UPSC IAS Mains History Optional Solved Exam Paper - 2003
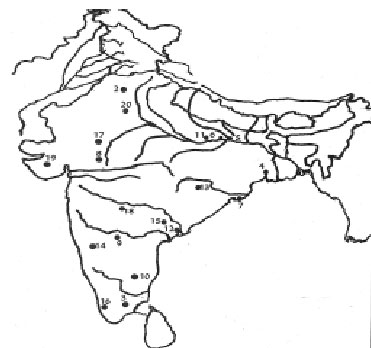
Q1. Mark any fifteen of the following places on the map supplied to you and
write short descriptive notes on places plotted by you on the map:
1. Kot Diji
2. Banamali
3. Tiruchirapalli
4. Tamralipti
5. Vaisali
6. Kundagrama
7. Puri
8. Ujjain
9. Badami
10. Guggara
11. Sarnath
12. Amravati
13. Jauguda
14. Kolhapur
15. Nagarjunkonda
16. Calicut
17. Haldighati
18. Golkonda
19. Somnath
20. Mathura
Answer.
1. Kot Diji: The place of Indus Valley civilization, Kot Digi
is situated at twenty four km to the south of Khairpur in the.Sindh province of
Pakistan and 40.24 km to the east of Mohanjodaro. Archaeological evidences show
that probably the preIndus village of Kot Digi was destroyed in fire and later
the people from the Indus civilization inhabited this place.
2. Banamali: It is situated in the dry bed of the lost
Sarasvati in district Hissar, Haryana. The excavations have revealed the remains
of the pre, mature, and post Harappan cultures. In the earliest phase, the
settlement was fortified with the mudbricks of the ratio 3:2:1 and later, of
4:2:1. Town planning was based on that of the Harappan form a citadel on the
higher level and a lower town segregated from the former by a massive wall. The
most important antiquity found over here is a complete clay model of a plough.
Other antiquities include terra-cota perforated jar, goblet, gold beads,
bronze/copper arrows, speadheads; beads of Lapis Lazuli, agate, carnelian: seals
and sealings etc.
3. Tiruchirapalli: At present, Tirucharapali is a district in
Tamil Nadu. Situated on the bank of river Kaveri. It was under the rule of the
Cholas, the Pandyas and also the rulers of Vijaya Nagar. Later, it was under the
governance of Madras Presidency. In the modem times, it was an important place
during the BritishFrench battle (the Karnataka battle).
4. Tamralipti: It is identified with modem Tamluk near the
mouth of the Ganges in the Midnapur district of West Bengal. It was the most
important seaport and the emporium of trade in eastern India. It was connected
with Taxila by land and river on one hand and with south-east Asia by sea on the
other. It is mentioned in Jatakas and other texts as a port where from the
merchants of northern India sailed to Suvarnadvipa, i.e. Java and Sumatra.
5. Vaishali: Vaishali has been identified with the village
Basarh which is situated 20 miles away from Mujaffarpur district headquarters in
Bihar. In 6th century BC it was the capital of the Lichchavi republic and also
the headquarters of the powerful Vajji confederacy. It was annexed by Ajatshatru
to the state of Magadh. Later a Lichchavi princess Kumaradevi married Chandra
Gupta I and this event was glorified in the Gupta coins
6. Kundagram: Kundagram is situated in the Vaishali district
of Bihar. Mahavir was born here. The remains of the ancient Vaishali are found
here. The republic of Jataka dynasty was established during the 6th century BC.
Kundagram is a very important place of pilgrimage for the Jams.
7. Puri: It is situated in the state of Orissa. The temple of
Vishnu-Jagannatha and the “Black Pagoda” of Konarak (built in the 15th century)
are situated here, making the place an important pilgrimage. The “Black Pagoda”
is a temple of Surya, the sun-god. It was formerly one of the largest and most
splendid temples of India. Though the exceptionally frank eroticism of many of
the Konarak sculptures has given the ‘Black Pagoda’ a rather infamous
reputation. Possibly it was a centre of a tantnc cult though erotic sculpture
doesn’t suggest the solemn ritual of the sakras, but something much less
inhibited.
8. Ujjain: Ujjain lies on the eastern bank of the river
Shipra in Madhya Pradesh. It was the capital of Avanti, one of the Sixteen
Mahajanpadas in the sixth century BC. During the Mauryan period, it was the seat
of a governor (Kumara) which was occupied by Ashok before he was sent to Taxila.
Ozene’or Ujjain was under the rule of Saka king Chastana at the time of Ptolemy
(2nd Century AD). Ujjain was situated on the trade route from the north and
north-west to the western coast and was an important emporium of trade.
According to the Periplus, the commodities from different parts of the country
were first brought to ‘Ozene and then sent to Bargaya for export to foreign
countries’. It was also an important religious centre and was traditionally
associated with Mahakala Shiva as one of the seven holy cities of India.
9. Badami: Badami, earlier called Vatapi, is situated in the
Bijapur district of Karnataka. It was the capital of the early Chalukyas under
whom it developed as an important centre of rock cut architecture. There are
four caves here three of Brahminical faith, dedicated to Shiva and Vishnu and
one of Jaina faith. They were dug in the 6th century A.D, as an inscription of
King Mangiest dated 578 in cave III indicates. The Brahminical caves here are
the earliest rockcut caves in South India, and show an advance over the earlier
Brahminical caves at Udaygiri (Bhilsa, MP).
10. Guggara: Guggara is located at Punjab of Pakistan, and it
is famous for a dam.
11. Sarnath: Sarnath is situated 5 km north of the Varanasi
city in U.P. It is one of the four holiest cities of the Buddhists as Buddha
preached his first sermon here, called in the Buddhist texts as the
“dharma-chakra parivartana’. Saranath is quite rich in Buddhist antiquities.
Ashoka had built a Dharmarajika stupa here and erected a
pillar surmounted by a magnificent capital of four lions and an abacus having
wheels with twenty four spokes representing ‘dharma-chakras’. An edict is also
inscribed on it warning the monks and nuns not to create dissensions in the
Buddhist vihars. It indicates the present of a large number of Buddhists at
Sarnath. A monastery probably dating from the Gupta times is also here.
12. Amravati: It is situated in Guntur district on the
southern bank of the river Krishna, about sixty miles above its mouth. Lying on
the outskirts of the ancient town of Dharnikota, it is famous for the Buddhist
strips and its marble like limestone sculptures which represent the earliest
Buddhist monuments in the Krishna Valley and range from 200 BC to AD 300.
13. Jaugada: Located in Ganjam district of Orissa, Jauguda is
known for the discovery of Ashokan major rock edicts which include two separate
edicts called the Kalinga edicts. The latter edicts are addressed to the
officers and ministers of a town Sampa, identified with Jaugada itself, and
instruct them to be judicious and fair in their dealings with the people so that
Ashoka’s policy of ‘Dhamma’ could achieve the desired results.
14. Kolhapur: Kolhapur is situated near Tungbhadra, tributary
of Krishna river. In the middle ages it was the main centre of the Marathas. In
1707, Tarabai, the wife of the youngest son of Shivaji, led a battle against
Shanu here. Later, Shanu conceded independence of Kolhapur state. A box with an
inscription from the times of Ashoka has been discovered in a large stupa at
Kolhapur. It was also an important place under the rule of Satvahans.
15. Nagarjunakonda: It lies on the right bank of the river
Krishna about 100 km west of Amravati. It was the capital of the Ikshvaku kings
in the thirdfourth century AD and was known as Vijaypuri. It was a centre of
the Purvashaila and Aparshaila schools of Mahasamghika sect of Buddhism and
famous for the great Buddhist stupa called Mahachaitya, and about thirty other
Buddhist monuments. It is one of the most intensively excavated site and has
revealed the evidence of neolithic and megalithic phases of culture. During
Satavahana and lkshavaku periods it became an important settlement. It was
inhabited by a number of merchants and artisans who were organized in guilds.
Terracota objects, beads of semi-precious stones, ivory bangles etc. have been
recovered here. The copper coins of the Satvahanas and the lead coins of the
Ikshavakus have also been found. Roman coins indicate the trade connections with
the Romans.
16. Calicut: It is situated on the coast of Malabar in Kerala.
On 17th May, 1948, Vasco de Gama discovered a new sea route to India and reached
near this famous port of Calicut. This really had ‘farreaching repercussions
from the civilized world. Through this Portuguese were the first among the
European nations to embark on the adventures in the East. At that time, Calicut
was ruled over by the Hindu ruler bearing the hereditary title of `Zamorin’.
17. Haldighati: Haldighati is situated near Aravali hills in
Rajasthan. A fierce battle was fought at Haldighati near Kumbhalgarh on 18th
June, 1976 between Akbar and Ranapratap, the Sisodia Rajput King. The place is
mainly famous for his gallantry and heroic battle against Akbar. His army fought
bravely but at last he had to take sojourn in the hills. Hunted from rock to
rock by his implacable enemy, and ‘feeding his family from the fruits of his
native hills’, he continued the war with undaunted spirit and energy and had the
satisfaction of recovering many of his strongholds before he died on 19th
January, 1597, at the age of fifty-seven.