Cyber Security : Important Topics for UPSC Exams

Cyber Security : Important Topics for UPSC Exams
Cyber security refers to preventing any form of unauthorized and malafide access to any of the electronic pr digital device. With evolving technological landscape cyber security has been dominating the public discourse from quite some time. For Ex: National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) stated that India recorded 9,622, 11,592 and 12,317 cases of cybercrime in 2014, 2015 and 2016 respectively, experts stated that this data accounted for merely 1% of the cybercrimes that actually took place in the country.
Certain features of cyberspace make it a challenge to be tackled for ex: Absence of any geographical barriers, Rapidly evolving technologies and innovations in the field, difficulty in locating the attacker because of anonymity that the cyberspace offers and there are always loopholes in the technologies to be exploited.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF CYBER CRIMES
1. The crimes in which the computer is the target. Examples of such crimes are hacking, virus attacks, DOS attack etc.
2. The crime sin which the computer is used as a weapon. These types of crimes include cyber terrorism, IPR violations, credit card frauds, EFT frauds, pornography etc.
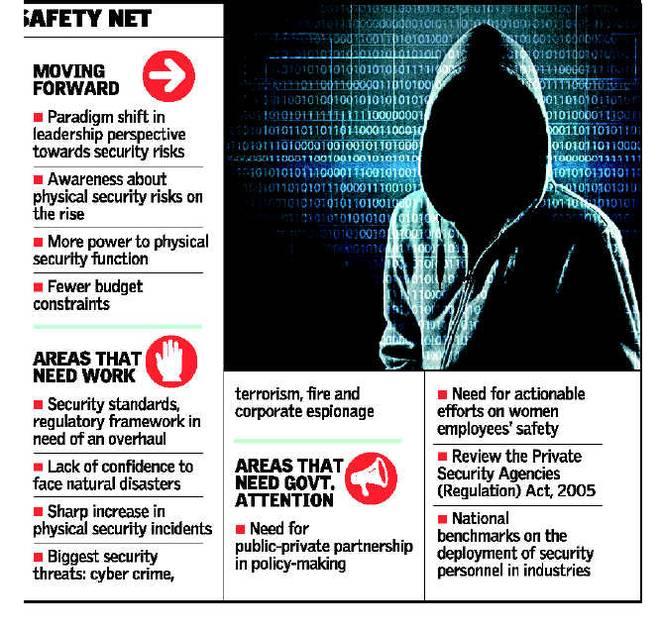
Steps taken by the government of India
-
Legislative framework: IT act 2000 provides for legal provisions for cyber security, Enacted with prime objective to create an enabling environment for commercial use of I.T. The IT Act specifies the acts which have been made punishable.
-
The Indian Penal Code, 1860 has also been amended to take into its purview cyber crimes.
-
Policy framework: National cyber security policy 2013 lays down the future path to be traced in this regard.
-
Set up different bodies to tackle various levels of threats.
-
Create a National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
-
Create a workforce of around 500,000 trained in cyber security
-
Indigenizing technological development in this regard.
-
Promoting education and awareness in this field
-
The policy also aims for public-private partnership for enhancing the security of cyberspace.
-
To enable effective prevention, investigation and prosecution of cybercrime and enhancement of law enforcement capabilities through appropriate legislative intervention.
Buy Printed Complete Study Materials for UPSC IAS PRELIMS Exam
Online Crash Course for UPSC PRE Exam
-
Institutional framework :
-
National Critical information infrastructure protection centre has been set up to identify the critical information and take steps for its protection.
-
CERT-In is the nodal agency for responding to computer security incidents as and when they occur.
-
Collection, analysis and dissemination of information on cyber incidents. Leading the response activities etc.
-
It strengthens security-related defense of the Indian Internet domain
-
Forecasts and alerts of cyber security are also issued by it.
-
Sectoral CERT’s are proposed to be established and some are already established ex: Telecom Sector and Financial Sector inter-linkages, Power & Defence CERTs, CERT-FIN for financial sector. Prominent among these is CERT-Fin
-
Cert-Fin will collect, analyse and disseminate information on cyber incidents across financial sectors
-
It will forecast and send alerts on cyber security incidents.
-
It will also take emergency measures on cyber security incidents. It will coordinate responses and activities for cyber incidents and issue guidelines, advisories, and white papers relating to vulnerabilities and information security
-
I4C (Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Center) – This is recently established by the government of india . This will deal with various cybercrimes. It is set up under cyber and information security division of ministry of home affairs.
-
I4C will assist in cyber security investigations, prioritize the development of response tools.
-
Bring together private companies to contain the problem of cyber security.
-
It will also block websites not in compliance of Indian norms(pornographic, racially and communally sensitive content)
-
Centre would maintain a list of suspects and the leads generated during investigations in cybercrime cases would be shared with law enforcement agencies through a “secured internal network”.
Lacunas
Despite having a scheme of things the goal remains elusive due to various lacunas like understaffing of CERT, Underreporting of cybercrimes in India Ex: only 1% of Cyber crimes are reported in India according to NCRB. India’s dependency on imports for various critical defense and information equipment which can be tampered is also one of the major challenges.
Various schemes of the GOI in this regard:
-
Recently launched Cyber Surakshit Bharat initiative by MeitY(in collaboration with industry partners) :
-
the mission to spread awareness about cybercrime and building capacity for safety measures for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT staff across all government departments.
-
It will work for Awareness, Education and Enablement.
-
To conduct workshops on best practices and enablement of the officials with cyber security tool kits to manage and mitigate cyber threats.
-
Cyber Swachhta Kendra’s: Botnet Cleaning and Malware Analysis Centre
-
It is a part of the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In).
-
It has been set up for analyzing BOTs/malware characteristics and providing information and enabling citizens for removal of BOTs/malware.
-
It also collaborates with the Internet Service Providers to notify the end users regarding infection of their system and providing them assistance to clean their systems.
International Initiatives:
Budapest Convention:
-
The Convention on Cybercrime, also known as the Budapest Convention on Cybercrime or the Budapest Convention, is the first international treaty seeking to address Internet and computer crime by harmonizing national laws, improving investigative techniques, and increasing cooperation among nations
-
It was drawn up by the Council of Europe in Strasbourg, France, with the active participation of the Council of Europe's observer states Canada, Japan, South Africa and the United States.
-
The following offences are defined by the Convention: illegal access, illegal interception, data interference, system interference, misuse of devices, computer-related forgery, computer-related fraud, offences related to child pornography, and offences related to copyright and neighbouring rights.
-
India has declined to adopt the Convention on the grounds that it did not participate in its drafting.
Way forward:
-
India may consider accession to Budapest convention.
-
Enhanced information and education on the subject
-
Development of offensive capabilities for deterrence in the field.
-
Development of human resource in cyber security
MODEL QUESTIONS
:: MCQ’s ::
1. Select the correct statements from the following:
A. Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Center is set up under MeITY.
B. It is set up under cyber and information security division.
Select the correct statements from above.
a) A only
b) B only
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Correct answer: b
2. Select the correct statements regarding Cyber surakshit bharat from the following:
A. Cyber Surakshit Bharat is the first public-private partnership for cybersecurity.
B. It is being implemented by MeITY.
Select the correct statements from above.
a) A only
b) B only
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Correct Answer: c (Both A and B)
3. Refer to the following statements regarding Cyber Swacchta Kendra
A. It is a botnet Cleaning and Malware Analysis Centre.
B. It facilitates free botnet removal tools under this initiative
Select the incorrect statements from above.
a) A only
b) B only
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Correct Answer: d (none of the above)
4. Budapest convention is related to which of the following
a) Missile technology control
b) Space nuclearisation
c) Women rights
d) Cybercrime

