(Sample Material) Current Public Administration Magazine - "Disaster Management"
Sample Material of Current Public Administration Magazine
Disaster Management
Disaster Planning & Management
The institutional and policy mechanisms for carrying out response, relief and rehabilitation after disasters in India had been well-established since Independence. The increasing frequency and ferocity, the rising extent and sweep as well as the mounting human and economic toll due to disasters necessitated a reappraisal of institutional and policy frameworks and development of new frameworks for holistic disaster management of disasters.Heralding this paradigm shift in public policy, the Tenth Five-Year Plan (2007-12) stated:
The traditional perception relating to the management and mitigation of natural disasters has been limited to the idea of “calamity relief,” which is seen essentially as a non-plan item of expenditure. However, the impact of major disasters cannot be mitigated by the provision of immediate relief alone, which is the primary focus of calamity relief efforts. Disasters can have devastating effects on the economy; they cause huge human and economic losses, and can significantly set back development efforts of a region or a State. With the kind of economic losses and developmental setbacks that the country has been suffering year after year, the development process needs to be sensitive towards disaster prevention and mitigation aspects. There is thus a need to look at disasters from a development perspective as well.
The Plan also laid down a blue-print for the future:
The future blue-print for disaster management in India rests on the premise that in today’s society while hazards, both natural or otherwise, are inevitable, the disasters that follow need not be so and the society can be prepared to cope with them effectively whenever they occur. The need of the hour is to chalk out a multi-pronged strategy for total risk management, comprising prevention, preparedness, response and recovery on the one hand, and initiate development efforts aimed towards risk reduction and mitigation, on the other. Only then can we look forward to “sustainable development.
Based on this philosophy, a holistic National Disaster Management Framework was developed in 2004, which highlights the interdependence of economy, environment, and development. This framework also links the issues of poverty alleviation, capacity building, community empowerment and other structural and non-structural issues of prevention and preparedness, response and recovery for effective disaster risk mitigation and management.
A comprehensive legal and institutional framework for disaster management has been set up through the Disaster Management Act passed by the Indian Parliament in 2005 and the National Policy on Disaster Management that was approved in 2009.
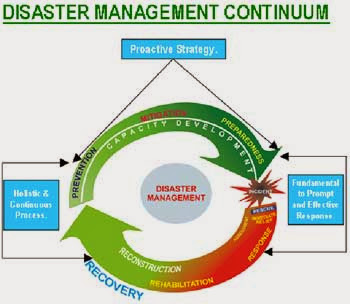
Till recently, the approach to Disaster Management has been reactive and relief centric. A paradigm shift has now taken place at the national level from the relief centric syndrome to holistic and integrated approach with emphasis on prevention, mitigation and preparedness. These efforts are aimed to conserve developmental gains as also minimize losses to lives, livelihood and property.
A typical Disaster Management continuum as shown below, comprising of six elements i.e., Prevention, Mitigation and Preparedness in pre-disaster phase, and Response, Rehabilitation and Reconstruction in post-disaster phase, defines the complete approach to Disaster Management.
Disaster Management Act 2005
The Disaster Management Act, 2005 came into the statute book on 26 December 2005 by a Gazette notification, exactly on the first anniversary of the devastating tsunami of 2004, which killed nearly 13,000 people in India alone and affected 18 million people. The Act provides a legal and institutional framework for “the effective management of disasters and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.” It provides for establishment of National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA) and District Disaster Management Authorities (DDMA) at the National, State and District levels with adequate financial and administrative powers and creation of the National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM) with the mandate of undertaking training and capacity building, Develop Training Modules on various aspects of Disaster management, Undertake Research and Documentation, Formulate and implement comprehensive HRD Plan covering all aspects of DM, Provide assistance in national level policy formulation and Provide assistance to state governments and State Training Institutions. The act also provides guidelines for creation of National Disaster Response Fund, National Mitigation Fund, Establishment of funds by State Government and Allocation of funds by Ministries and Departments for Emergency procurement. The act also provides for establishment of National Disaster Response Force (NDRF).
National Policy on Disaster Management 2009
The National Policy on Disaster Management was approved by the Government in November 2009. This comprehensive policy document lays down policies on every aspect of holistic management of disasters in the country. The policy has thirteen chapters as under:
1. Preamble
2. Approach and Objectives
3. Institutional and Legal Arrangements
4. Financial Arrangements
5. Disaster Prevention, Mitigation and Preparedness
6. Techno-Legal Regime
7. Response
8. Relief and Rehabilitation
9. Reconstruction and Recovery
10. Capacity Development
11. Knowledge Management
12. Research and development
13. Road Ahead
Salient Features of India’s National Policy on Disaster Management:
India’s National Policy on Disaster Management was approved by the Union Cabinet of India on 22nd October, 2009 with the aim to minimize the losses to lives, livelihoods and property, caused by natural or manmade disasters with a vision to build a safe & Disaster resilient India by developing a holistic, proactive, integrated, Multi-disaster oriented and technology driven strategy. With this national Policy in place in India, a holistic and integrated approach will be evolved towards disaster management with emphasis on building strategic partnerships at various levels. The themes underpinning the policy include Community based Disaster Management, Capacity development in all spheres, Consolidation of past initiatives and best practices and Cooperation with agencies at National and International levels with multi-sectoral synergy.
The Policy is also intended to promote a culture of prevention, preparedness and resilience at all levels through knowledge, innovation and education. It encourages mitigation measures based on environmental sustainability. It seeks to mainstream disaster management into the developmental planning process and provides for Institutional and Financial arrangements at national, State, and District-levels for Disaster Prevention, Mitigation, Preparedness and Response as it ensures adequate budgeting for disaster mitigation activities in all Ministries and Departments.
-
State Policies on Disaster Management: The States of Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Kerala have formulated State Disaster Management Policies. policies. Tamil Nadu, Chattisgarh, Uttranchal, Meghalaya, Bihar, Rajasthan, Delhi, Orissa and West Bengal have prepared draft policies.
- State Relief Codes/ DM Codes: Many States have manuals and codes for management of drought, floods etc. Now many states are in the process of changing their State Relief codes into Disaster Management Manuals.
Guidelines of NDMA:
- Management of Biological Disasters
- Management of Chemical (Industrial) Disasters
- Management of Chemical (Terrorism) Disasters
- Management of Cyclones
- Management of Drought
- Management of Earthquakes
- Management of Floods
- Management of Urban Flooding
- National Disaster Management Information and Communication System
- Plan to counter the threats to Muncipal Water Supply and Water Reserviors
- Scaling, Type of Equipment and Training of Fire Services
- Strengthening of Safety and Security of POL Tankers
- Incident Response System
- Management of Landslides & Snow Avalanches
- Role Of NGOs in Disaster Management
- Management of Nuclear & Radiological Emergencies
- Psycho Social Support & Mental Health Services in Disasters
- Preparation of State Disaster Management Plans
- Management of Tsunamis
- Revamping of Civil Defence in The Country, National Policy Approach Paper
- Hand Book for Training and Capacity Building of Civil Defence and Sister Organisaions
Suggestive Strategies, Recommendations and Action Plan for Disaster Mitigation, Prevention and Preparedness:
Government of India has taken several initiatives for strengthening disaster reduction strategies. Government of India constituted an Expert Group to examine the related issues and evolve recommendations for improving preparedness and prevention with respect to natural disasters caused by earthquakes, floods and cyclones.
Questions:
-
Till recently, the approach to Disaster Management has been reactive and relief centric. Comment.
-
A holistic and integrated approach will be evolved towards disaster management with emphasis on building strategic partnerships at various levels. Discuss.
(With inputs from Government of India websites and report)
- Government of India (Sources) - http://ndma.gov.in
- http://www.bmtpc.org (Ministry of Urban Development)
- http://ndmindia.nic.in (Ministry of Home Affairs)
-
Click Here to Buy Hard Copy of Public Administration Study Kit
-
Click Here to Join Online Coaching of Public Administration
IAS MAINS-PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION Online Coaching DEMO
-
IAS MAINS-PUB AD Chapter Demo
-
IAS MAINS-PUB AD Home Assignments Question Demo
-
READ BATCH-1 SCHEDULE
-
Live Chat DEMO
-
Discussion Forum Demo
<< Go Back to Current Affair Main Page

