Malimath Committee Recommendations : Important Topics for UPSC Exams

Malimath Committee Recommendations : Important Topics for UPSC Exams
Context:
Government has decided to review the recommendations of Malimath committee on India’s criminal justice system
WHAT is Criminal justice system?
Criminal justice system refers to the collective institutions through which an accused offender passes until the accusations have been disposed of or the assessed punishment concluded. The criminal justice system is essentially an instrument of social control.
Parts of criminal justice system :
Major Objectives of criminal justice system :
|
Buy Printed Complete Study Materials for UPSC IAS PRELIMS Exam
Online Crash Course for UPSC PRE Exam
Problems of India’s criminal justice system :
1. India has many crimes but very few criminals, according to crime statistics. The criminal justice system in place is unable to apprehend them, put them on trial with proper evidence and get them convicted even after spending much time, money and human resources.
2. Personnel of the law (POLICE):
-
Not sufficiently motivated and adequately trained for the job with accountability for performance.
-
Political interference and infrastructural deficiencies.
-
Police officers face excessive workload due to lack of manpower
3. PROSECUTORS:
-
The appointment to these positions is often patronage to party
workers and sympathizers in the profession
-
They are also paid much below the market rates for their services.
4. COURTS:
-
Subjectivity pervades the system and judge’s professionalism.
-
The trial courts grant frequent adjournments on flimsy grounds.
-
System carries certain unwritten principles, which work in favor of criminals under the adversarial processes. These principles include “proof beyond reasonable doubt”, “the benefit of the doubt to the accused”, “burden of proof on the prosecution”.
-
Low judge population ratio because of which the pendency of work increases.
Consequences :
-
Erosion of faith in the enforcement and legal mechanisms as also noted by 239th law commission report: This manifests itself in mob violence, khap panchayats and parallel illegal and unofficial justice mechanisms .
-
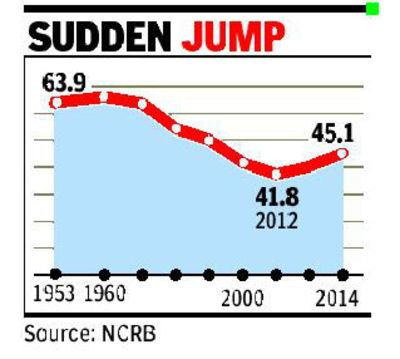
Thousands of under-trial prisoners are kept in overcrowded jails pending investigation and trial.
-
Cases involving the security of the country and safety of women and children are getting delayed enabling evidence to disappear in the process.
-
Many from weaker sections of society are unable to get bail or proper legal assistance Ex: More than 50% of people in jails were dalits, muslims and tribal people in 2013 according to NCRB(National Crime Record Bureau) despite that their proportion in population is around 39%.
-
Delayed justice also amount to justice denied.
-
Weakness of system was brought to fore in the recent Arushi murder case where following the long trial , The Allahabad High court acquitted the parents on basis of shoddy investigations and contradictory conclusions
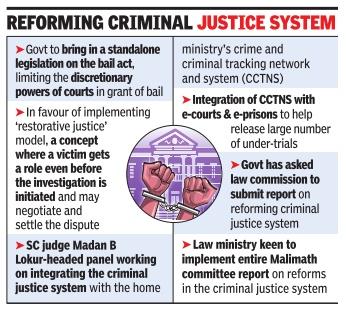
Key Recommendations of MALIMATH COMMITTEE:
(These recommendations are in line with Supreme court’s recommendations in PRAKASH SINGH case on police reforms)
It also has laid recommendations for humanitarian angle to the reforms by recommending permanent statutory committee to prescribe sentencing guidelines and reforms regarding offenses against women. It also calls for periodic review of the entire criminal justice system.
|
Concerns with the recommendations :
-
One of the controversial recommendation wants confessions to the police admissible in court as evidence if a senior police office of Superintendent of Police(SP) rank or above signs off on the statement.
-
Confessions to police have repeatedly come under scrutiny because of allegations of custodial torture, instances of custodial deaths, fake encounters and tampering with evidence.
-
Other recommendation suggests slightly lowering the criteria for appreciating evidence from the extant “proof beyond reasonable doubt” to improve the conviction rate.
-
Diluting the proof beyond reasonable doubt precept will prove to be counterproductive.
Other major reforms suggested by the committee are forward looking and aims to revamp the criminal justice system of india by making it more victim friendly and citizen oriented and calls for structural reforms in the judiciary, police and prosecution.
WAY FORWARD:
Appointing more judges and police personnel, deploying scientific techniques, beefing up forensic labs, and other infrastructure investments is the need of the hour.
Recommendations could be implemented in blocks of dozen, spread over a definite time period
MCQ’s
1. Historic Prakash singh judgemen of the Supreme Court is significant for which of the following ?
-
Reforms in Coal Allocation
-
Police reforms
-
Doctrine of colorable legislation
-
Removal of governor
Correct Answer : B
2. Malimath committee, recently in news is related with which of the following?
-
Electricity sector
-
Financial sector
-
Criminal Justice
-
Banking reforms
Correct Answer : C
3. Which of the following statements regarding india’s criminal justice system is/are correct?
-
Indian courts follow the principle of “Beyond reasonable doubt” as the basis to convict an accused.
-
The courts under the present system have a power to summon any person whether or not listed as witness for examination.
-
1 only
-
2 only
-
Both 1 and 2
-
None of the above
Correct Answer : A

