(Download) UPSC IAS Mains Exam Paper - 2017 : Chemistry

(Download) UPSC IAS Mains Exam Paper - 2017 : Chemistry
CHEMISTRY
(Paper I)
- Time Allowed : Three Hours
- Maximum Marrls : 250
QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS
Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
There are EIGHT questions divided in Two Sections and printed both in HINDI and in ENGLISH.
Candidate has to attempt FIVE questions in all.
Question Nos. 1 and 5 are compulsory and out of the remaining, THREE are to be attempted choosing at least ONE question from each Section.
The number of marks carried by a question/part is indicated against it.
Answers must be written in the medium authorized in the Admission Certificate which must be stated clearly on the cover of this Question-cum-Answer (QCA) Booklet in the space provided. No marks will be given for answers written in medium other than the authorized one.
Coordinate diagrams, wherever required, shall be drawn in the space provided for answering the question itself.
Unless otherwise mentioned, symbols and notations carry their usual standard meanings.
Assume suitable data, if considered necessary, and indicate the same clearly.
Word limit in questions, wherever specified, should be adhered to.
Attempts of questions shall be counted in sequential order. Unless struck off, attempt of a question shall be counted even if attempted partly. Any page or portion of the page left blank in the Question-cum-Answer Booklet must be clearly struck off.

SECTION “A”
1. (a) What is resonance energy? What are the conditions which permit structures to have resonance ? Discuss resonance taking the example of CO23- ion.
(b) For an ideal gas, the distribution law of molecular speed is,

where,
dNc = Number molecules within the speed range c and (c + dc).
N = Total number of molecules.
m = Molecular mass.
T = Temperature in Kelvin scale,
Derive the expression of most probable speed of this gaseous system.
(c) Define Joule-Thomson coefficient (mJT). What is its unit in SI system ? Show that

(d) (i) Four-phase sulphur system (in equilibrium) is impossible. Explain.
(ii) In open container, on heating, solid sulphur melts, but solid iodine sublimes. Explain.
1.(e) Write down the Debye-Hückel limiting equation with symbolic significances and their units. Calculate mean ionic activity co-efficient of 0.1 M NaCl (aq) solution at 25°C. The value of Debye-Huickel constant (A) is 0.51 mol-12 L1/2
2.(a) (i) What is the dimension of viscosity co-efficient ? What is its unit in SI system ? The temperature effect on viscosity co-efficient of ideal gas is positive. Explain.
(ii) Define Boyle temperature of non-ideal gas. Obtain its expression for van der Waals' gas.
(b) Find the change in surface area and energy when two identical mercury droplets of diameter 2 mm merged isothermally to one drop. Given that surface tension of mercury is 490 dyne cm at experimental temperature.
(c) Calculate the equilibrium constant for the disproportion reaction :

3.(a) At constant pressure, the temperature of a fixed amount of hot tea in a cup decreases spontaneously to room temperature. What will be the sign of (I) DH and (II) DG of this process ? Give reason(s) in support of your answer.
(ii) DG (J mol-1) for an electrochemical reaction, as a function of temperature, T (K) is given by DG = a + bT+ cT2 where a, b and c are constants and independent of T.
(I) What are the units of a, b and c? and
(II) Find the expressions of DS and DH as a function of T.
(b) What is its unit in SI system ? Is it intensive property ? Answer with justification. What factors influence its value ?
(c) Polonium crystallizes in the cubic system. Using X-ray of wavelength 0.154 nm, first order Bragg reflections occur at sind values 0.225, 0.316 and 0:388 from (100), (110) and (111) planes respectively. Determine the class (SC or BCC or FCC) of the cubic crystal and edge length (a) of unit cell.
4.(a) (i) For a particle in one-dimensional box of length a calculate the probability of its locating between zero and a/2.
(ii) Write the complete wave function for 1s-orbital and deduce its shape.
(b) Explain the paramagnetism of NO with its molecular orbital diagram.
(c) Using valence bond theory justify the presence of two lone electron pairs in XeF4.
SECTION 'B'
5.(a) For zero-order reaction, write down the Arrhenius equation, indicating name of the symbols and their units in SI system. What is high temperature limiting value of rate constant ?
(b) What is ISC (Inter System Crossing) for an excited molecule in singlet state ? Answer using Jablonski diagram.
(c) At constant pressure and temperature, adsorption of a gas on solid surface occurs spontaneously. For this natural process, what will be the signs of (i) DG, (ii) DS and (iii) DH ? Give reason(s) in support of your answer.
(d) Explain the following properties of Ferrocene :
(i) Easy electrophilic substitution of its Cp ring.
(ii) Oxidation is difficult in comparison to that of cobaltocene.
(e) “Magnetic moment of Lanthanide (III) ions is generally different from the value predicted by spin state.” Explain.
6. (a) (i) What are the characteristics, essential for catalysis with specific reference to surface catalysis ?
(ii) Define activation energy, Ea of a chemical reaction. A gas-phase reaction completes 25% in 30 min at 27°C and in 10 min at 37°C. Determine the Ea in SI unit.
(b) Using a particular wavelength of light, a solution of a substance (molar mass 294 g mol-1) transmits 80% of incident light. Determine the concentration of the solution in mol L-1. Given that optical path length of the spectrophotometer tube is 1.0 cm and absorptivity of the substance is 2.0 L g-1 cm-1.
(c) In aqueous solution, at 298 K, the mobility of NH+4 ion is 7.62 x 10-8 m2 s-1 V-1 Calculate its (i) molar conductivity; (ii) velocity if 15.0 V is applied across the electrodes of 25.0 cm apart. Calculate the transport numbers of the ions in CH3COONH4 (aq) solution if the mobility of CH3COO- ion is 4.24 x 10-8 m2 s-1 V-1 under same condition.
7.(a) (i) Write Vaska's catalyst with structure and show its oxidative addition with HCl and oxygen.
(ii) How is K4[Fe(CN)6] is converted into sodium nitroprusside ? Write reaction of S2-ion with sodium nitroprusside.
(b) Define prosthetic group in cytochromes. How do they differ from haemoglobin ? What is their main function ?
(c) What are silicones ? How are they obtained ? Discuss the important properties and applications of organosilicon polymers.
8. (a) (i) What is meant by EAN rule applied to the complexes ? Apply the concept of EAN rule on the following two complexes [Fe(CN)6]4- and [Fe(CN)6]3- and draw your conclusion about the validity of the rule.
(ii) Explain crystal field theory. How does it differ from valence bond theory? How does this theory account for the fact that [CoF6]3- is paramagnetic while [Co(NH3)6]3+ is diamagnetic though both are octahedral.
(b) "High oxidation states are more common in early actinides than lanthanides but the +2 oxidation state for americium and nobelium are more stable relative to those of other actinides. Explain.
(c) Define phosphazenes with formulae for ring and chain types. Write two examples of substitution reactions of cyclophosphazenes.
DOWNLOAD 10 YEARS UPSC MAINS CHEMISTRY PAPERS PDF
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS G.S. (1-4) SOLVED PAPERS PDF
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS G.S. 10 Year PAPERS PDF
DOWNLOAD UPSC IAS EXAMS E-BOOKS PDF
UPSC Mains General Studies Study Kit
CHEMISTRY
(Paper II)
Time Allowed : Three Hours
Maximum Marrls : 250
QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS
Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
There are EIGHT questions divided in Two Sections and printed both in HINDI and in ENGLISH.
Candidate has to attempt FIVE questions in all.
Question Nos. 1 and 5 are compulsory and out of the remaining, THREE are to be attempted choosing at least ONE question from each Section.
The number of marks carried by a question/part is indicated against it.
Answers must be written in the medium authorized in the Admission Certificate which must be stated clearly on the cover of this Question-cum-Answer (QCA) Booklet in the space provided. No marks will be given for answers written in medium other than the authorized one.
Coordinate diagrams, wherever required, shall be drawn in the space provided for answering the question itself.
Unless otherwise mentioned, symbols and notations carry their usual standard meanings.
Assume suitable data, if considered necessary, and indicate the same clearly.
Word limit in questions, wherever specified, should be adhered to.
Attempts of questions shall be counted in sequential order. Unless struck off, attempt of a question shall be counted even if attempted partly. Any page or portion of the page left blank in the Question-cum-Answer Booklet must be clearly struck off.
SECTION A
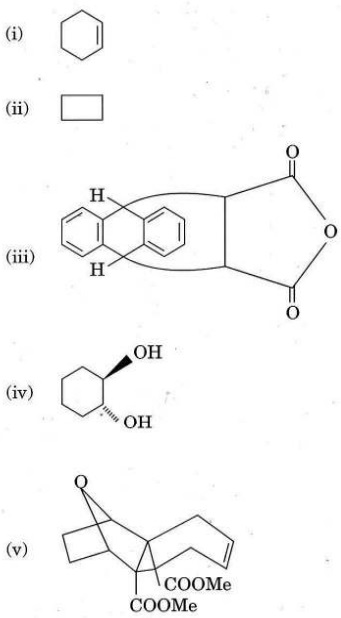
Q1. (a) Classify the following examples into aromatic, anti-aromatic and non-aromatic. Justify your answer.

(b) Write the structure of products A and B and mention the major/minor products in each of these conversions (i) and (ii) with justification.

(c) Write the product of the following reaction and depict the mechanistic pathway for its formation.
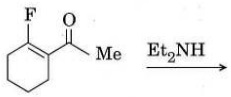
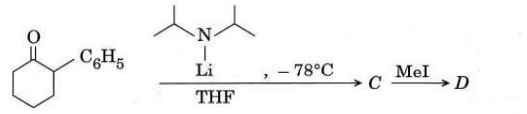
(d) Give the structures of C and D and account for their formation.
(e) Write the structure of the product with proper stereochemical outcome, in each of the following reactions and justify your answers with the help of FMO theory.

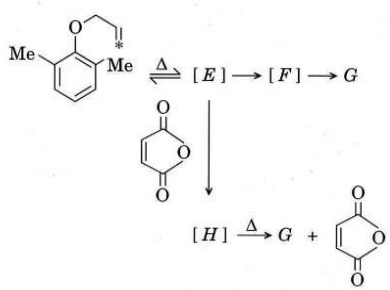
Q2. (a) Give the structures of E to H showing the position of the labelled carbon [*] in each.
(b) Out of 3,5-dimethyl-4-nitrophenol and 2,6-dimethyl-4-nitrophenol, which one is more acidic and why?
(c) Write the structures of I to K. The conversions mentioned below involve a rearrangement at one step. Name it and depict the corresponding mechanism.

(d) Predict the product in each of the following reactions and write the mechanism for each conversion.

Q3. (a) What happens when 2,4-pentadione is treated with one equivalent of MeMgl? How can you convert the mentioned dione to 2,4-hexadione?
(b) Write a method of preparation of a tertiary alcohol containing two identical alkyl groups. Write one method for distinguishing primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
(c) Write the stereo structures of L to N and comment on the specific rotation of N. Specific rotation of the starting alcohol is + x.
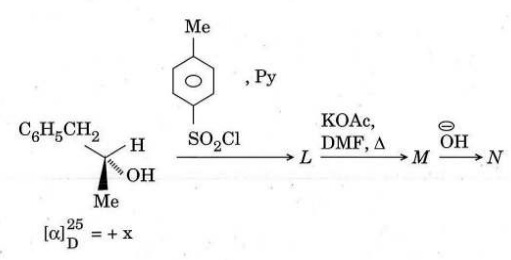
(d) Write the structure of the product(s) for each of the following transformations and write the name of each reaction.

(e) Write the structure of the product of the following reaction and depict the mechanism.
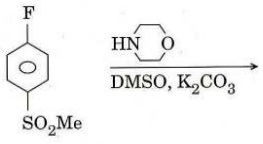
Q4. (a) Predict the final product obtained after the following sequence of reactions and also suggest the corresponding plausible mechanistic pathway.
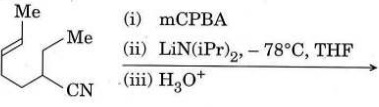
(b) Predict the product(s) with mechanism and justify your answer.
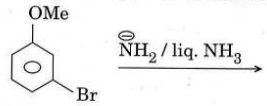
(c) Write the reagent(s) for the following conversions and write the mechanism for reaction (i).
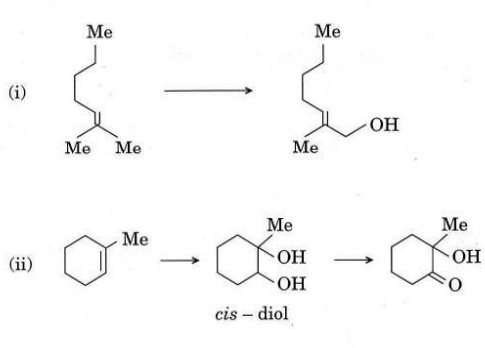
(d) Predict the product(s) and justify your answer discussing on the stereochemical requirement of the reactions.
(e) Write specific reagents necessary for each of the following transformations. Out of 'stereospecific' and 'stereoselective', which one suits for each reaction ?

SECTION B
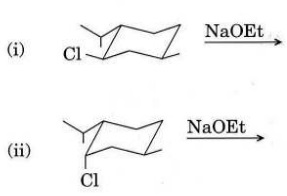
Q5. (a) Explain why concerted 1,3-sigmatropic shift of hydrogen is thermally forbidden and give Woodward-Hoffmann selection rules for sigmatropic rearrangement reactions.
(b) How will you convert the following reactant into product by a two-step process ? Also give the mechanism.

(c)
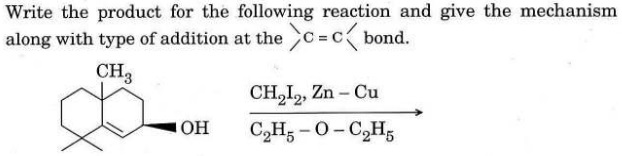
(d) Define a regio specific reaction. How will you convert aniline into p-phenylene diamine ?
(e) How can you distinguish between the following pairs of compounds by using IR spectroscopy ?
(i) Salicylic acid and p-Hydroxy benzoic acid
(ii) Propionaldehyde and Acetone
Q6. (a) Predict the products of the following reactions.

(b) What will be the stereochemical course of thermal cyclization of
(i) Pentadienyl anion, and
(ii) Pentadienyl cation ?
(c) Write the products for the following reactions.

(d) Compounds A and B undergo photodecarbonylation resulting in the formation of I and II (From A) and III and IV (From B). Give their structures.

(e) Give the structures of nucleosides and nucleotides and discuss the primary structures of DNA and RNA.
Q7. (a) (i) Write the intermediates and possible products in the following photochemical reaction.
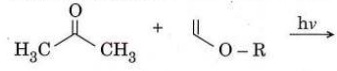
(ii) How many 'H NMR signals do you expect for 1-bromopropane and 2-bromopropane? Give their splitting pattern.
(iii) How will you distinguish the following compounds by IR spectroscopy? Which will absorb more wave number in cm-1, and why?
.jpg)
(b) Identify the major product (Z) formed in the following reactions.

(c) How can you distinguish between cis and trans isomers of stilbenes from UV spectral study? Explain.
(d) Write structures of repeating units of natural rubber, polystyrene and teflon. How will you prepare terylene and PVC ?
Q8. Suggest suitable starting compounds and structures for the synthesis of the following heterocyclic compounds.

.jpg)
(b) Predict the M+ peaks and mass spectral fragmentation for the following compounds.

(c) Identify the product in the following reaction and provide the mechanism for the formation of the product.

(d) An unknown organic compound having molecular formula C9H1002 exhibited the following spectral data:
UV: 270 nm; IR : 1680 cm-1
1H NMR : d7-6 (2H, d, J = 8 Hz), 6-9 (2H, d, J= 8 Hz), 3-9 (3H, ), 2-0 (3H, s).
Deduce the structure of the compound.
(e) How do you prepare the following compounds ?