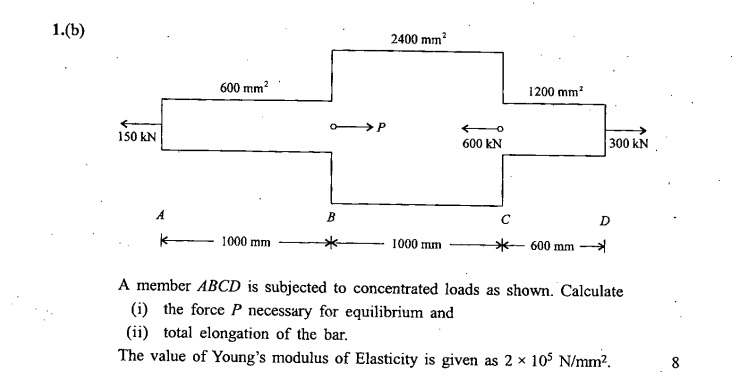
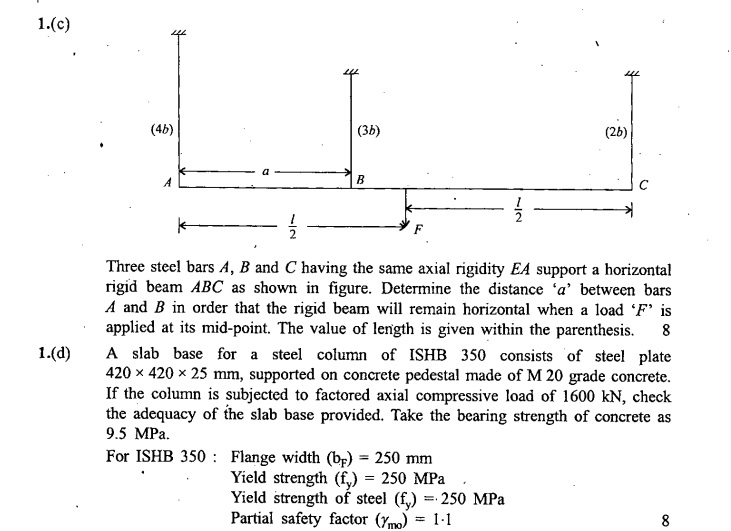
Model Questions for UPSC PRE CSAT Set-9
(English Comprehension)
Passage 1
There are a instances of diseases that have laid waste huge tracts of forests throughout India. Caused mainly by pathogens and pests, these diseases are deadly and are capable of wiping out entire forests and plantations, causing immense economic as well as ecological loss.
Meanwhile, forest pathologists and entomologists are grappling with new maladies that are surfacing almost every year. But with meagre resources and just a few experts working on the issue, things are heading virtually towards a cul-de-sac.
Moreover, no assessment has been made so far to quantify the devastation. While large chunks of forests fall prey to maladies, it is also an opportunity for some politicians and timber merchants to cash in on it. Research and documentation on forest disease, particularly on forest pathology, began in India way back in 1929, by pioneering pathologists KD Bagchi and BK Bagchi. Although it has been eight decades since then, not much headway has been made in this direction. The forestry sector today is ailing due to its misplaced priorities, resource crunch, and mismanagement. “Forest management lacks scientific approach,’ says Surendra Kumar, director of the Himalayan Forest Research Institute (HFRI), Shimla.
The scientific community involved with forest diseases is today a dispirited lot. With only a few stalwarts left in this field, forest disease is a neglected area of research. Moreover, bureaucracy is increasingly taking over the scientific institutions and scientists in most of these institutes are a marginalised group.
To top it all, there are no institutions dedicated to forest diseases. Although the ministry of environment and forests is the facilitator for such research, it is not paying enough attention to promote scientific research on forest diseases. In fact, the government’s lackadaisical approach came to the fore with the Sal borer epidemic in Madhya Pradesh in 1998. While forest bureaucracy slept, the beetles merrily continued to wipe out entire tracts of precious Sal forests. Eventually, with no solution in sight, thousands of valuable trees were hacked. There were also allegations that the Sal tragedy was a chance for the timber mafia in the state to cash in on timber through the legal loophole, with the nexus of politicians.
Today, things haven’t changed one bit. India’s forest department and research institutes have yet to formulate contingency plans to face any assault of similar dimensions.
Forest diseases are elusive. Although experts claim that they know quite a lot about forest diseases, there are still aspects of the maladies that are not completely understood. Says RS Bhandari, entomologist in the Forest Research Institute (FRI), Dehradun, “We know about all the important pests and insects, their life cycles and their development. But there are a few diseases which remain an enigma.” According to Jamaluddin, head of the pathology department in the Tropical Forest Research Institute (TERI), Jabalpur, “Due to micro climatic changes, we are discovering new aspects of the same disease every year. Diseases have also increased manifold.” Another FRI scientist points out that although forest diseases are increasing, there is no study to estimate the economic and ecological damage caused by these pests and pathogens.
Varying with different geophysical regions and climatic conditions, pathogens and pests are essentially responsible for the tree maladies and then mortality. When the pristine, natural and mixed forests existed, forest diseases acted as a natural control measure to check the proliferation of a particular species that could threaten the balance of the ecosystem. Perhaps, this is why forest diseases paled into insignificance in the past. But today, with shrinking forests and increasing monoculture plantations, any outbreak of disease takes on a virulent form.
To top this, changed climatic and forest patterns and environmental pollution have given rise to newer forms of forest diseases. While trees are forced to take an additional load of human-induced environmental changes, the introduction of mono culture has substantially increased the problems. Whatever little we know about forest diseases today comes primarily through mycology, the study of forest pathogens. Mycology explains that the prime pathological reasons for forest disease are fungi, bacteria and viruses. “Among these, fungi playa major role, while the other two are relatively less significant. There are 150 to 200 major pathological infections in central India. Out of these, only five per cent are bacterial. The rest are fungal,” says Jamaluddin.
Most of these pathogens stay close to a tree waiting for a chance to infiltrate. Their entry points are small openings or wounds in the tree. However, invasion is not always easy. Like human beings, trees also have antibodies that fight anything alien. In case of invasion from the trunk of a tree, the sapwood acts as a shield and secretes enzymes to fight pathogens. But when attacked and conquered, there are tell-tale signs in the form of knotty growths of fruit bodies that are extensions of the fungi in the tree.