Inter-State Migration : Important Topics for UPSC Exams

Inter-State Migration
Rising regional disparities in developmental front causes an unprecedented level of inter-state migration in India. Economic survey, 2016-17 stated that as high as 9 Million people migrated for both labor and education within India. Data shows Delhi to be the largest recipient of migrants accounting for more than half the total number, followed by Mumbai and other big metropolitans.
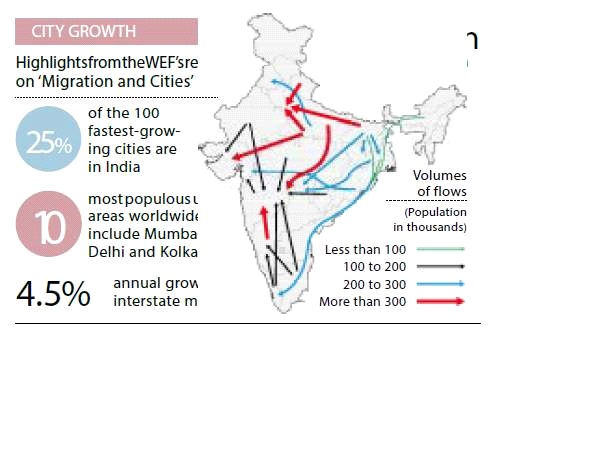
Pronounced trends in inter-Regional migration-
- The inter-state migration is being diversified. Laborers from Hindi-speaking states migrated not only in same language state, but also in southern states like Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- It indicates that language is reduced to be a barrier in inter-state migration.
- Economic survey has mentioned that the less affluent states like Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh show out-migration trends while more affluent states like Delhi, Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu show in-migration trends.
Causes of Inter-state migration-
Push Factors-
- People migrate due to various reasons. Majority of inter-regional migration occurs from less developed rural or semi-urban areas to more developed metropolitans. The prevalent reason are scarcity of cultivable lands, low agricultural productivity and very few source of income other than agriculture.
- In semi-urban and relatively less developed urban areas, unavailability of enough job opportunities and lack of better educational opportunities are the prevalent causes of migration.
- From some regions, where education level in high and living conditions are good, women migrated after marriage to Metropolitans where their husbands work. This type of migrations are prevalent in Kanpur and Jaunpur city of Uttar Pradesh.
Pull Factor-
- India is the fastest growing economy in the world. The economic centers of the country like Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, Chennai etcetera, therefore, requires huge chunk of cheap labor.
- There exists all kind of unskilled or semi-skilled works in the region which attracts poor laborers from less affluent regions.
- There regions are having better education opportunities, better health facilities and high standard of living. This attracts migrants very much.
Consequences of Migration-
- In India, migration is a two edged sword-- it has its own benefits and problems. The effects of migration can be understood under various factors--
- Demography of both in-migrating and out-migrating states changes. With high young population migrating towards big cities, old and children population increases in source region. While the young population increases in the receiving state.
- Migration results in the intermixing of diverse cultures and it broaden our understanding of different social and cultural aspects. However, sometimes migration create sense of dejection within individual and they fall crime and drug abuse.
- Economically, migration enhances the remittance in the source region which help in the development of the source region. However, in many instances, a section of locals become dissatisfied with the job loss in the region due to high in-migration. The recent incident of exploitation and violence with migrants in Ahmedabad, Gujarat is a prevalent example of these issues.
- Large migration in an area causes heavy burden over resources. The low skilled workers have to live in slums which are lacking in all kinds of basic amenities such as drinking water, electricity, sewage etc.
Laws and Regulations for migrants in India-
- Former President of India Dr. Kalam, vision Provision of Urban Amenities in Rural Areas (PURA) which aims to the comprehensive development of rural area, along with economic development in the region. This will reduce high out-migration from source region and balance the inter-state migration in the country.
- Inter-state migrant workmen Act, 1979 and other labor laws stated clearly that migrant workers should be entitled to basic human rights in the source state. Besides, the source state governments are expected to issue license to the contractors who take workers away and also monitors their working and living conditions in the destination state.
Way Forward-
- High migration in India is a reality. We may balance them with better policy implementation that my reduce regional disparities, but there is a need to recognize the issues with migrants and resolve them with full political will.
- All the laws that protect migrant workers, are on the table. However, their implementation is an issue. According to World Economic forum, we need to see migration as a dynamic part of new India. Then only we can solve the complex problem of Urbanization. For instance, Smart city project should include migrants and slum development into consideration.
Mains question-
There is a high probability that a question over migration may be asked in GS 1 after the recent Gujarat incident. The format may be--
Q. Migration in India is both a result as well as the reason of economic development. Comment. Also discuss the visible consequences of migration.
Hint-Try to read the question sincerely. They asked about two things-- how migration causes economic development and how economic development pull people from different states. Try to stick to the demand of the question. Introduce by some facts like Economic survey data or census. In the body part go with two sub heading reason and result. Then discuss 3 or 4 important consequences and conclude with a positive note.
Try to demonstrate migration status by some rough diagram if possible. It will provide you an edge over others.

