(Download) UPSC IAS Mains Exam Paper - 2017 : Geography

(Download) UPSC IAS Mains Exam Paper - 2017 : Geography
GEOGRAPHY
Paper - I
- Time Allowed : Three Hours
- Maximum Marks : 250
Question Paper Specific Instructions
Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions :
There are EIGHT questions divided in TWO SECTIONS and printed both in HINDI and in ENGLISH.
Candidate has to attempt FIVE questions in all.
Questions no. 1 and 5 are compulsory and out of the remaining, any THREE are to be attempted choosing at least ONE question from each section.
The number of marks carried by a question / part is indicated against it.
Answers must be written in the medium authorized in the Admission Certificate which must be stated clearly on the cover of this Question-cum-Answer (QCA) Booklet in the space provided. No marks will be given for answers written in a medium other than the authorized one.
Word limit in questions, wherever specified, should be adhered to.
Illustrate your answers with suitable sketches/maps and diagrams, wherever considered necessary.
These shall be drawn in the space provided for answering the question itself.
Attempts of questions shall be counted in sequential order. Unless struck off, attempt of a question shall be counted even if attempted partly.
Any page or portion of the page left blank in the Question-cum-Answer Booklet must be clearly struck off.
SECTION A
Q1. Answer the following questions in about 150 words each :
(a) Write a note on pseudovolcanic features.
(b) Distinguish between low energy coasts and coral coasts.
(c) Discuss the impacts of ocean currents on air mass behaviour.
(d) Describe the characteristics of biological deserts.
(e) Explain the concept of micro carbon sink and its relevance.
Q2. (a) Discuss the forces which govern the air movement on the Earth's surface.
(b) “The knowledge of slope analysis has limited field application in the slope management.” Explain.
(c) Describe the configuration of the Pacific Ocean floor.
Q3. (a) "Climate change is a reality.” Explain with suitable examples.
(b) Distinguish between the characteristics of Chernozem and Sierozem Soils.
(c) Give a classification of plants based on the amount of water requirement.
Q4. (a) Discuss the concept of Periglacial cycle as propounded by Peltier.
(b) "Climate, slope gradient and rock structure influence the avulsion of channels.” Explain.
(c) Discuss the Perception, Attitude, Value and Emotion (PAVE) Theory of environmental management.
SECTION B
Q5. Answer the following questions in about 150 words each :
(a) Explain the concept of Time-Geography.
(b) “Whittlesey's agricultural regions are relevant even today.” Discuss.
(c) Write an explanatory note on geographical systems.
(d) “The traditional cultural identities are at loss with the growth of global connectivity.” Explain.
(e) Give an account on sustainable development and its components.
Q6. (a) Discuss the contemporary paradigms of Geography.
(b) "The intensity of energy crisis varies regionally.” Explain.
(c) Examine the causes and consequences of forced migration of population in the present context.
Q7. (a) Discuss the applicability of Christaller's Central Place Theory.
(b) “There are considerable demographic similarities between West European nations and Japan.” Explain.
(c) Define the quality of life and explain its parameters with adequate examples.
Q8. (a) "The Heartland Theory is gaining importance once again". Comment.
(b) Examine the role of small towns in the regional development process.
(c) Explain the concept of social capital in relation to India.
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS GEOGRAPHY OPTIONAL PAPERS PDF
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS GS 10 Year PAPERS PDF
DOWNLOAD UPSC MAINS GS SOLVED PAPERS PDF
DOWNLOAD E-BOOKS for UPSC Exams
UPSC Mains General Studies Study Kit
UPSC Exam Complete Study Materials (Pre, Mains, Interview COMBO Study Kit)
GEOGRAPHY
Paper - II
Time Allowed : Three Hours
Maximum Marks : 250
Question Paper Specific Instructions
Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions :
There are EIGHT questions divided in TWO SECTIONS and printed both in HINDI and in ENGLISH.
Candidate has to attempt FIVE questions in all.
Questions no. 1 and 5 are compulsory and out of the remaining, any THREE are to be attempted choosing at least ONE question from each section.
The number of marks carried by a question / part is indicated against it.
Answers must be written in the medium authorized in the Admission Certificate which must be stated clearly on the cover of this Question-cum-Answer (QCA) Booklet in the space provided. No marks will be given for answers written in a medium other than the authorized one.
Word limit in questions, wherever specified, should be adhered to.
Illustrate your answers with suitable sketches/maps and diagrams, wherever considered necessary.
These shall be drawn in the space provided for answering the question itself.
Attempts of questions shall be counted in sequential order. Unless struck off, attempt of a question shall be counted even if attempted partly.
Any page or portion of the page left blank in the Question-cum-Answer Booklet must be clearly struck off.
SECTION-A
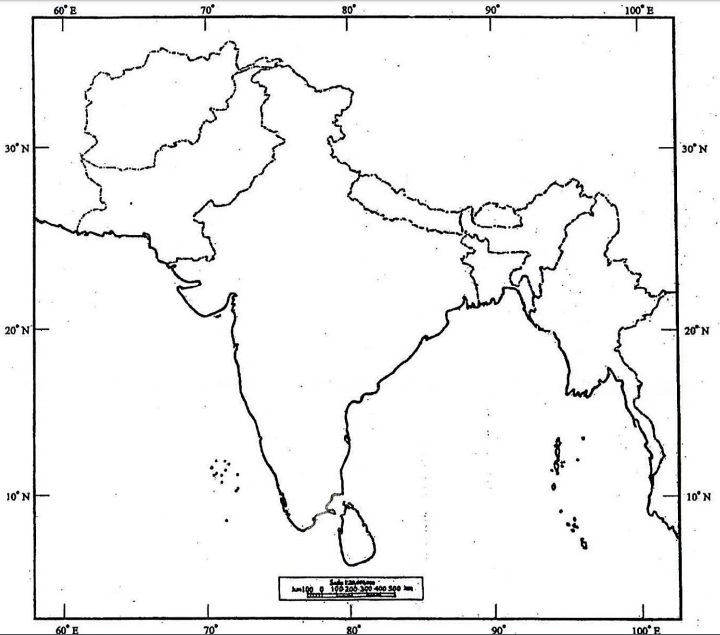
Q1. (a) On the outline map of India provided to you, mark the location of all of the following. Write in your QCA Booklet the significance of these locations, whether physical /commercial/economic/ecological/environmental/cultural, in not more than 30 words for each entry :
(i) Thumba
(ii) Nayachar Island
(iii) Doddabetta
(iv) Devasthal
(v) Pangong Lake
(vi) Hampi
(vii) Havelock Island
(viii) Luni River
(ix) Daringbadi
(x) Dudhsagar Waterfalls
INDIA
WITH AFGHANISTAN, BANGLADESH, BHUTAN, NEPAL, MYANMAR (BURMA), PAKISTAN AND SRI LANKA
(b) Give a reasoned account of unusual pattern of distribution of monsoonal rainfall in India in 2017.
(c) Explain the inter-State issues involved in implementation of the Satluj-Yamuna Link Canal Project.
(d) Small towns in India have problems and prospects of their own. Elaborate.
Q2. (a) Discuss the freshwater crisis in India and prepare a blueprint for its sustainable management.
(b) Identify the Naxal-affected areas in India and discuss their socio-economic problems.
(c) Critically examine the feasibility of development of a comprehensive network of airways in India.
Q3. (a) "An effective three-tier Panchayat Raj System will strengthen the bottom-up approach to multilevel planning in India.” Explain.
(b) “Linguistic diversity is an asset as well as a challenge in India." Explain the statement focussing on the distribution of languages and the major steps taken to address the related issues.
(c) How may tourism in hilly areas of India be developed as an important source of economy?
Q4. (a) Mention various methods of functional classification of towns in India and explain the method applied by Asok Mitra.
(b) Farmers' suicide is one of the major agrarian problems in India. Bring out its causes and suggest the remedial measures with special reference to Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh and Punjab.
(c) Land reform is a key to modern agriculture in India. Describe various measures taken in this direction after Independence.
SECTION-B
Q5. Answer the following questions in about 150 words each :
(a) Explain the role of 'Hill Transport Subsidy Scheme' in reducing regional imbalances in areas identified by the Government of India.
(b) Bring out the geopolitical implications of Doklam dispute in the context of Indo-China relations.
(c) Bring out the significance of Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS).
(d) Mini steel plants can act as an instrument of decentralization of iron and steel industry in India. Explain.
(e) Goods and Services Tax (GST) has differential impact on developed and backward States of the country. How and why?
Q6. (a) Interlinking of rivers may serve as a major source of assured irrigation and all-weather inland navigation in India. Comment on its feasibility taking into account physical, economic and ecological implication.
(b) Religious minorities are largely concentrated in border States of India. Discuss its causes and consequences.
(c) What do you understand by soil pollution? Delineate the areas vulnerable to it in India and suggest remedial measures.
Q7. (a) Integrated development of road and rail networks in a complementary framework is a prerequisite for regional development. Explain with reference to North-Eastern Region of India.
(b) Describe the salient features of Sagar Mala Project and highlight its role in port-led development of coastal regions in India.
(c) Justify the inclusion of Meghalaya in Peninsular India and discuss its vegetation and soil types.
Q8. (a) Name the major industrial regions of India indicating the bases of their identification. Highlight their basic problems.
(b) Drainage pattern in Peninsular India is a result of its geological structure and topography. Elaborate.
(c) Why has solar energy in India not been developed to desired level in spite of its high potential?


