(Premium) Gist of Press Information Bureau: September 2013
Premium - Gist of Press Information Bureau: September 2013
-
POWER GENERATION CAPACITY IN INDIA ()
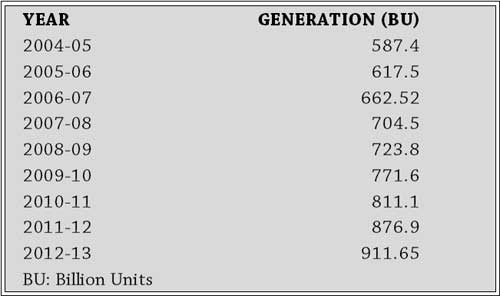
Target for power generation is fixed on an annual basis. As against the power generation target of 930 BU for the year 2012-13, 911.65 BU has been achieved, which is 98% of the target. The overall electricity generation in power utilities in the country as well as import from Bhutan since the beginning of 9th Plan is as under:
The total All India Installed Capacity of electric generating stations as on 31st March, 2013 was 2,23,343.60 MW and the demand was 1,35,453 MW.
The following steps have been taken / are being taken by the Government to achieve the electricity generation target during 2013-14:
- Renovation and Modernization of old power plants.
- Efforts are being made to make coal and gas available for power sector.
- Review of progress of power projects is being done at the highest level by the Minister of State for Power (Independent Charge), Secretary, Ministry of Power and Chairperson, Central Electricity Authority, to identify the constraint areas and facilitate their faster resolution, so that the projects are commissioned on time.
Power sector has grown positively over the 11th Plan period. It registered a growth rate of 3.96% in 2012-13. The peak deficit in the year 2012-13 was 9% against the deficit of 10.6% in the year 2011-12. The decision to add generation capacity of 88,537 MW, import 82 Million Tonnes of coal, reduction in transmission and distribution losses etc. is expected to bridge the gap between peak demand and peak met.
As per Planning Commission, capacity addition of 88,537 MW is planned from conventional sources for the 12thFive Year Plan on an all-India basis. Steps taken to meet the power requirement in the country inter-alia are:
- Rigorous monitoring of capacity addition of the on-going generation projects.
- Review meetings are taken by Ministry of Power regularly with CEA, equipmentmanufacturers, State Utilities/ CPSUs/Project developers, etc. to identify the bottlenecks in capacity addition and resolve the issues.
-
In view of the increasing requirement of capacity addition to meet the demand, the capacity building of main plant equipment has been carried out in the country with the formation of several joint ventures for manufacture of main plant equipments in the country.
- Thrust to make coal and gas available for power sector.
- Thrust is being given to power generation from renewable sources. As per MNRE, grid interactive renewable capacity addition likely during 12th Plan is about 30,000 MW.
Steps taken by the Government to bridge the gap between demand and supply of power in the country which inter-alia include the following:-
- Planned Capacity addition of 88,537 MW during 12th Plan period (2012-2017).
- Rigorous monitoring of capacity addition of the on-going generation projects.
- Development of Ultra Mega Power Projects of 4,000 MW each.
- Augmentation of domestic manufacturing capacity of power equipment through Joint Ventures.
- Coordinated operation and maintenance of hydro, thermal, nuclear and gas bases power stations to optimally utilize the existing generation capacity.
- Thrust to import of coal by the power utilities to meet the shortfall in coal supplies to thermal power stations from indigenous sources.
- Renovation, modernization and life extension of old and inefficient generation units.
- Strengthening of inter-state and interregional transmission capacity for optimum utilization of available power.
With the aim to reduce the Aggregate Technical and Commercial Losses (AT&C) up to 15% in the country and improvement in power distribution sector, Government of India has launched the Restructured-Accelerated Power Development and Reforms Programme (RAPDRP) in July 2008. The focus of R-APDRP is on actual demonstrable performance by utilities in terms of sustained AT&C loss reduction. Projects under the scheme are taken up in two parts in towns having population more than 30,000 (10,000 for special category States) as per census 2001. Part-A of the scheme is for establishing IT enabled system for energy accounting / auditing, customer care, computerized billing & collection etc. and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) for big cities (population:4 lacs and Annual Energy Input: 350 MU) whereas Part-B is for up-gradation, augmentation & strengthening of electrical infrastructure in projects in towns.
So far, under R-APDRP, projects worth Rs.33832.17 Crores (Part-A: Rs.6713.08 Crores covering 1401 towns and 65 SCADA projects in 65 towns; Part-B: Rs.27119.09 Crores in 1134 towns) have been sanctioned.
R-APDRP Scheme is still under implementation and as on 31.03.2013, 306 towns have been integrated with data center under Part- A of the Scheme. Initial assessment indicate reduction of AT&C losses on an average 6 to 7% in these towns. It is expected that on successful completion of the scheme, the AT&C losses is likely to be reduced to the extent of 15% in the project areas. As per PFC’s report, AT&C losses at national level has been reduced from 36.64% in 2002-03 to 26.15% in 2010-11.

