(HOT) UPSC Current Affairs 2025 PDF
NEW! The Gist (NOV-2025) | E-BOOKS
Why to impose Carbon Tax in India : Important Topics for UPSC Exams
Why to impose Carbon Tax in India
Introduction
- Air pollution is one of the biggest public concerns in world and India today.
- After LPG reform and particularly from early 2000s, carbon emissions have increased because of high growth in the Indian economy.
- The aim of carbon tax is to set a price on the carbon content of goods & services to discourage their use.
- Emissions can be curbed only if people move away from polluting fossil fuels and adopt greener forms of energy. To achieve this we need carbon tax.
Carbon footprint in different sector of economy
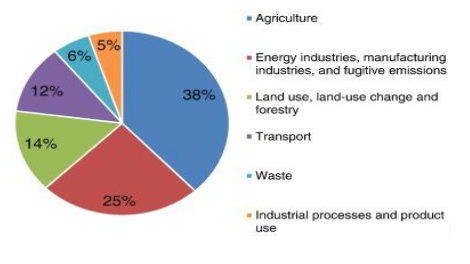
Credit: ScienceDirect.com
Why carbon tax
- A part of the carbon revenue thus generated can be used for a systemic overhaul of the energy mix and in promotion of green energy.
- Energy mix needs to be remodelled through investments in clean renewable energy and low-emissions bioenergy.
- It raises the level of energy efficiency by investing in building retrofits, grid upgrades, and industrial efficiency using green technology.
- This energy mix requires an additional 1.5% of GDP annually over the next two decades.
- This amount can be obtained by the carbon tax, which will be a revenue-neutral policy with no Implications on the fiscal deficit.
Why need for a Policy to Curb Pollution
- According to Lancet report around 19 lakh people die prematurely every year due to diseases caused by indoor and outdoor air pollution.
- A study shows that the lungs of children who grow up in polluted environments like Delhi Mumbai are 10% smaller compared to the lungs of children who grow up in the pollution free environment. This is a public health emergency.
- In 2014, India's total carbon emissions were more than three times the levels in 1990, as per World Bank data.
- India is heavily dependent on fossil fuels and there is dramatically low level of energy efficiency.
- Industry actors do not need to actively monitor and limit their C02 output.
- About 75% of all greenhouse gas emissions are C02 emissions produced through burning fossil fuels -oil, coal and natural gas.
- Therefore we need a comprehensive policy to curb pollution.
Buy Printed Study Material for UPSC Pre General Studies (Paper-1)
Online Crash Course for UPSC PRE Exam
From Carbon Subsidy to Carbon Tax
- By imposing higher tax on petroleum products India is trying to reenergizing the renewable energy sector.
- India shifted from a carbon subsidization regime to carbon taxation regime.
- This has significantly increased petrol and diesel price while serving as signal to reduce C02 emissions.
- India has increased the coal cess to rs 400 per ton
- India is promoting electrical vehicle to curb pollution by vehicle.
- It is subsidizing wind and solar energy to decrease the carbon footprint
Benefits
- Will Balance Marginal social costs: The carbon tax will be a Pigovian Tax which balances the marginal social costs such as disease etc and additional emissions.
- Greener alternatives: high price of the materials or energy source according to their carbon content will induce households, including the rich, to shift towards greener alternatives.
- Employment generation: It will provide more employment since the employment elasticity in greener forms of energy is higher than those in fossil fuel-based energy.
- Expenditure will come down: a significant part of more than 3% of India's GDP currently spent on pollution-induced diseases will come down.
- Increase tax-revenue :It will also increase tax-revenue which can be used for other green projects.
Concern/challenges of taxing carbon
- Carbon tax is regressive in nature -it affects the poor more than the rich.
- Inflation : high transportation cost will lead to inflation and affect the informal sector.
- Alone insufficient: increasing carbon taxes is alone insufficient to reduce emissions as income levels rise.
- The highest rise in price will be in fuel and energy which affects the poor.
Way forward
- Universal travel passes with a pre-loaded balance to compensate for the rise in transport costs.
- Encourage the use of green public transport.
- Carbon tax regime in india will be effective only if it is harmonised internationally and carbon tax is levied in other countries too because energy-intensive businesses may move to less strict national regimes.
- Most practical way to change energy consumption habits is to lower the price of renewable energy and energy efficiency.
MODEL QUESTIONS
Q.Consider the following statements with respect to Carbon Credits?
1. Certified Emission Reduction (CER) certificate is not eligible for Carbon
Credits
2. Transfer of carbon credits is taxable in India.
Which of the above statements is/are correct
A. Only 1
B. Only 2
C. Both 1 & 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
Correct Answer: b


