Gist of Union Budget 2014

Gist of Union Budget 2014
Table of Content:
-
Budget 2014-15
-
Direct tax in Budget 2014
-
Indirect Tax
-
Non-Tax Revenue
-
Revenue Expenditure
-
Subsidy
-
Capital Account
The Union Budget of India, referred to as the Annual Financial Statement in Article 112 of the Constitution of India presented every year on the last working day of February by the Finance Minister of India in the Parliament. Budget has to be passed by the parliament before it can come into effect. This year because of general elections interim budget was presented by previous government. Interim budget is presented in the election year, which is budget from 1st of april till new government forms. Interim budget was presented by Ex- Finance minister P. Chidambaram on 28th of feb 2014 and full budget for 2014–2015 was presented by Arun Jaitley on 10th July 2014.
All the money for union budget goes in three accounts Consolidated fund of India(Article 266), Public account of India(Article 266) and contingency fund of India(Article 267). Consolidated fund of India(CFI) has all the revenue collected, loans raised and interset or principle received. Government needs parliamentary approval to take money out of CFI. Public accounts are those for whom government act as a banker. It contains National investment fund, prarambhik shiksha kosh, PF account, postal deposit, small saving scheme etc., government does not need a parliamentry approval in order to spend money from it. Contingency fund is for unforeseen circumstaces and it is under president of India maintained by finance seceratry. This also does not need parliamentry approval. In India government can not spend without the approval of the parliament so government puts an appropriation bill under the Article 266 of the constitution.
Article 112 of the constitution says budget has to be presented in Revenue and the other form. So government presents budget in two forms Revenue and Capital. Both of them then further subdivided into receipt and expenditure. Revenue receipt is divided in tax and nontax part. And tax part of revenue receipt is further subdivided into direct and indirect taxes. Direct tax are those in which identity of the taxpayer can be established, they are income tax, coorporate tax, wealth tax and securities transaction tax.
Budget 2014-15
Direct tax in Budget 2014
In this budget Income tax slab for 10% bracket is 2.5 to 5 lakh range, similarly 20% bracket is 5 to 10 lakh range and for 30 % range is more than 10 lakhs. Coorporate tax is around 34 percent, Minimum alternatetax around 21% and wealth tax over 30 lakhs is 1%.
Provisions to increase savings:-
Savings in India has came down heavily from around 36% in 2007 to around 30% this year. This budget has taken steps to increase the savings.
- Non taxable investment under 80c limit has been increased to 1.5 lakhs from 1 lakh.
- Pension, Insurance and home loan interest has been increased.
Boosting industries and investment:-
- 10 year tax holiday for power generation companies.
- Uniform TDS on foreign bonds issued by Indian companies.
- Allowed domestic companies to obtain advance ruling with regard to their direct and indirect tax liabilities.
This is the first budget prepared by newly elected government. Expectations of various sections of the society are high on the government. India has seen below 5 percent growth for last two years along with hugh inflation so growth was high on agenda for government.
Indirect Tax
Four indirect taxes which are collected in India are; Custom Duty, Excise Duty, Service tax, CST(Given entirely to States). India has custom act and excise act but no service act, it is only a chapter in finance act. Service tax is not applicable in J&K and also for srvice provider with less than 10 lakh income.
Changes in Indirect Taxes:-
- Reduction in custom duty for Raw materials used in Spandex Yarn, Fatty acids, Crude glycerin, Dolomite, Battery waste and Battery scrap, Ethane, propane, etthylene, methyle alcohal etc.
- Custom on CRT, LCD and LED panels(<19") and Custom duty on Solar cell raw material has been reduced to Zero.
- Wind mill- steel rings has been reduced to 5% and for all variety of coal has been made same as 2.5% custom and 2% CVD.
- Clean energy cess has been increased on coal, peat, lignite.
- 24/7 clearance facility on selected airports and seaports.
- Indian Customs single Window project for traders.
- Excise duty has been increased on smart cards, carbonated softdrinks and Tobacco products(Gutka 70%, Cigar(<65mm) 72%).
- Service tax is 12% and educational cess is 3%, which makes effective service tax to be 12.36%.
- 17 negative list category for service tax including Government services, basic post office, RBI services, Renting home for residence, Vocational loans, Educational services etc.
- Ads on online site, Radio-taxis, Human drug testing, Ac contract carriages etc has been included in the service tax list.
- Tour operator(foreign), Biomedical waste, cotton storage, loading etc, has been exempted from service tax list.
Tax collection sequence in Revised estimate 2013 is Corporation Tax> Income Tax>Excise>Custom>Service Tax>Wealth tax. But Tax collection sequence in Budget estimate 2014 is Corporation Tax> Income Tax>Service tax>Excise>Custom>Wealth tax.
Non-Tax Revenue
Government also has non tax revenue Dividend of public holding companies, Income on investments, income on services rendered by government of India and the grants provided to government of India. In general Dividends>Services>Interest>External Grants>UT Non-Tax is the sequence but this year government expects that services will give the maximum non tax revenue.
Revenue Expenditure
Revenue expenditure is expenditure on unproductive assets. It includes interset payment, Subsidies, defence, pension, grants to states. Descending order of revenue expenditure heads is Interest payment-Subsidies-Defence-Pension-Grants to state.
Subsidy
Type of subsidies include Food, Energy, Urea, LPG etc. Total subsidy bill this year is expected to be 251800 crore rupees, it will include food subsidy of 115000 crore, fertilizer subsidy of 73300 crore rupees and 63500 crore for fuel subsidy. Subsidy problems include not all of them reach poor and distortion of supply side resource allocation Butrient based subsidy was introduced in India in 2010 with objectives of ; Reduction in subsidy bill, Proper use of nutrients in the field; in India farmers use N,P,K in the ratio of 8.2:3.2:1 but ideal ratio is 4:2:1. In NBS Urea was kept outside, which remained cheaper which lead to higher import of urea and increased CAD.
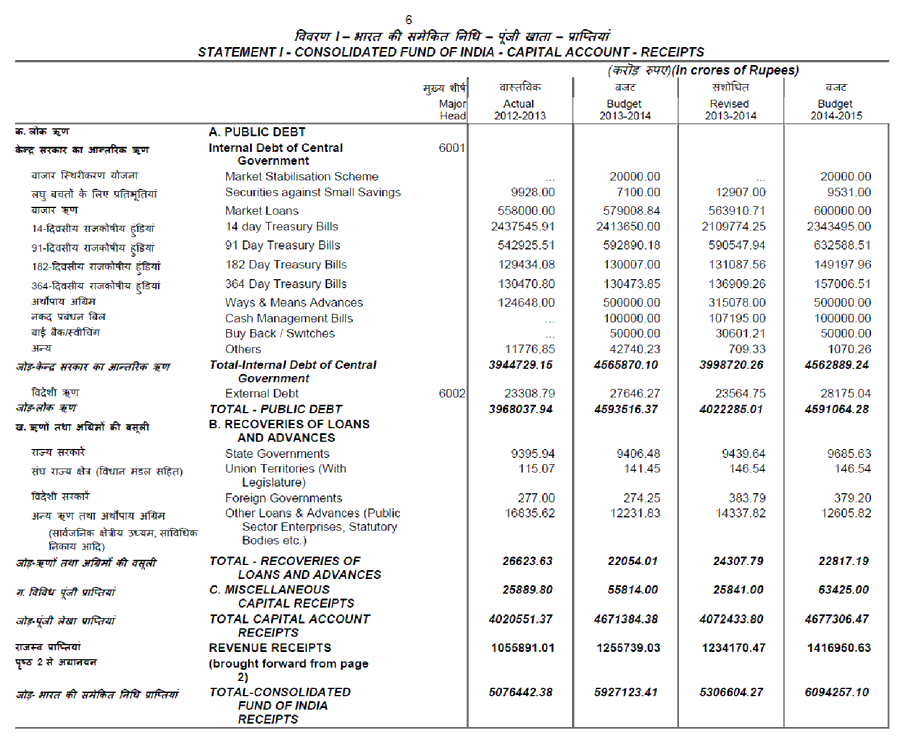
Capital Account
Capital Receipt:
Capital receipts has two domains Debt and Non-Debt. Debt creating receipts include loans both internal and external, provident fund and small savings. While Non-Debt creating capital receipts include loan recovery, Disinvestment.
Capital Expenditure:
It has two parts plan and Non-plan. Plan expenditure includes those expenditure which are provided for five year plans and used for capital creation while non plan expenditure are those which are used for maintainence of assets, Defence, loans etc.
Some new schemes announced in Budget
Deendayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana
“Deendayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana” for feeder separation will be launched to augment power supply to the rural areas and for strengthening sub-transmission and distribution systems. Its long term aim is to provide 24×7 uninterrupted power supply to all homes. A sum of Rs. 500 crores has been set aside for this scheme.
Shyama Prasad Mukherji Rurban Mission
Shyama Prasad Mukherji Rurban Mission will be launched to deliver integrated project based infrastructure in the rural areas. The scheme will also include development of economic activities and skill development. The preferred mode of delivery would be through PPPs while using various scheme funds. It is based on the example of Gujarat that has demonstrated successfully the Rurban development model of urbanization of the rural areas, through which people living in the rural areas can get efficient civic infrastructure and associate services.
Soil Health Card Scheme for Every Farmer
The deteriorating soil health has been a cause of concern and leads to sub optimal utilization of farming resources. The Government will initiate a scheme to provide to every farmer a soil health card in a mission mode. A sum of Rs 100 core for this purpose has been kept aside by the government. An additional Rs 56 crores have been allocated to set up 100 mobile soil testing laboratories across the county. There have also been growing concerns about the imbalance in the utilization of different types of fertilizers resulting in deterioration of the soil.
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana
The Government has proposed to initiate the scheme “Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana”. It is proposed to meet the need to provide assured irrigation to mitigate risk to the farmer since bulk of the farm lands are rainfed and depend on monsoon. This scheme would facilitate access to irrigation. A sum of Rs.1,000 crores is being set aside for this scheme.
A Dedicated TV Channel ‘Kisan TV’ to be Launched for Farmers
Kisan TV, dedicated to the interests of the agriculture and allied sector will be launched in the current financial year. This will disseminate real time information to the farmers regarding new farming techniques, water conservation, organic and farming etc.
Multi Skill Programme – Skill India
The Government has announced the launch of a national Multi-Skill programme called Skill India. This programme would skill the youth with an emphasis on employability and entrepreneur skills. It will also provide training and support for traditional professions like welders, carpenters, cobblers, masons, blacksmiths and weavers etc. Convergence of various schemes to attain this objective is also proposed.
Integrated Ganga Conservation Mission ‘Namami Gange’
The Government has proposed to set up an Integrated Ganga Conservation Mission called (Namami Gange). An amount of Rs. 2037 crore has been set aside for the Mission in the current Budget. The Mission is being launched because a substantial amount of money has been spent in the conservation and improvement of the river Ganga but the efforts have not yielded desired results because of the lack of concerted effort by all the stakeholders. To harness the enthusiasm of the NRI Community to contribute towards the conservation of the river Ganga, an NRI Fund for Ganga will be set up which will finance special projects.
Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao Yojana Launched
Government has introduced a new scheme called Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao, which will help in generating awareness and improving the efficiency of delivery of welfare services meant for women with an initial corpus of Rs 100 crore. The government would focus on campaigns to sensitize people of this country towards the concerns of the girl child and women. The process of sensitization must begin early and therefore the school curriculum must have a separate chapter on gender mainstreaming.
Digital India Programme
Centre has proposed to launch a pan India Programme called “Digital India” to further bridge the divide between digital “haves” and “have-nots”. This would ensure Broad band connectivity at village level, improved access to services through IT enabled platforms, greater transparency in Government processes and increased indigenous production of IT hardware and software for exports and improved domestic availability. Special focus would be given on supporting software product startups. The Government has also proposed to set-up A National Rural Internet and Technology Mission for services in villages and schools, training in IT skills and E-Kranti for government service delivery and governance scheme with an initial corpus of Rs. 500 crore. A programme for promoting “Good Governance” will also be launched and a sum of Rs.100 crore will be set aside for this.
Housing for All by 2022
Government has proposed to set up a Mission on Low Cost Affordable Housing to be anchored in the National Housing Bank. A sum of Rs 4,000 crore has been earmarked for National Housing Bank with a view to increase the flow of cheaper credit for affordable housing to the urban poor/EWS/LIG segment. The Government has already outlined some other incentives such as easier flow of FDI in this sector and is willing to examine other positive suggestions. The government has included slum development in the list of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) activities to encourage the private sector to contribute more towards this activity.

