Current & future prospect of Indian Economy : Important Topics for UPSC Exams

Current & future prospect of Indian economy.
Introduction
- After witnessing sluggish growth for five successive quarters, GDP growth in July-September was 6.3%, up from 5.7% in the previous quarter.
- The Gross Value Added (GVA) growth accelerated to 6.1% from 5.6% in the first quarter.
- The positive result has been impacted significantly by growth in manufacturing sector which was failing in previous quarter.
- The economic slowdown has been reversed, but the task of sustaining the trend remains matter of concern.
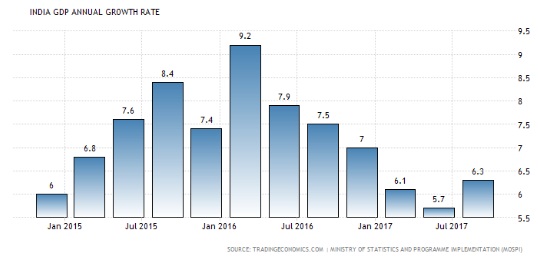
Recent Improvements in Indian economy
- India now ranks at 23rd among all countries in the Global Competitiveness Index compared to 39th rank in 2016-17.
- Moody Upgraded India’s sovereign ratings from Baa3 to Baa2).
- India now rank 100th in the World Bank’s ‘ease of doing business’ index which is jump of 30 as compared to 130th rank in 2016.
Future Prospects of Indian economy
- India is 2nd fastest growing major economy after China.
- it is projected that by 2050, India’s economy will be the world’s second-largest, behind only to China.
- Demand in the domestic market as well as international market is picking up, which should help the Indian economy.
Reasons for fall in private sector investment
- Low capacity utilization- current capacity of private sector is not fully utilized due to slowdown in market so there is no incentive for private for fresh investment.
- Reducing loan burdens: as companies are reducing loan burdens so they are not very enthusiast to take fresh loan.
- Poor insolvency resolutions: Although Insolvency and bankruptcy code has been passed but still process of insolvency have not become smooth.
- Large influx of imports, especially manufactured goods which further decreases private investment.
- Incompetency of banking system: The present banking system does not have core competency for efficient project appraisal and manage long-term project loans.
- Stalled projects, both in terms of value and number, is a cause of concern.
- Clearance issue: Issues like land acquisition, environmental clearances and other market conditions.
- Falling exports: also seriously affected investment as in absence of export production will fail to pick up to its potential.
- NPA problem: due to growing NPA banks are in difficult position to give loan to private sector.
Buy Printed Study Material for UPSC Pre General Studies (Paper-1)
Online Crash Course for UPSC PRE Exam
Concerns / Challenges
- Inefficient utilization of demographic dividend: India has the world’s largest youth population, but it is not yet fully utilizing this potential demographic dividend.
- According to the OECD over 30% of India's youth are not in employment, education or training so India is losing out significant contribution which they could have made
- Corruption: the businesses consider corruption to be the most problematic factor they face when doing business within the country
- Poor Inclusive Development Index: India is at 60th among the 79 developing economies in the World Economic Forum’s Inclusive Development Index.
- Rise in inequality: the rise in inequality is compromising the pace at which India is lifting people out of extreme poverty.
- Automation: the growing ability of machine learning to replace human workers is also a challenge.
- The rising crude oil prices pose a serious challenge.
- Sluggish Agriculture: agriculture remains in a slump though it is a significant contributor to rural incomes and consumption demand.
- Low grain production: Food grain output in the kharif season contracted, which could lead to inflationary pressures on food prices
- India’s sluggish exports: due to which economy is not picking up at the pace which it should.
- Falling investment: Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) or investment expenditure is falling
- Rising Incremental Capital Output Ratio (ICOR) which means more capital is required for doing business.
- Fiscal Deficit-reached 96% of annual target. Revenue expenditure is growing at 10% instead of targeted 5%.
Way forward
- Inclusive growth: growth needs to be more inclusive for broadening India's tax base.
- Participation of women in workforce: India needs to get more women working
- Improving the quality of all government services, from the police and courts to education and health.
- Better infrastructure and logistics so that investor can find it easy to invest.
- Rationalizing logistic cost: abolishing cross subsidization which increases rail freight rates
- Reforms: Major reforms in the markets for land & labour laws to incentivize private investment.
- Industrial revival and increase in private sector investment are necessary for sustained growth in employment and output.
- Fixed capital formation needs high policy priority.
- Large job creating sectors need more focus: like construction, agriculture, textiles, leather and tourism etc
- Focus on -sustaining consumption, energizing agriculture, and giving a big fillip to exports.
MODEL QUESTIONS
The State Financial Corporation have given assistance mainly to develop which of the following sector in states.
A. Irrigation projects
B. small-scale industries
C. medium-scale industries
D medium and small-scale industries
Correct answer: d
Civil Services Mains Examination
Despite its high potential of growth Indian economy fails to see high growth. What are the reason for the same and suggest some reforms in the direction to revive the growth of Indian economy.

