
UPSC Prelims 2017 Exam GS Paper Analysis & IAS Exam Strategy
With UPSC prelims 2017 paper, UPSC has again proved the unpredictability of the civil service prelims exam. While last two years saw the share of direct current affairs based question increase, 2017 exam year upsc question were bit tricky and not directly based on the facts as in case of 2016 paper. Many of the question required serious brainstorming and therefore for many two hours might have proved to be insufficient. This article tries to go into the depth of last year paper and see how a candidate can calibrate her/his approach for such surprises in the exam hall.
Following is the topic wise breakup of the UPSC pre paper for last 3 years:
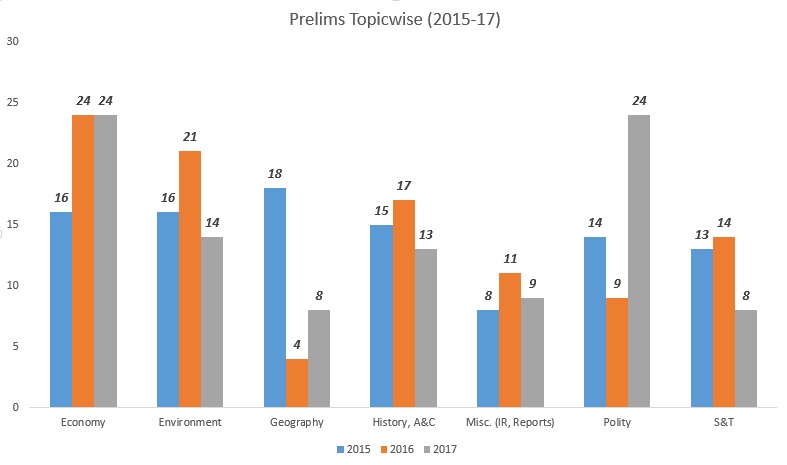
No singular pattern about the weightage of the subject can be discerned from the above chart.
Point to be noted my lord!! The attitude of leaving one or two low weightage subjects based on the previous year papers is not at all fine with UPSC. It loves to surprise the candidate and therefore when you might have thought that S&T does not matter that much anymore, UPSC 2018 paper may house more than 15 questions as in case of polity this year.
You have to be battle ready for any kind of Thali that UPSC will serve to you on the D-Day!!
Should I focus on the fundamental part or the current affairs?
This is the most common doubt for every aspirant. There is no definite answer to that nor there can be unless UPSC comes out with a white paper on the subject (Which we know is never going the happen).
While UPSC 2016 paper was heavily skewed in the favor of Current Affairs, UPSC 2017 paper tilted towards the fundamental part as can be gauged from the increased share of polity.
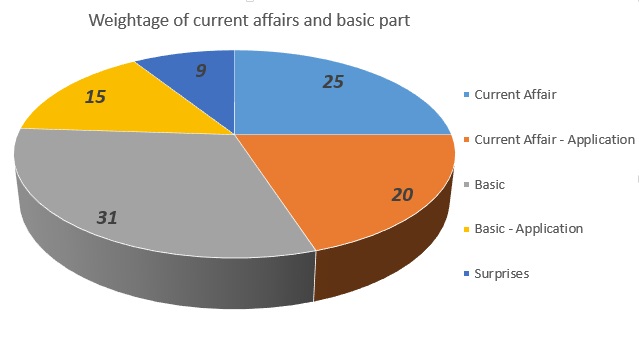
UPSC Question Paper Analysis
|
For election to the Lok Sabha, a nomination paper can be filed by
(a) anyone residing in India.
(b) a resident of the constituency from which the election is to be contested.
(c) any citizen of India whose name appears in the electoral roll of a constituency.
(d) any citizen of India
|
Basic
|
Direct question. Can be attempted easily if
you have gone through the book of M. Laxmikant
or IAS EXAM PORTAL GS STUDY KIT
|
|
If you travel by road from Kohima to Kottayam, what is the minimum number of States within India through which you can travel, including the origin and the destination?
(a) 6
(b) 7
(c) 8
(d) 9
|
Basic - Application
|
Requires application of only basic knowledge of Indian maps. Rote learning will not suffice in this question
|
|
Recognition of Prior Learning Scheme’ is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to
(a) Certifying the skills acquire by construction workers through traditional channels.
(b) Enrolling the persons in Universities for distance learning programmes.
(c) Reserving some skilled jobs to rural and urban poor in some public sector undertakings.
(d) Certifying the skills acquired by trainees under the National Skill Development Programme.
|
Current Affairs
|
Often covered in daily news. A direct question from the newspaper.
|
|
In India, if a species of tortoise is declared protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, what does it imply?
(a) It enjoys the same level of protection as the tiger.
(b) It no longer exists in the wild, a few individuals are under captive protection; and not it is impossible to prevent its extinction.
(c) It is endemic to a particular region of India.
(d) Both (b) and (c) stated above are correct in this context.
|
Current Affairs - Application
|
Must know what does the Schedule I of the act means
and other animals that are covered under the schedule.
|
|
With reference to the religious history of India, consider the following statements:
1. Sautrantika and Sammitiya were the sects of Jainism.
2. Sarvastivadin held that the constituents of phenomena were not wholly momentary, but existed forever in a latent form.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
|
Surprise
|
Not covered in any conventional sources and requires in
depth knowledge of the subject.
Not possible to cover such questions during preparation
and therefore candidate has to be selective about attempting such questions
|
What to do then?
It is clear that a candidate has to make a habit of balancing the studies between the two. A candidate must:
-
Read the NCERTs thoroughly and revise them at least one. If possible underline the important concept or make note out of them. you can consider NCERT Notes for UPSC exams to cover everything easily.
-
Read only one reference books for every subject and revise it again. Selected candidate have always emphasized on this aspect of the preparation and is relevant for both upsc mains and prelims equally. It is a common mistake to burden oneself with too many thick books and ending up with zero retention of what one had read in those books.
-
Pick up one newspaper like The Hindu or in case it is not available them Indian express and make a habit of reading it thoroughly every day and make notes out of it. These notes come in handy in the last month before prelims where focus has to be on revision.
-
Go through IAS EXAM PORTAL daily current affairs and daily quiz based on current affairs. Go through them and note the concepts that you might have not covered in your newspaper.
-
If possible go through the latest economic survey and budget speech which will cover all the important relevant concepts of economy as it has been a direct source of many questions in the past like these.

-
If for some reason it is not possible to go through the eco survey cover to cover then do go through at least 2 summaries of the budget and eco survey as they cover important schemes as well.
-
Be selective in reading of India Year book. If you have a group of 3-4 friends them you can divide the important chapters amongst yourself and make note to share with each other
-
Don’t fall into the trap of subscribing to plethora of magazines and trying to go through them