
(Success Story) UPSC 2022 TOPPER, AIR-23 Sadaf Choudhary Shares Success Story for UPSC Exams
Sadaf Choudhary of Amroha, Uttar Pradesh has secured an all-India rank of 23 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination of 2020. She did her schooling at Amroha. Later she cleared JEE Mains and took admission in Chemical Engineering, in NIT Jalandhar. After completing her degree, she went on to work in a US-based bank in Delhi. In 2018, she finally quit her job and moved back home to prepare for UPSC Civil Services. Her optional was Political Science and International Relations.
Sadaf’s Preparation Strategy
Sadaf used self-study as her chosen method of preparation. She now hopes to guide more aspirants to go through it.
-
The Syllabus Is Key
The UPSC syllabus is the first step to understanding the demand of the exam. Sadaf recommends downloading a detailed analysis and module-wise divided form of the syllabus hosted by Insight IAS online. She says although each stage of the exam has overlapping portions in the syllabus, however; they also have as many exclusive sections. Understanding the need of each phase is paramount to final success. Sadaf recommends printing out the detailed syllabus and using it as an everyday guideline when studying.
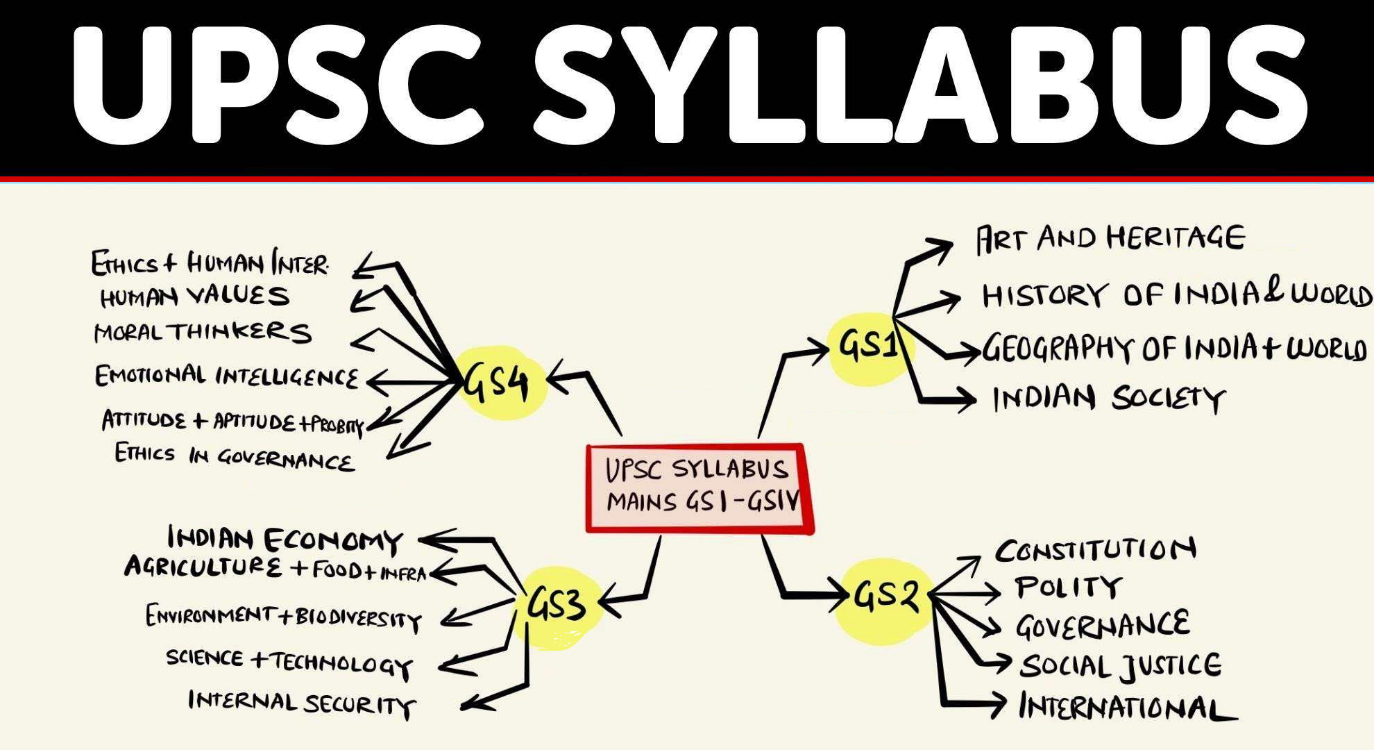
-
Choose Your Resources Wisely
Another recommendation Sadaf has is to only choose resources that cover almost all parts of a given section of the syllabus. Scouring the internet for topics is a monumental waste of time, time that a UPSC aspirant simply does not have. Instead, stick to a single source that easily explains the material and covers all bases. Sadaf had spent a considerable amount of time going through available sources before shortlisting it down to around 15 source materials which she used for her entire journey. Not every popular resource will suit everyone. Choose according to your comfort.

-
Choose The Right Strategy
Before you go into battle, devise a plan. Without a plan, your chances of success go down drastically, while your proximity to failure increases exponentially. Knowing this, Sadaf ensure she had an ironclad strategy before jumping into preparation. She studied blogs and watched UPSC topper interviews. However, no strategy is one-size-fits-all. So Sadaf uses plans by other toppers to make her own. She recommends every aspirant should do the same.

She built a one-year plan, divided into weekly and monthly goals. She ensured that she maintained a disciplined lifestyle despite all the distractions of staying at home. She never missed a goal throughout that year and this discipline helped her clinch this win.
Message to Aspirants
Remember, no one can stop you from achieving whatever you put your mind to. However, no one can make you work hard and be disciplined. This is something you have to practice and earn from within. And without tenacity and discipline, no one can achieve a target as huge as UPSC Civil Services. Sadaf Choudhary wishes you all the very best.
wishes you all the best.
© IASEXAMPORTAL
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD UPSC TOPPERS NOTES





















