(IGP) IAS Pre: GS - Indian History - Ancient India : Post Mauryan Period (200. BC-300 AD) (Part -2)
Indian History
Post Mauryan Period (200. BC-300 AD) (Part -2)
The Vijaynagar Empire
| 1. Amaram | Land with a fixed revenue given to Nayaks. |
| 2. Manyam | Tax free land |
| 3. Sist | Land tax - 1/6 |
| 4. Valangais | Right — handers’, a group of industrial class |
| 5. Idangais | ‘Left handers’ a group of industrial class |
| 6. Ayagars | 12 hereditary village unctionaries who took over the functions of the village assembly. |
| 7. Rajya/Mandaam/Chavadi | Province |
| 8. Nadu | District |
| 9. Astadiggajas | Eight eminent scholars in the court of Krishna Deva Raya. |
| 10. Varahas | Gold coins issued by Viajyanagara rulers, of 56 grains, issued in their haf and quarter denominations |
| 11. Pagodas | Gold Varahas termed as by the foreigners particularly the portuguse |
| 12. Rirupkasha | God Shiva, the main God of the early Vijayanagara rulers. |
| 13. Lord Venketswara of | Associated with God Vishnu, who replaced Virupkasha during the origin of Venkata II, as the Tirupati principal deity |
| 14. Andhra Bhoja | The names associated associated with Krishna Deva Ray a, because of his granting of liberal ptronage to |
| Abhinav Bhoja Telugu literature. | |
| Andhra Pitamah | |
| l5. Amuktamalyada | A Telugu work on polity by K. D. Raya |
| 16. Car Festival | The concluding event of a festival celebration in a temple in which the idol of the deity was taken out in a chariot. |
| 17. Amaranayakas | Feudatories who held lands of Icings and were bound by military ties |
| 18. Raichur Doab | The region between the rivers Krishna & Godavari, the bone of contention between the Bahamanis and the Vijaynagar a rulers. |
| 19. Chaturvedimangalams | Villages given in grants to the Brahmins. |
| 20. Brahmadaya | Villages given in grants to the Brahmins |
| 21. Mandalam | Province (in Tamil region |
| 22. Nayankara | Military Chiefs who were granted amaran lands by kings |
| Nayakara | They had to pay a fixed annual financial contributions to imperial exchequer which was generally 14 (Reference from NUNTZ). Maintained troops to assist kings in times of war. They were guardian of law and order and administration in their areas. Office became hereditary later on when the kings became weak. |
| 23. Devadana | Land gra nt to temples |
The Pallavas
| 1. Damirike / Limerike | The Southern region of India mentioned in Ptolemy’s writings |
| 2. Vishnugopa | King of Kanchi, mentioned in Allahabad Prashasti |
| 3. Kinchipulo | Kanchipuram, referred to by Hieun Tsang |
| 4. Talopicha | The Dravida region (country), referred to by Hieun Tsang |
The Cholas
| 1. Vellala | Agriculturists |
| 2. Variyam | Committee |
| 3. AlunGanam | Executive Committee |
| 4. Salabhoga | Tennures meant for educational purpose |
| 5. Manigramam | Great Nagaram |
| 6. Nanadesis | Merchant guild having wide network |
| 7. Valanjiyar | Merchant guild |
| 8. Anjuvanam | Foreign merchant organization |
| 9. Taniyur | A very large village, administrated as a Single unit |
| 10. Mandalam | Province |
| 11. Valandu | District |
| 12. Nadu/Kurram/Kottam | Group of villages |
Click here to download full Chapter
Click Here for Post Mauryan Period MCQ
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS HISTORY 11 YEARS SOLVED PAPERS PDF
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS HISTORY 10 Years Categorised PAPERS
Study Noted for UPSC MAINS HISTORY Optional
Sources
(A) Literary
(i) Purana.
- Nitishastra of Kamandak- This book was equivalent to Arthasastha of Kautilya.
- Book was written by Sikhar, Prime Minister of Chandragupta Vikarmaditya.
(ii) Kaumudi Mahotasava:- A drama written by Kishorika or Vajika.
(iii) Devichandraguptam and Mudrarakshas of Vishakhddutta. Mudrarakshas gives us the details of religion of Cluptaperiod.
(iv) Setubandh Kavya written by Pravarsen II.
(v) Ravan Badh written by Bhatti. This is also called Bhatti Kavya.
(B) Description of Foreign Travellers
(1) Fa-hein of China (399-414 A.D)
- He Came India during Chandraçupta Vikrarnaditya is period.
- He gives the details description of exchange system during Gupta period, which were done by kaudi.
- He describes about Chandal. Although Chandal were emerged in Indian society in 5 B.C. But in 5th century A.D. their number were very high. (2) It-Sing (675 A.D)
- He describes about Srigupta who was founder of Gupta period.
- He claims that he had seen the Ashokan statue as a Buddhist Monk.
(C) Inscriptions
(a) Allahabad Inscription:- This was incription of Samudragupta. The writer were Harisena, who was the minister of war and peace called Sandhi-vigrahi.
(b) Iron pillar inscription of Mehraulli:- This was considered as inscription of Chandragupta Vikramaditya
(c) Udalyagiri Cave inscription:-
- This was inscription of Chandragupta Vikramaditya.
- This was written by Virsen Saba, who was also minister of war and peace.
(d) Bhitary Inscription:-
- This was inscription of Skandagupta.
- This gives as the details of Huna attack.
(e) Indore pillar Inscription:
- It was inscription of Skandagupta.
(f) Eran Inscription:- 510 Ad.
- This was inscription of Bhanugupta. First epigraphica1 record of Sati system was found in this inscription.
(D) Coins
Guptas issued hightest number of gold coin in India.
- Chandragupta Vikramaditya issued first silver coin among all Gupta ruler.
- This coin was based on Saka’s coin.
- Firstly this type of coin were in use in Saurastra state. Kumar Gupta distributed in who Gupta Dynasty.
- Samudra Gupta issued 8 types of coins.
- On Sumudra Gupta’s coin lion was shown.
- On Surnudra Gupta’s coin picture of Ashwamegh Yagya was shown:
- On Sumudra Gupta’s coin the picture of playing violin was shown because he himself played violin very well.
- On Chandragupta Vikramaditya’s coin tiger were shown.
- Ox were shown on Skandhgupta’s coin.
Coin of Gupta periods
Gold coin - Nishka, Pala
Silver coin - Rupak, Satmana, Panna
Copper - Kakini, Kasharpan.
- Highest number of remnant coins of Gupta a e was found in Bayana (Rajasthan).
Political History
- Founder - Srigupta (275A.D)
- Capital - Prayaga
- State language - Sanskrit
- Religion - Neo vaishnavism.
Chandra Gupta I (319-335 A.D)
- First Indian ruler who has taken title of Maharajadhiraj.
- He issued Gupta Samvat. (319-20A.D).
- He was married with Kumaridevi Princess of Lichehavi ruler.
- On the coin of Chandragupta 1. One side had the picture of Kumaridevi and Chatidra Gupta I and on the otherside picture of Lakshmi and Lichawayah were written.
Samudra Gupta: (335-380 A.D)
- V. A. Smith called him Napolian of India.
- Title:- Kacha, Kaviraja, Kridant Parsu, Sarv-raja. Hero of 100. wars.
War Policy of Samudragupta
1. In Northern India Digvijaya.
2. In Southern India Dharmavijaya.
- Allahabad Inscription of Samudragupta gives the details of war.
- According to Chinese sources Samudragupta was contemporary of Meghvarman of Sri Lanka.
- He was very good violin player.
- According to some scholor he has written Krishnacharitam.
- He patrnoised two Buddhist monk Vasubandhu and Asang.
Chandragupta II chandragupta Bikramaditya. (389-412 A.D)
- TitIe- Sakari, Sahshank, Devraj, Rajrajarshi, Param Bhagwat.
- Chandragupta II was also called the lord of Ujjain and Patliputra. It seems that his another capital was Ujjain.
- His Wife was Druvadevi.
- Son Kumargupta.
- His daughter Prabhayati was married to Vakatak ruler Rudrasen II.
- During his tenure Fa4iien came India.
Nine gems of Chandragupta II court.
- Kalidasa
- Amar Singh
- Varahmihir
- Dhanvantari
- Betal Bhatta
- Sanku
- Ghatt-Karpar
- Var-ruchi
- Kshapanak
Chandragupta patronised Dignaga. Dignaga was considered as father of Justice. He written the book Nyaya Prakash.
Kumaragupta I. (415-455. A.D)
- He was follower of Kartikeya.
- He founded Na1nda University.
- First Huna attack happened in his period.
- Lord Shankar and Parvati were shown as wife husband on Kumargupta’s coin.
Skandhgupta (455-467 A.D)
- Titles:- Vikrarnaditya, Sakraditya, Lord of hundred ruler.
- Lord Vishnu and Laxmi were shown as wife husband on Skandh Gupta’s coin.
- His vaisya officer Prandutta reconstract the Sudarshana Lake.
- Bhitari inscription his victory over Hunas.
Purugupta — (4 72-4 73 A.D
Narsingh Gupta Baladitya — (473-476 A.D)
- Buddh Gupta:- He was last great Gupta ruler.
- Title- Avanisingh, Prithvipati
- Jivak Gupta: He was last Gupta ruler.
Religion of Gupta
- Guptas were the follower of Vaishnav religion. During Gupta period two important change came into Vaishnav religion.
(1) Concept of Incarnation- Ten incarnation of Vishnu.
- Matasaya
- Kuruma
- Varah
- Narsingh
- Vamana
- Rama (Parsurama)
- Rama - Dashrathi (Rama)
- Rama Bhargava (Krishna)
- Buddha.
- Kalki - yet to come.
(2) Concept of wife of God.
(a) Parvati wife of Shankar.
(b) Laxmi & Vaishnavi wife of Vishnu. Sakti Pooja was evolved after evolution of concept of wife of God. Later on Durga, Kali were worshiped as Goddess. ci Earlist structure of Hindu temple was first made in Gupta period.
- Shiva was also worshiped in Gupta period.
- In this age Shiva was also worshiped as Ardhnarishwar.
Administration of Gupta
- Gupta ruler believes the king as a God.
- Samudra gupta was considered as God, who came to life on earth.
- Gupta ruler started appointing their successor as king,
- During Gupta period officers post was heridatory.
Administrative Setup
State (Country) Bhukti
District Vishay
Sub-District Vithi
Group of village Pethak
Village Gram
- Head of country called Gopa.
- Head of Bhukti called Uparika.
Other important officer
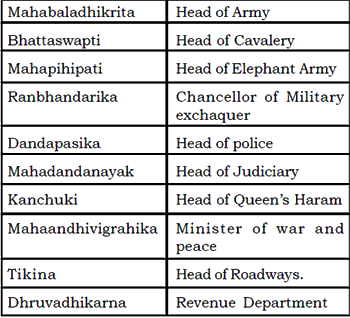
Vishaypati was head of vishay (District). Following persons helped him in completion of his work.
(a) Nagar sresthi — Head of his work
(b) Sarthvaha — Chief of traders.
(c) Kulika — Chief Architect.
(d) Pratham Kayas a — Chief ceribe
Village head were called Bhojak, Gramika
Army — Three part of Army
- Infantry
- Cavalery
- Elephantry
General army were called Chat. Small group of army were called Chamu and head of them were called as Chamupa.
Judiciary
- King was the chief of judiciary.
- Mahadandanayak also see the work of judiciary.
- Diwani and faujdari law were first separated in Gupta period.
Economy
- During Gupta period the trade tax was reduced and land tax were increased.
- There were mainly 18 taxes in Gupta period.
Main taxes
(a) Udranga - tax on permanent peasants.
(b) Uparikara - tax on temporary peasants.
(c) Hiranaya - the villages pay the tax in form of Gold,
(d) Purastha - tax given to the officer who were collecting land tax.
Type of land
Kshetra - Fertile land
Khil - Unfertile land
Aprabata - Forested land
Vastu - Habitable land.
Literature
Special features of Gupta Literature
- Book were written mainly secular type.
- All most all the books have good ending except Mirchkatikam written by Sudrak.
- Higher class male used Sanskrit language.
- But lower class people and generally females used Prakrit language.
- Both epic Mahabharat and Ramayana were written in Gupta Age.
- The collection of many Purana had taken place in Gupta age.
Main Poets
(a) Kalidasa Malvika Agnimitra, Ritusanghar, Kumarsambhava. Abhigyan Sakuntlam, Vikramovarshium, Raghuvansha
(b) Vatsayan - Kamsutra, Nyaybhasya.
(c) Ishwarkrishna - Sankhya Karika.
(d) Dignaga - Praman Samuchaya, Nyaya Pravesh.
(e) Amar Singh - Amarkosh (Dictionary of Sankrit).
Science
(a) Aryabhatt- Aryabhattium, Suryasiddhanta.
- He calculated the value of (n) which was 3.142.
- He calculated perimeter of earth. 40,232 km.
- He also discovered the location of status on the basis of Babilonians.
- He also finded out the causes of solar and Lunar eclipses and said sun is fixed at point and earth is revolving around the sun.
- He also said that earth is round.
(b) Varahmihir:- Written Brihatjatak, Laghujatak and Panchsiddhantika.
(c) Brahmgupta:
He discovered that due to natural reason all the goods falls, down from upper level to lower level.
- He Written Brahmasphutta.
- Khand — Khandayanka.
(d) Palakalpa:- Written book Hasti Ayurveda. This was written on Animal Husbandary. In field of Mathematics the Ancient Indians ‘have three contribution
- Use of notation system.
- Use of Decimal system.
- Use of zero.
Architecture:
- Structural architecture of Gupta’s period was not in good stage.
- Important architecture was Dashawatar Temple of Devgarh.
Painting
- Painting was highly developed in Gupta period.
- Highest quality of painting was Ajanta.
- Total cave in Ajanta - 29.
- 16 & 17th caves are very important.
- Ajanta cave was built between I AD- 7th AD. But mostly built in Gupta Age.
- Name of Painting in Ajanta — Fresco.
- Colour — Blue.
- Other were painting of Ellora & Bagh.
Society
- Gupta age is considered as Rennaissance of Hindu age that’s why Brahmana were dominating in that age.
- During Gupta age many sub-castes emerged.
- Tribals were incorporated in Hindu society in Gupta age.
- During Gupta age women & Sudra’s position were little bit uplifted.
Marriage
Lovemarriage system had gone down in Gupta age.
- Widow remarriage was prevalent in society.
- Sati system was known in Gupta age.
- Slave system was known in Gupta age.
Pushyabhuti Dynasty
Sources:- (A) Huen-Sang (629-644. A.D.).
- Huen-Sang is considered as prince of pilgrims & Sakya Muni.
- His book was- si-yn-ki.
- He indicated sudra as peasant, who were important person in society.
- According to Hiuen-sang there were 60,000 elephant in Harsha’s army,
- According to Hiuen-sang all the works of king were accounted and for this Harsha established one Archive.
- Indians were vegetarians. They never had taken betal.
(B) Vanbhatta:- Harsheharit, Kadarnbari, Parvati Parinaya, Chandi-satak.
(C) Harsha:-
- Harshvardhan had written three plays. Priyadarshika, Nagananda, Ratnavali.
- He had also written two Buddhist poems. (a) Suprabhat (b) Astamahasree Chaitya.
Harsha’s Banskhera Inscription:- This gives the account about Harsha that his writing was very nice. He was Khutswis.
According to Vanbhatta:- This dynasty was established by Pushyabhati. After that h describes about Prabhakar Vardhan.
Prabhakar Vardhan:- He has two sons- (I) Rajyavardhan (ii) Harshvardhan, and one daughter - Rajyasree.
Title of Prabhakav Vardhan — Huna / Harinkesari.
Rajyavardhana: (696 AD) — Gaur-ruler Shashank killed him by deceive.
Harshavardhan:- (606447 A.D)
Title- Rajputra, Siladitya, Ruler of five country (Punjab, Gaur, Mithila, Orissa, Kankubjya).
- When he came as a ruler his first task war to release his sister from Gaur ruler Shashank of Bengal.
- In 612 A.D. Harsha became ready to take over the charge of Kannouj, which was the kingdom of his sister.
Religion of Harsha
(I) Harsha was a Shaiva.
- Later on he shifted to Budhism of Hinyana. Finally with influence of Hiuen-sang he shifted to Mahayan.
(II) Harsha organised a Sabha in 643 A.D.
(A) Kannauj
Aim:-
- To honour Hiuen-sang.
- In this Sabha there was attack on Marsha and Bluen-sang.
(B) Prayag Sahha
- This was also organised in 643 AD., which was known as Mahanioksha.
- Harsha describes that he organises this type of Sabha every five years and this was the sixth Sabha.
- Harsha was the first-ruler established political relationship with China. He send his anthassdor to China in 641 AD.
Administration of Harsha
- Harsha administration was feudal. Harsha payed his officers in form of land.
- Harsha followed administration of Guptas.
State
Bhukti
Vishaya
Pethan
Gram
- Governor of state was called as Lokpal.
- Village head were called as Ashaptalika.
Vanbhatta- Describes about the officers.
(1) Avanti — Foreign Minister
(2) Mahabaladhikrit Head of Army.
(3) Koutuk— Head of Elephantry.
(4) Videshwar — Head of Cavalery
General army were known as chatta or Bhatta.
Economy
Three Taxes
(1) Bhage—Land tax l/4 to 1/6
(2) Bali —
(3) Hiranaya — This tax were paid by agriculturist and traders in form of cash.
Huen-sang discussed that income generated from Crown land were distributed among-
(a) Forking.
(b) For scholars.
(c) For payment of officers.
(d) For religious work.
- During Harsha's age the head of Nalanda University was Shibhadra.
- Harsha Donated 200 villages for look after of Nalanda University.
- Hiuen-sang described that capacity of Nalanda university was 10,000.
- Bhaskarvarman ruler of kamrup was very good friend of Harsha.
- Southern expedition of Harsha were stopped by Pulkesin II.
- Last expedition of Harsha was Ganjam (Orissa).
- Nepal and Kashmir were out of Harsha kingdom.
- Harsha received the remnant of Budha's teeth from Kashmir and the established that in Kannauj.
Click here to download full Chapter
Click Here for Post Mauryan Period MCQ
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS HISTORY 11 YEARS SOLVED PAPERS PDF
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS HISTORY 10 Years Categorised PAPERS
Study Noted for UPSC MAINS HISTORY Optional
© UPSCPORTAL.COM


