Model Agricultural land leasing Act, 2016 : Important Topics for UPSC Exams

Model Agricultural land leasing Act, 2016
- The Model act was prepared by an expert panel under Dr. T Haque. The act seeks to permit and facilitate leasing of agricultural land to improve access to land by the landless and marginal farmers. It also provides for recognition of farmers cultivating on leased land to enable them to access loans through institutional credit.
- Lease is defined as a contract between the land owner and cultivator, who uses the land owner's land for agriculture and allied activities for a mutually agreed specified period. The laws related to the Leasing of land is different in different states as land is a state subject in seventh schedule of the constitution.
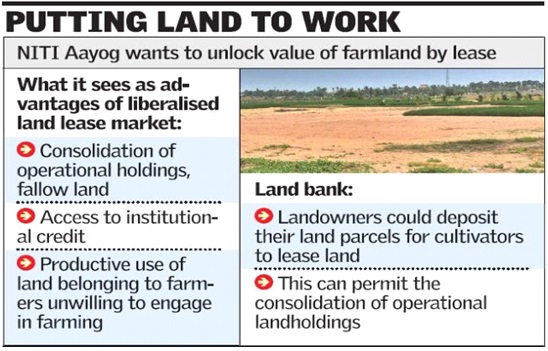
Why a model land leasing law :
- There is an absence of a sound institutional framework that deals with the land leasing laws in the country.
- Many states have very restrictive land leasing laws which affects the efficiency and profitability in agriculture.
- Due to the lack of any legal backing, in most of the states the tenant farmers are not able to connect with the agricultural credit facilities in the states.
Salient features of Model Act :
- Model act propose to legalize land leasing to promote agricultural efficiency, equity which ultimately help in poverty reduction.
- This provision secure complete security of land ownership right for land owners and security of tenure for tenants for agreed period.
- The act proposes to remove the clause of adverse possession of land in land laws of various states as it interferes with free functioning of the land lease market.
- The model act allow automatic resumption of land after the agreed lease period without requiring any minimum area of land to be left with the tenant with the termination of the tenancy.
- The model act facilitate all tenants including share croppers to access insurance bank credit and bank credit against pledging of expected output.
- The act is also a step in the direction of motivating the tenants to make investments in land improvement.
Uniqueness of the Act :
- The model act is meant to provide security in relation to the leasing agreement.
- The model act is a balanced approach that provide assurance to both owners and tenants.
- The act, however, befits more to the tenants as it would enable them to financial services, which was not adequately dealt with in any prior leasing acts.
Drawbacks and Limitations :
- A section believe that, the model act, if implemented in original form, would endorse diversion of agricultural land from crop cultivation to commercial usages.
- There are certain questions that the model act is not answering convincingly; like the status of contract farming. It is not clear whether contract farming comes under this model act.
- A section believe that the act is somewhat biased in favor of tenants. As they question that soil damage done by tenants is not defined in the model act.
- The act is being opposed by the farmer groups in the country. They have strongly advocated against giving land to corporates in their names.
- Activists also opposed providing grazing land of animals to the corporates in the name of fallow land.
Way forward :
The model act is a good step in providing benefit both to the landlord and tenant. There are certain things like diversion of cultivable land for non-agricultural purposes, that need to be resolved. Other issues like biased attitude towards tenants need to be dealt with. The changes need to be made by involving all the stakeholders. Ultimately, the provisions of the act can be applied only by convincing the states and for that states also need to be listened.
There are chances that a question asked in GS paper 2 or 3. The format may be-
Q. The model tenancy act is trying to resolve the issues of land leasing that are historically exist in India. Explain the extent this act is successful in this direction. Explain.
Hint- Do some research in historical background of land leasing in India like in permanent settlement and other forms in India. The extent means we have to talk both about positive and negative aspects of the model act. You can easily pick points from the article.

