
Companies Amendment Bill - In Light of Ease of Doing Business : Important Topics for UPSC Exams
In the Indian case, a large body of research clearly shows that productivity growth, the ultimate driver of economic growth, has been held back by burdensome regulation, which has choked off the growth of firms in India.This calls for a sustained effort in order to realise the aim of making India a manufacturing hub. India has taken a number of reforms in the recent past like GST, IBC, single window clearance, Shram Suvidha Portal etc. Recent amendment to Companies act is also a significant step in further easing the doing of business in India.
EASE OF DOING BUSINESS INDEX:
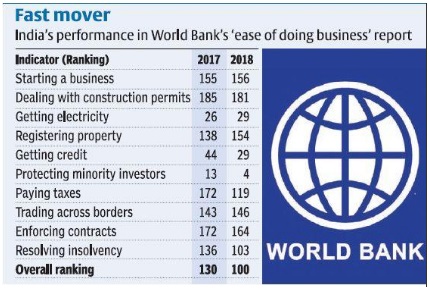
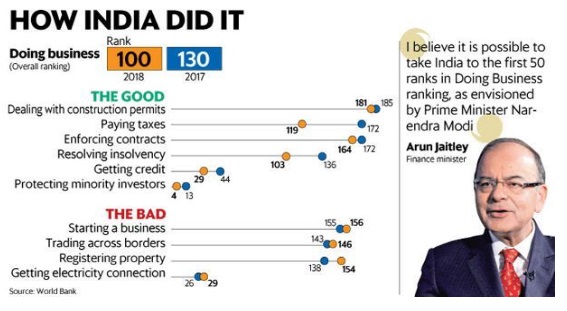
World bank has placed India at 100 out of 190 countries.
• India fared well in following categories :
1.Paying taxes
2.Resolving insolvency
3.Protecting minority investors
4.Access to credit
• India could not improve its ranking because of following areas
1. Starting a business
2. Trading across border
3. Dealing with construction permits
4. Getting electricity connection
Factors for improvement in the ranking :
1. Paying taxes
2. Dealing with construction permits
3. Getting credit (Ex: IBC )
4. Trading across border
5. Starting a business
The Companies (Amendments) Act 2017, which became law after the approval of the Rajya Sabha during Parliament's winter session in December, aims to strengthen corporate governance standards, improve ease of doing business in the country and puts restrictions on the managerial remuneration of defaulting companies. It also has provisions for initiating strict action against defaulting companies
Major Highlights:
-
Harmonisation with SEBI and RBI : Perhaps for the first time, several provisions have been amended to align the Act with various rules and regulations of the SEBI and the RBI. Sections 194 and 195 of the Act, which dealt with insider trading and forward dealing, have now been omitted since the SEBI regulations are wide enough to cover all instances of such frauds. Further disclosures to be made in the prospectus have also been aligned with the SEBI’s power to regulate IPOs.
-
Rationalisation of penalties: One of the most applauded amendments made in the Amendment Act – the quantum of penalty will now be levied taking into consideration the size of company, nature of business, injury to public interest, nature and gravity of default, repetition of default, etc. Penal provisions for small companies and one person companies are reduced.
-
Private placement process made easier: Private placement process made easier: The private placement process is simplified by doing away with separate offer letter details to be kept by company and reducing number of filings to Registrar.
In order to ensure that investor gets adequate information about the company, the disclosures are made under Explanatory Statement referred to in Rule 13(2)(d) of Companies Change in definition of private placement is proposed to cover all securities offer and invitations other than rights. The Companies would be allowed to make offer of multiple security instruments simultaneously.
4.Loans to directors: This was done to address the difficulties being faced in genuine transactions due to the complete embargo on providing loans to subsidiaries with common director.
Now the companies are permitted to give loans to entities in which directors are interested after passing special resolution and adhering to disclosure requirements. This would give big relief to the companies.
-
Disqualification for Independent Director further clarified: Section 149 of the Act deals with the qualifications and disqualifications of independent directors. Sub section (6) provides for various disqualifications for becoming an independent director , one of which is having a pecuniary relationship with the company , its holding , subsidiary or related party
The amendment clarifies that this pecuniary relationship excludes the remuneration to such director or having transaction not exceeding 10% of his total income or such amount as may be prescribed.
-
Company Annual Return: All companies are required to file an annual return with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs each year. The Companies Amendment Act, 2017 has proposed to provide an abridged form of annual return for One Person Company and small company. The abridged form of annual return will make annual compliance for a company simpler for small businesses.
-
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): The amendment has liberalized the CSR regime.
Safeguards :
-
As per an amendment, companies, which have defaulted on their dues to banks and financial institutions, will now require the prior approval of these creditors, besides approval in a general meeting in case the payment of managerial remuneration exceeds 11 per cent of the net profits, as was anyway required by the original Act.
-
Auditors Report: It mandates requirement that Statutory Auditor of company to report in its Auditors Report on compliance of provisions of managerial
-
Besides, "the Amendment Act now allows companies to issue shares at a discount to its creditors when its debt is converted into shares in pursuance of any statutory resolution plan such as resolution plan under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code or debt restructuring scheme,
-
The changes to the Act also prohibit a registered valuer from undertaking valuation of any asset in which he has direct or indirect interest for a period of three years before or after his appointment, the statement added.
Way Forward
India needs to further work on reducing the bureaucratic hassles to change India’s perception as having Red tape to India as having a red carpet for investors
-
Market Reforms : Availability of lands and labour reforms need to be worked at .
-
Need of proper trade policy for enhancement of business opportunities.
-
The banks are stressed and the corporate sector is overleveraged. Though the bank recapitalization was first good step, it has to be followed up with changes in how banks do their businesses.
-
The issues with the index itself needs to be looked at the level of world bank.
MCQ’s
1. Which of the following organization releases Ease of doing index ?
-
World bank
-
IMF
-
WEF
-
None of the above
Correct Answer: (a)
2. Which of the following statements regarding Ease of doing business index is correct?
-
The index takes into account the progress of all the states in India.
-
The index takes into account only the legal statues and not its actual implementation on ground.
Choose the correct answers
-
1 only
-
2 only
-
Both 1 and 2
-
None of the above
Correct Answer: b (2 only)
Explanation: The EOD index takes into account the progress in only 2 cities in india and not the entire india.
It also sees only de jure progress that is changes in the legal statutes and not the actual situation on ground.
Mains Questions
-
India has recently leapfrogged in the ranking of Ease of doing business index. What are the issues to be addressed in order to fulfill the government’s target of taking India’s ranking to top 50. Discuss enumerating the recent reforms in this regard
-
Corporate governance has been in news for quite some time. What do you understand by it. What are the legal structures in place for enforcement of corporate governance