatory capacity,” said Dr Nata Menabde, WHO Representative to India. ”India is one of the largest manufacturers and exporters of vaccines world-wide, reinstating our thrust on maintaining highest quality and efficacy of the products that are manufactured within our country. I am happy that we have been able to strengthen and enhance the current regulatory system as per the spirit of the Mission of CDSCO and the requirements of the World Health Organization to ensure safety and efficacy of the products that are manufactured and exported from India,” said Dr G.N Singh, Drugs Controller General (India). One of the requirements to become eligible and to retain the prequalification status is to have a National Regulatory Authority (NRA) assessed as functional against the WHO published NRA indicators. The regulatory functions of the Indian NRA (Central Drugs Standards Control Organization) and its affiliated institutions were assessed for compliance against the revised WHO NRA indicators endorsed by the international consultation of experts in 2011. In addition to the general framework for the system, the following regulatory functions were evaluated: marketing authorization and licensing; post-marketing surveillance, including for adverse events following immunization; lot release by the national regulatory authority; laboratory access; regulatory inspections of manufacturing sites and distribution channels; and authorization and monitoring of clinical trials.
With a regulatory system for vaccines assessed as functional by WHO, vaccine manufacturers in India continue to remain eligible to apply for prequalification of specific products. WHO prequalification, which is a guarantee that a specific vaccine meets international standards of quality, safety and efficacy, is a prerequisite for manufacturers to supply to countries through United Nations procuring agencies. ”The Government of India has undertaken committed efforts to ensure that the regulatory oversight of the NRA for vaccines continues to meet international standards,” said Dr David Wood, Coordinator of the Quality, Safety and Standards Team of the Department of Immunization, Vaccines and Biologicals of the World Health Organization. As for all NRA assessments, sustainability of the gains made in regulatory capacity is critical. For this purpose, the team which has just completed the assessment in India has drawn up a detailed Institutional Development Plan. The plan will outline additional activities to be undertaken to further strengthen regulatory capacity in India for the period 2013-2015.
Steps Taken for Protection of Endangered Species
The Government has taken several steps for protection of endangered species of wild animals in the country, which are as following:-
i. Legal protection has been provided to wild animals against hunting and
commercial exploitation under the provisions of the Wild Life (Protection) Act,
1972.
ii. The Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 has been amended and made more
stringent. Thepunishment for offences under the Act have been enhanced. The Act
also provides for forfeiture of any equipment, vehicle or weapon that is used
for committing wildlife offence(s).
iii. Protected Areas, viz., National Parks, Sanctuaries, Conservation Reserves
and Community Reserves covering important wildlife habitats have been created
all over the country under the provisions of the Wild Life (Protection) Act,
1972 to conserve wild animals and their habitats.
iv. Financial and technical assistance is provided to the State/ Union
Territory Governments under the Centrally Sponsored Schemes of ‘Integrated
Development of Wildlife Habitats`, ‘Project Tiger’ and ‘Project Elephant’ for
providing better protection to wildlife, and improvement of its habitat.
v. The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has been empowered under the Wild
Life (Protection) Act, 1972 to apprehend and prosecute wildlife offenders.
vi. The State/Union Territory Governments have been requested to strengthen the
field formations and intensify patrolling in and around the Protected Areas.
vii. The Wildlife Crime Control Bureau has been set up to strengthen the
enforcement of law for control of poaching and illegal trade in wildlife and its
products.
viii. Strict vigil is maintained by the officials of State Departments of
Forests and Wildlife.
The periodic assessments carried out in respect of prioritized species, rhinoceros and lion, have indicated improvement in their population status.
The Ministry of Environment & Forests also provides financial assistance to State Governments for undertaking “Recovery Programmes for saving critically endangered species” as a component of the Centrally Sponsored Scheme of ‘Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats’. Budget is not allocated separately for this component. At present, sixteen species have been prioritized for taking up such recovery programmes which include Snow Leopard, Bustards (including Floricans), River Dolphin, Hangul, Nilgiri Tahr, Marine Turtles, Dugongs and coral reefs, Edible-nest Swiftlets, Asian Wild Buffalo, Nicobar Megapode, Manipur Brow-antlered deer, Vultures, Malabar civet, the great one-horned rhinoceros, Asiatic Lion, Swamp deer and Jerdon’s Courser.
Under the component “Recovery Programmes for Saving Critically Endangered Species” of the Centrally Sponsored Scheme “Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats” (CSS-IDWH) financial assistance has been provided for eight critically endangered species including Snow Leopard, Hangul, Dugongs, Edible-nest Swiftlets, Asian Wild Buffalo, Manipur Brow-antlered deer, Vultures and Asiatic Lion as per the proposals received from various State/Union Territory Governments. The details of financial assistance released to the State/Union Territory Governments for undertaking Recovery Programmes for saving critically endangered species under the Centrally Sponsored Scheme “Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats” during the last three years are as follows:
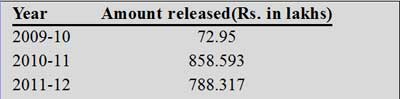
The National Policy for Children, 2012
The Union Cabinet today gave its approval to the National Policy for Children, 2012. The Policy reaffirms the government‘s commitment to the realisation of the rights of all children in the country. It recognizes every person below the age of eighteen years as a child and that childhood is an integral part of life with a value of its own, and a long term, sustainable, multi-sectoral, integrated and inclusive approach is necessary for the harmonious development and protection of children. The policy lays down the guiding principles that must be respected by national, state and local governments in their actions and initiatives affecting children. Some of the key guiding principles are: the right of every child to life, survival, development, education, protection and participation; equal rights for all children without discrimination; the best interest of the child as a primary concern in all actions and decisions affecting children; and family environment as the most conducive for all-round development of children.
The policy has identified survival, health, nutrition, education, development, protection and participation as the undeniable rights of every child, and has also declared these as key priority areas. As children‘s needs are multi-sectoral, interconnected and require collective action, the policy aims at purposeful convergence and strong coordination across different sectors and levels of governance; active engagement and partnerships with all stakeholders; setting up of a comprehensive and reliable knowledge base; provision of adequate resources; and sensitization and capacity development of all those who work for and with children. A National Plan of Action will be developed to give effect to the policy and a National Coordination and Action Group (NCAG) will be constituted to monitor the progress of implementation. Similar plans and coordination and action groups will be constituted at the state and district levels.
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights and State Commissions for Protection of Child Rights are to ensure that the principles of the policy are respected in all sectors at all levels. There is a provision for review of the policy every five years. The Ministry of Women and Child Development will be the nodal ministry for overseeing and coordinating the implementation of the policy and will lead the review process.
Environmental Taxes
There is no proposal to levy environmental taxes to discourage pollution and boost green technology. However the Government levy cess under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Cess Act, 1977 on the consumption of water by persons carrying on certain industries and by local authorities, with a view to augment the resources of the Central Pollution Control Board and the State Pollution Control Boards for prevention and control of water pollution. The Government allow 25% rebate to the industries on the amount of cess payable by them provided the industries consume water within the prescribed limits and comply with the provisions of section 25 of the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974 and also the environmental norms notified under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 by installing appropriate pollution treatment technologies. The countries such as USA, UK, Germany and Japan have adopted the system of taxation to control emission of hazardous gasses and also introduced upper limits for disposal of such gaseous emissions. This was stated by Shrimati Jayanthi Natarajan Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Environment and Forests, in a written reply to a question in the Lok Sabha today.
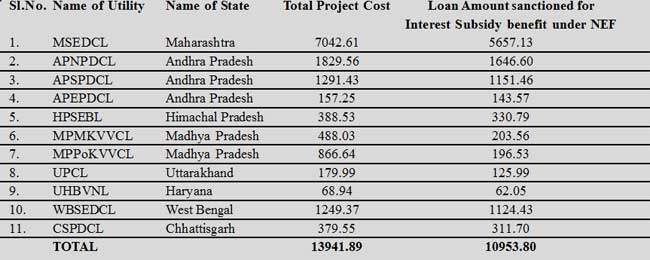
National Electricity Fund
Government of India launched the National Electricity Fund (Interest Subsidy Scheme) in July 2012 to provide interest subsidy on loans raised by both public and private Distribution Companies (DISCOMS), for capital works sanctioned by financial institutions to improve the infrastructure in distribution sector during the financial year 2012-13 and 2013-14.Projects worth Rs. 10,953.80 Crores have been sanctioned by the Union Government to various Utilities/States for consideration of Interest subsidy benefit under National Electricity Fund.Government of India has approved setting up of National Electricity Fund (Interest Subsidy Scheme) to provide interest subsidy on loans disbursed to the State Power Utilities, Distribution Companies (DISCOMS) – both in public and private sector for the loans taken from Private & Public Financial Institutions, to improve the infrastructure in distribution sector.Rural Electrification Corporation (REC), would be the Nodal Agency to operationalise the scheme.Under NEF scheme, interest subsidy would be provided on loans taken by private and public power utilities in distribution sector for non Rajiv Gandhi Grameen Vidyutikaran Yojana (RGGVY) and non Restructured Accelerated Power Development and Reforms Programme (R-APDRP) projects. The preconditions for eligibility are linked to reform measures taken by the States and the amount of interest subsidy is linked to the progress achieved in reforms linked parameters. The preconditions of eligibility areoperationalisation of State Electricity Regulatory Commission (SERC), formulation of business plan for turn around of utilities, re-organization of State Electricity Boards (SEB), release of subsidy by State Government to DISCOMs, submission of audited annual accounts and timely filing of tariff petition.There will be two categories of States for working out the interest subsidy– Special category and focused states, and States other than special category and focused states. Each power utility eligible for subsidy on interest would be assigned marks based on reforms measures i.e. reduction in AT&C losses; reduction in revenue gap (Average Cost of Supply (ACS) - Average Revenue Realized on subsidy received basis); return on equity and multi year tariff (MYT).
Based on the consolidated score achieved on these parameters, the utilities would be categorized and will be eligible for subsidy in interest rates from 3% to 5% in States other than Special category and focused states and 5% to 7% in Special Category and focused states.National Electricity Fund would provide interest subsidy aggregating Rs. 8466 crore spread over 14 years for loan disbursement amounting to Rs. 25,000 crore for distribution schemes sanctioned during the 2 years viz., 2012-13 and 2013-14.
Amendment in Money Laundering Act
The Government has recently amended the Money Laundering Act. The objectives of recent amendment in Prevention of Money-laundering Act, 2002 is to strengthen the legislative and administrative framework of the country to prevent money laundering and countering financing of terrorism and capabling to handle the new evolving threats. Bullion traders have expressed that Germs and jewellery sector be kept out of the purview of Prevention of Money-laundering Act. The Act imposes reporting obligations on “person carrying on designated business and profession”, which would include “dealer” in precious metals, precious stones and other high value goods as and when notified by the Central Government. At present they have not been notified. This was stated by Minister of State for Finance, Shri Namo Narain Meena, in written reply to a question in the Lok Sabha today.
Nirbhaya Fund
The Finance Minister in his budget speech, 2013-14 has announced setting up of a Nirbhaya Fund with Government contribution of Rs. 1000 Crores for empowerment, safety and security of women and girl children. Government’s efforts at empowerment and safety of women have been a continuous process. Ministry of Women and Child Development provides financial assistance for empowerment and safety of women through a number of schemes like Working Women’s Hostels, Shelter Home schemes of Swadhar and Short Stay Homes, Ujjawala, micro-credit facilities through RashtriaMahilaKosh, National Mission for Empowerment of Women etc. Utilization of Nirbhaya Fund would be preceded by formulation of viable schemes and necessary approvals from the competent authority. This was stated by Smt. Krishna Tirath, Minister for Women and Child Development, in a written reply to the Lok Sabha today.
E-Biz Portal to Ease G2B Services
As part of the Government‘s initiative to improve the business environment and the ease of doing business in the country, the Department of Industrial Policy & Promotion, Ministry of Commerce & Industry launched the eBiz portal on 28.01.2013 comprising the License and Permits Services component that will allow business users to obtain a customized list of licenses, permits, and regulations that they require or need to comply with across all levels of government. eBiz will serve as a 24X7 online single-window system for providing efficient and convenient Government to business (G2B) services to business community, by reducing the complexity in obtaining information and services related to starting businesses in India, and dealing with licenses and permits across the business life-cycle. It will function as one-stop-shop for obtaining information and forms; submission of forms/applications; online payment and routing of fees; and routing of forms/applications and fees to various departments for licenses, permits, registrations, approvals, clearances, permissions, periodic filings and compliances throughout the life-cycle of business entity. During the pilot phase, 29 services of year -1 and 21 services of year 2&3 i.e. total 50 services are envisaged to be integrated with the eBiz portal which include 26 services of Central Government departments and 24 services in each of the 5 pilot states i.e. Andhra Pradesh, Delhi, Haryana, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
E-Biz Portal to Ease G2B Services
As part of the Government‘s initiative to improve the business environment and the ease of doing business in the country, the Department of Industrial Policy & Promotion, Ministry of Commerce & Industry launched the eBiz portal on 28.01.2013 comprising the License and Permits Services component that will allow business users to obtain a customized list of licenses, permits, and regulations that they require or need to comply with across all levels of government. eBiz will serve as a 24X7 online single-window system for providing efficient and convenient Government to business (G2B) services to business community, by reducing the complexity in obtaining information and services related to starting businesses in India, and dealing with licenses and permits across the business life-cycle.

