(Current Affairs) International Events | September: 2013
International Events
- US Surveillance on top Internet Servers via PRISM Programme (Free Available)
- The Arms Trade Treaty Signed (Free Available)
- UNSC Eased Sanctions against Iraq (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- Japan’s L0 Series Maglev Bullet Train (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- UK and China signed Currency Swap Deal worth 200bn Yuan (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- Egypt’s Supreme Court invalidated the Country’s Shura Council (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- Agreement on 1.3 trillion Dollar Budget for 2014 to 2020 for European Union (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- China’s First Pilot Carbon Emission Trading Scheme (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- Draft Law for Protection of Hindu Religious Property Approved in Bangladesh (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- Japan and South Korea suspended US Wheat Imports (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- US exempted India and 8 Other Countries for Importing Oil from Iran (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- Indians and Pakistanis to pay 4600 US Dollars more for British Visa (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- Mali’s Presidential Election to be held on 28 July 2013 (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- UNESCO increased Pressure on Australia to conserve Great Barrier Reef (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- North and South Korea held their First Official Talks after Years (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
- Kevin Rudd sworn in as new Australian Prime Minister (Only for Online Coaching Members and Premium Members)
US Surveillance on top Internet Servers via PRISM Programme
Top secret documents obtained by The Guardian claimed that US National Security Agency (NSA) has obtained direct access to the systems of Facebook, Google, Apple and other US internet giants. All this was done under the secret program of US to search the data potentially linked with terrorism, espionage or nuclear proliferation. The US agency tapped into the central servers of different internet giants under the six-year old programme, code-named PRISM. Under this program, the FBI and NSA searched for the emails, videos, photographs, search history, the content of emails, file transfers, live chats and other documents. Existence of the program PRISM was confirmed by James Clapper, US Director of National Intelligence. As per Clapper, the information accessed under the programme is among the most valuable intelligence information collected by the agency and has been helpful in protecting US from a wide range of threats.
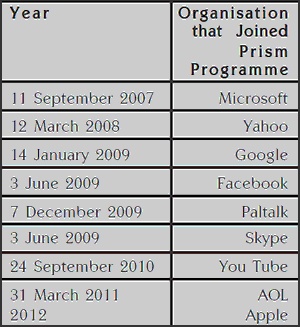
The IT companies which were directly into surveillance of the US Agency were Microsoft, Yahoo, Google, Facebook, PalTalk, AOL, Skype, YouTube and Apple and all these companies denied the knowledge of surveillance despite the of the claims that the programme was assisted by them.
The program was started in the George Bush Era in the year 2007, with Microsoft as the first company to be involved in the Programme. President Barack Obama renewed the changes in surveillance laws in the year 2012, which were made under Bush making information accessible by NSA. US spent 20 million dollar annually on PRISM and its operations; this is a small percentage of 8 Billion Dollar annual budget for NSA. Since its beginning, the number of intelligence reports cited by PRISM is 77000. As per the latest data, the NSA issued about 2000 PRISM-based reports every month. In the year 2012, NSA issued a total of 24005 reports.
The Arms Trade Treaty Signed
Over 65 countries of the world signed the Arms Trade Treaty on 3 June 2013. The United States, in the meanwhile announced that it will sign the treaty in near future. The Arms
Trade Treaty regulates the multibillion-dollar global arms trade. Signing the treaty will start the first crucial international campaign in order to curtail the illicit trade in weapons which results in fuel conflicts as well as extremists. The number of nations to sign the treaty is likely to increase.
The US Secretary of State John Kerry announced that US was the largest dealer of arms in the world and that it will sign the treaty soon, but the strength of the treaty was dependent on support by major arms importers and exporters. The Arms Trade Treaty was approved by the UN General Assembly on 2 April 2013. Signing of the treaty is first step of its ratification and it will take only be effective after ratification by 50 countries. The co-sponsors of the Arms Trade Treaty- United Kingdom, Finland, Japan, Argentina, Australia, Kenya and Costa Rica announced at a conference on 3 June 2013 that on first day, the treaty was signed by a lot of countries.
Objective of Arms Trade Treaty
- Every minute, one person dies because of armed violence. Arms Trade Treaty is required for controlling the unrestrained flow of the arms as well as ammunition.
- The aim of this Arms Trade Treaty is to set the standards for the purpose of cross-border transfers of weapons ranging from attack helicopters to tanks.
- The treaty would create requirements for all the countries to review the crossborder contracts in order to make sure that these weapons would not be used for the illegal purposes such as organised crimes, human rights abuses, violation of humanitarian law as well as terrorism.
About the Arms Trade Treaty The Arms Trade Treaty is the multilateral treaty which regulates international trade in the conventional weapons. It is estimated that the trade of international weapons has reached 70 billion US dollar on an annual basis. The treaty was discussed at the global conference from 2 July 2012 to 27 July 2012 in New York. No agreement was reached at that time, and eventually a new conference was held on the same from 18 March 2013 to 28 March 2013.Finally, on 2 April 2013, the Arms Trade Treaty was adopted by the UN General Assembly.
Provisions of the Arms Trade Treaty
- The Arms Trade Treaty covers light weapons, attack helicopters, battle tanks, missile launchers, warships, missiles, armoured combat vehicles, small arms and large-calibre artillery systems.
- The treaty proscribes the countries that ratify the treaty from transferring conventional weapons in case these weapons promote genocide or violate the arms embargoes.
- The treaty additionally forbids export of these conventional arms in case these arms could be used in the attacks on civilian buildings or civilians.
- If a country wants to consider whether the export of arms should be authorised or not, it should evaluate the weapons on grounds of violation of human rights laws or their employment for terrorist activities or organised crimes.
- The treaty also requires all the countries for taking the measures in order to prevent diversion of the conventional weapons to illicit markets.


