
(Paper) MPPSC: Online Examination of State Engineering
Service (Pre.) Exam - 2014 Second Paper (Mechanical Engineering)
Mechanical Engineering


Q1 : A steel rod of 2 m long is heated through a
temperature of 1000C . The coefficient of linear expansion is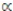 = 6.5 X 10-6/0C and E= 2 X 106N/cm2.
The stress induced in the bar is
= 6.5 X 10-6/0C and E= 2 X 106N/cm2.
The stress induced in the bar is
A 1000 N/cm2
B 1200 N/cm2
C 1300 N/cm2
D 1400 N/cm2
Answer Key: C
Q2 : The design calculations for members subjected to
fluctuating loads with the same factor of safety yield the most conservative
estimates when using
A Gerber relation
B Soderberg relation
C Goodman relation
D None of these is correct
Answer Key: B
Q3 : A leaf spring 1 m long carries a central point load
of 2000 N. The spring is made up of plates each 5 cm wide and 1 cmthick. The
bending stress in the plate is limited to 100 N/mm2. The number of
plates required will be
A 3
B 5
C 6
D 8
Answer Key: C
Q4 : The stress due to suddenly applied load as compared
to the stress due to the same load gradually applied to the same rod is
A half
B same
C double
D three times
Answer Key: C
Q5 : Choose the wrong statement
A The shear force at any section of a beam is equal to the
total sum of the forces acting on the beam on any one side of the section,
B The magnitude of the bending moment at any section of a beam is equal to the
vector sum of the moments (about the section) due to the forces acting on the
beam on any one side of the section,
C A diagram which shows the values of shear forces at various sections of
structured member is called a shear force diagram,
D A simply supported beam is one which is supported on more than two supports.
Answer Key: D
Q6 : Two blocks with masses 'M' and 'm' are in contact
with each other and are resting on a horizontal frictionless floor. When
horizantal force (F) is applied to the heavier body mass 'M', the blocks
accelerate to the right i.e. towards the application force. The force between
the two blocks is
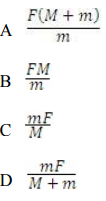
Answer Key: D
Q7 : A thick walled pressure vessel is subjected to an
internal pressure of 60 MPa. If the hoop stress on the outer surface is 150 MPa,
then the hoop stress on the internal surface is
A 105 MPa
B 180 MPa
C 210 MPa
D 135 MPa
Answer Key: C
Q8 : A Mohr's circle reduces to a point when the body is
subjected to
A pure shear
B uniaxial stress only
C equal and opposite axial stresses on two mutually perpendicular planes, the
planes being free of shear
D equal axial stresses on two mutually perpendicular planes, the planes being
free of shear.
Answer Key: D
Q9 : In a close-coiled helical spring subjected to an
axial load and other quantities remaining the same, if the wire diameter is
doubled, then the stiffness of the spring when compared to the original one will
become
A two times
B four times
C eight times
D sixteen times
Answer Key: D
Q10 : Considering centrifugal tension, the power
transmitted by belt drive is maximum at velocity V equal to
Note: - T is total tension on tight side and m is mass
per unit length of belt.
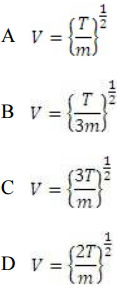
Answer Key: B
Q11 : In a hollow circular shaft of outer and inner
diameters of 20 cm and 10 cm respectively, the shear stress is not to exceed 40
N/mm2. The maximum torque which the shaft can safely transmit is
A 58.9 KN-m
B 57.9 KN-m
C 56.9 KN-m
D 58.7 KN-m
Answer Key: A
Q12 : Rope brake dynamometer uses
A oil as lubricant
B water as lubricant
C grease as lubricant
D no lubricant
Answer Key: D
Q13 : Whirling speed of a shaft coincide with the natural
frequency of the
A longitudinal vibration
B transverse vibration
C torsional vibration
D none of these is correct
Answer Key: A
Q14 : In slider crank mechanism, the maximum acceleration
of slider is obtained when the crank is
A at the inner dead centre position
B at the outer dead centre position
C exactly midway position between the two dead centres
D slightly in advance of the midway position between the two dead centres.
Answer Key: A
Q15 : Tresca theory of failure is applicable for which of
the following type of materials ?
A Elastomers
B Plastic
C Ductile
D Brittle
Answer Key: C
Q16 : A solid shaft is to transmit 20 kW at 200 rpm. The
ultimate shear stress for the steel may be taken as 360 MPa and a factor of
safety as 8. The diameter of solid shaft is
A 45 mm
B 46 mm
C 48 mm
D 50 mm
Answer Key: C
Q17 : A 1.5 m long column has a circular cross-section of
5 cm diameter. One end of the column is fixed and other end is free. Taking
factor of safety as 3 and E= 120 GN/m2 , safe load according to
Euler's theory is
A 13.00 kN
B 13.27 kN
C 13.47 kN
D 13.87 kN
Answer Key: C
Q18 : An internal gear having 60 teeth is meshing with an
external gear having 20 teeth. Module is 6 mm. The centre distance of two gears
is
A 120 mm
B 180 mm
C 240 mm
D 300 mm
Answer Key: C
Q19 : In a cam drive, it is essential to off-set the axis
of follower to
A decrease the side thrust between the follower and cam
surface
B decrease the work between the follower and cam surface
C take care of space limitation
D reduce the cost
Answer Key: C
Q20 : In equilibrium condition, fluids are not able to
sustain
A shear force
B resistance to viscosity
C surface tension
D geometric similitude
Answer Key: C
Q21 : The fluid forces considered in the Navier-Stoke's
equation are
A gravity, pressure and viscous
B gravity, pressure and turbulent
C pressure, viscous and turbulent
D gravity, viscous and turbulent
Answer Key: A
Q22 : A Brayton cycle (Air standard) has a pressure ratio
of 4 and inlet conditions of one standard atmospheric pressure and 270C.
Estimated air flow rate for 100 kW power output (when maximum temperature in the
cycle is 10000C, (γ =1.4, and Cp =1.0 kJ/kg.K) will be
A 0.24 kJ/kg
B 0.32 kJ/kg
C 0.36 kJ/kg
D 0.42 kJ/kg
Answer Key: C
Q23 : A turbine develops 8000 kW when running at 100 rpm.
The head on the turbine is 36 m. If the head is reduced to 9 m, the power
developed by the turbine will be
A 16000 kW
B 4000 kW
C 1414 kW
D 1000 kW
Answer Key: D
Q24 : Efficiency of steam turbine can be improved by
A reheating of steam
B regenerative feed heating
C binary vapour plants
D all options are correct
Answer Key: D
Q25 : Free convection flow depends on all of the following
except
A density
B coefficient of viscosity
C gravitational force
D velocity
Answer Key: D
Q26 : Which of the following cycle has maximum efficiency
A Rankine
B Brayton
C Carnot
D Joule
Answer Key: C
Q27 : The air standard Diesel cycle is less efficient than
the Otto cycle for the
A same compression ratio and heat addition
B same pressure and heat addition
C same rpm and cylinder dimension
D same pressure and compression ratio
Answer Key: A
28 : The knock in Diesel engine occurs due to
A instantaneous and rapid burning of the first part of the
charge
B instantaneous auto ignition of last part of charge
C delayed burning of the first part of the charge
D reduction of delay period
Answer Key: A
Q29 : Compensating devices are provided in carburators
A to charge the quantity of mixture depending upon load
B to provide always an economy mixture
C to modify the mixture strength depending upon requirements under various
operating conditions
D to supply extra fuel during acceleration only
Answer Key: C
Q30 : Which part is not common between the petrol and
Diesel engine ?
A air cleaner
B exhaust silencer
C battery
D fuel injector
Answer Key: D
Q31 : Which among the NC operations given below are
continuous path operations ? Arc welding (AW), Milling (M), Punching in sheet
metal (P), Drilling (D), Laser cutting of sheet metal (LC), Spot welding (SW)
A AW, LC and M
B AW, D, LC and M
C D, LC, P and SW
D D, LC, and SW
Answer Key: B
Q32 : The loss of available energy associated with the
transfer of 1000 kJ of heat from a constant temperature system at 600 K to
another at 400 K, when the environmental temperature is 300 K is
A 166.67 kJ
B 250.00 kJ
C 500.00 kJ
D 750.00 kJ
Answer Key: A
Q33 : If VN and α are the nozzle exit velocity and nozzle
angle in an impulse turbine, the optimum blade velocity is given by

Answer Key: D
Q34 : The entropy of universe tends to
A become zero
B remain constant
C be maximum
D attain a certain finite minimum value
Answer Key: A
Q35 : A counter flow shell and tube heat exchanger is used
to heat water with hot exhaust gases. The water (Cp = 4180 J/kg
0C) flows at a rate 2 kg/s while the exhaust gas (Cp = 1030
J/kg 0C) flows at the rate of 5.25 kg/s. If the heat exchanger
surface area is 32.5 m2 and the over all heat transfer coefficient is
200 W/m2 0C, what is the NTU for the heat exchanger ?
A 1.2
B 2.4
C 4.5
D 8.6
Answer Key: A
Q36 : A counter flow heat exchanger is used to heat water
from 200C to 800C by using hot gas entering at 1400C
and leaving at 800C. The log mean temperature difference for the heat
exchanger is
A 800C
B 600C
C 1100C
D not determinable
Answer Key: B
Q37 : The axis of movement of a robot may include
A elbow rotation
B wrist rotation
C X-Y coordinate motion
D all options are correct
Answer Key: D
Q38 : Automatic loading and unloading of materials can be
accomplished by means of
A power push or pull device
B power roller, belt and chain
C automatic couple and uncouple
D all options are correct
Answer Key: D
Q39 : Steam turbines are classified according to
A direction of flow
B principle of action
C number of cylinder
D arrangement of pressure drop
Answer Key: D
Q40 In nuclear power plants there are three main sources
of radioactive contamination of air. Out of three one of the source is :
A step-up transformer
B liquid metal
C fission of nuclei of nuclear fuels
D penstock
Answer Key: C
Q41 : Which of the following is not considered a method of
input control in a CAD system ?
A programmable function box
B joystick
C plotter
D touch material
Answer Key: C
Q42 : A transmission shaft subjected to bending loads must
be designed on the basis of
A maximum normal stress theory
B maximum shear stress theory
C maximum normal stress and maximum shear stress theory
D fatigue strength
Answer Key: A
Q43 : The flow of fluid through a pipe is laminar, when
A the fluid is ideal
B the fluid is viscous
C the Reynold's number is less than 2000
D the Reynold's number is more than 3000
Answer Key: C
Q44 : The radiation heat transfer rate per unit area in
(W/m2) between two plane parallel grey surfaces (emissivity = 0.9)
maintained at 400 K and 300 K (given Stefan Boltzmann's constant σ=
5.67X10-8 W/m2K) is
A 992
B 812
C 464
D 567
Answer Key: B
Q45 : For forced convection, Nusselt number is a function
of
A Prandtl and Grashoff number
B Reynolds and Prandtl number
C Reynolds and Grashoff number
D Reynolds number only
Answer Key: B
Q46 : The essential physical components of FMS is
A potentially independent NC machine tools
B a conveyance network to more parts and sometimes tools between machines and
fixturing stations
C an overall control network that coordinates the machine tools, the part-moving
elements and the workpieces
D all options are correct
Answer Key: D
Q47 : Refrigerant used in domestic refrigerators is
A ammonia
B air
C SO2
D freon-12
Answer Key: D
Q48 : The comfort conditions in air conditioning are at
A 00C DBT and 0% RH
B 200C DBT and 60% RH
C 300C DBT and 80% RH
D 400C DBT and 90% RH
Answer Key: B
Q49 : The use of refrigerant R-22 for temterature below
-300C is not recommended due to its
A good miscibility with lubricating oil
B poor miscibility with lubricating oil
C low evaporating pressure
D high compressor discharge temperature
Answer Key: D
Q50 : Basic law of heat conduction is
A Fourier's law
B Newton's law
C Stefan's law
D First law of thermodynamics
Answer Key: A
Q51 : The size of weld in butt welded joint is equal to
A 0.5 times throat of weld
B Throat of weld
C
 times throat of weld
times throat of weld
D Two times throat of weld
Answer Key: B
Q52 : If two pumps identical in all respects and each
capable of delivering a discharge Q against a head H are connected in series,
the resulting discharge is
A 2Q against a head 2H
B 2Q against a head H
C Q against a head H

Answer Key: C
Q53 : In interferometric measurement method, the path
difference between one bright band and the next is varied by
A Half wavelength
B Two half wavelength
C One quarter wavelength
D Two wavelength
Answer Key: B
Q54 : Wear allowance is provided on
A Go gauge
B Not go gauge
C Both go and not go gauge
D None of these is correct
Answer Key: A
Q55 : In ammonia vapour compression system, the
temperature of ammonia after compression will be
A 0o to 40oC
B 40o to 50oC
C 50o to 70oC
D 70o to 110oC
Answer Key: D










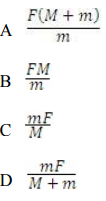
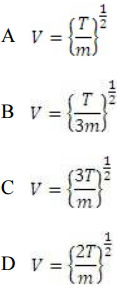

 times throat of weld
times throat of weld


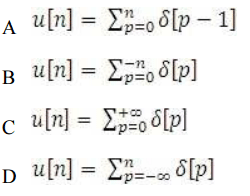
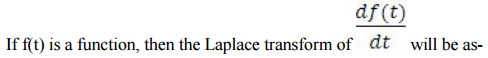
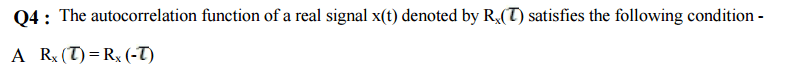
.gif)


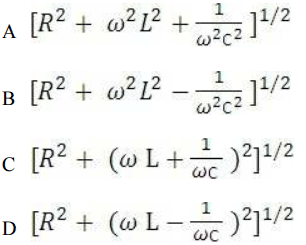
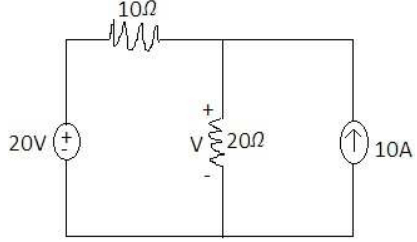


 is
is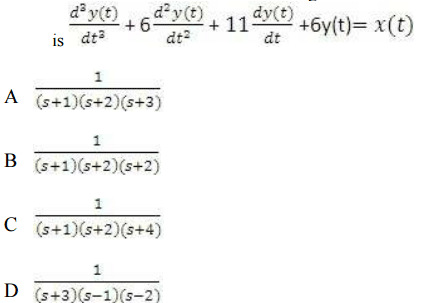
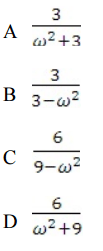
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
