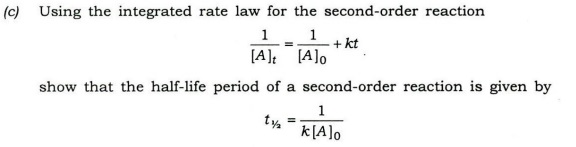(Download) UPSC: Geologist Examination Papers-2018
Exam Name : UPSC Geo-Scientist and Geologist Exam 2018
Subject : Chemistry Paper - II
Year : 2018
CHEMISTRY
Paper II
ITime Allowed : Three Hours
Maximum Marks : 200
QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS
Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting
questions.
There are FIFTEEN questions divided under THREE Sections.
Candidate has to attempt TEN questions in all.
The ONLY question in Section A is compulsory.
The number of marks carried by a question / part is indicated against it.
Attempts of questions shall be counted in sequential order. Unless struck
off, attempt of a question shall be counted even if attempted partly.
Any page or portion of the page left blank in the answer-book must be clearly
struck off. Answers must be written in ENGLISH only.
Neat sketches may be drawn to illustrate answers, wherever required.
Unless otherwise mentioned, symbols and notations have their usual standard
meanings. Assume suitable data, if necessary and indicate the same clearly.
Some useful fundamental constants and conversion factors
NA = 6.022 x1023 mol-1
Rydberg constant = 2.178x10-18 J
c = 2.998 x108 ms-1
kb = 1.38x10-23 J K-1
e = 1.602x10-19 C
me = 9.109x10-31 kg
F = 96485 C mol-1
R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1
h = 6.626 X10-34 J s
p = 3.142
1 amu = 1.66x10-27 kg
1 cal = 4.184 J
1 J = 1 kg m2 s-2
1 Å = 10-8 cm = 10-10 m = 0.1 nm = 100 pm
1 atm = 760 torr = 1.01325x105 Pa
1 bar = 1x105 Pa = 0.9869 atm
1 eV = 1.602x10-19 J
1 L atm = 101:34 J
SECTION A
1. Answer all of the following:
(a) At what temperature will the average speed of oxygen molecules be equal
to that of hydrogen molecules at 20 K?
(b) The fugacity (f) of a real gas will be greater than its observed pressure
(P) when intermolecular repulsive interactions are dominant. Justify with
reason.
(c) At room temperature, liquid water wets solid glass surface, but liquid
mercury does not. Explain why.
(d) Estimate the number of particles per unit cell of an fcc crystal.
(e) In a Joule-Thomson experiment, the temperature of the gas decreases. What
will be the sign of Joule-Thomson coefficient? Give reason.
(f) Show that DG = DA, for
isothermal expansion of fixed amount of ideal gas.
(g) We know
Kp = exp(-DGo/RT)
(Symbols have their usual meanings)
(i) What are the units in SI system) of Kp, and
DGo?
(ii) Does the Kp value of a chemical reaction depend on temperature
of reaction at equilibrium and mode of stoichiometric representation of the
chemical reaction?
(h) At 25 °C, pH of 10-8 mol L-1 aqueous HCl solution
is less than 7.0. Justify with reason.
(i) Boiling point of liquid depends on superincumbent pressure, not on external
pressure. Justify with definition of boiling point of liquid.
(j) For the reaction
I- (aq) + H2O2 (aq) → IO- (aq) +H2O(1)
predict whether the reaction rate will be increased, decreased or unchanged with
increase of ionic strength of the solution. Give reason(s) in support of your
answer.
(k) The spontaneous adsorption of gas on a solid surface at constant pressure
and temperature is an exothermic process. Give reasons with the help of
principles of thermodynamics.
(l) Conductivity of an ionic solution does not depend on its mass, but depends
on its temperature. Explain with reasons.
(m) The following photochemical reaction occurs when UV light is exposed to
anthracene (C14H10) in benzene medium :
2 C14H10 + hv → C28H20
What would be the expected quantum yield? The observed quantum yield is 0.5.
How will you explain it?
(n) Show that the function yn = N sin (npx
/ L) satisfies the Schrödinger equation for a particle in a
one-dimensional box with a potential function V(x) equal to zero for 0 < x < L
and infinity elsewhere. What is the eigenvalue?
(o) Which transition of the following corresponds to the second line of the
Balmer spectrum?
(i) 4p → 3s
(ii) 2s → 4p
(iii) 3d → 2p
(iv) 4d → 2p
(v) 4d → 3p
Give reasons.
(p) Determine the number of normal modes for vibrational motion of each of
the following molecules :
(i) Dinitrogen
(ii) Carbon dioxide
(ii) Water
(iv) Acetylene
(v) Ethylene
SECTION-B
Attempt any six questions :
2. (a) For fixed mass of an ideal gas, what would be the nature of the
plot of In (P/bar) against In (V/L) at constant temperature? Give reason(s) in
support of your answer.
(b) Find the Boyle temperature of He gas which obeys the van der Waals gas
equation. Given a = 0.0341 atm dm6 mol-2 and b = 2.38x10-2
dm3 mol-1.

4. 3.0 mol H2 (g) and 1.0 mol N2(g) are in two
compartments separated by a partition. The volume and temperature of both the
compartments are the same. What will be the change in entropy (DS)
of the system when the partition is removed and allowed to free mixing of gases?
Assume that two gases behave ideally.
5. The vapour pressure of benzene is 53.3 kPa at 60.6 °C, but it
lowers to 51.5 kPa when 19.0 g of a non-volatile organic compound is dissolved
in 500.0 g benzene. Calculate the molar mass of the organic compound, taking the
molar mass of benzene as 78.0 g.
6. The decomposition of HI (g) to H2 (g) and I2
(g) is a second-order reaction. The half-life of the reaction is found to be
13.5 min, when the initial pressure of HI (g) is 1.0 bar.
(a) Calculate the half-life when the initial pressure of HI (g) is 0-1 bar.
(b) Calculate the reaction time required for the pressure of HI (g) to fall from
1.0 bar to 0.1 bar.
7. The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle (HUP) can be given
mathematically as
For a particle trapped in a one-dimensional box of length L, the maximum
value of Dx is L. Calculate the minimum value of
Dpx for an electron trapped in a linear molecule of
length L = 3:0 nm and clearly state the units.
8. (a) Find the inter-planar distance between two successive
110-planes of a bcc crystal having unit cell edge length as 100.0 pm.
(b) Write down the expression of the 'Langmuir adsorption isotherm' in terms of
the fraction of surface sites covered (0) and equilibrium pressure (P) of the
adsorbed gas at constant temperature. How would you determine the constant
involved in this equation?
9. (a) With increase of temperature of HCl (aq) solution, the
transport number of the H+ ion decreases, though its velocity increases. Explain
with reason(s).
(b) The conductivity of KCl04 (aq) solution at 25°C is 13.78 mS m-1
when its concentration is 1.0 mmol dm-3. Calculate its molar
conductivity.
10. (a) The anti-Stokes lines of the pure rotational Raman spectrum of
a molecule are roughly of the same intensity as the Stokes lines, but
anti-Stokes lines of the vibrational Raman spectrum are generally much weaker
than the Stokes lines. Account for the observation.
(b) In the pure rotational Raman spectrum of a diatomic molecule, the first
three transitions are observed at 26.52 cm-1, 44.20 cm-1
and 61.88 cm-1.
(i) Calculate the rotational constant B of the molecule.
(ii) What other information would you need to calculate the equilibrium bond
length of the molecule? Explain your answer.
SECTION-C
Attempt any three questions :

(b) Obtain the expression of e.m.f (E) of the following galvanic cell in
terms of its standard e.m.f. (E°), molality of aqueous solution (m) of the
electrolyte and its mean ionic activity coefficient (g+)
:
Zn | ZnCl2 (aq, m) | AgCl, Ag
(c) The electronic spectrum of a diatomic molecule A, shows a series of bands
converging to a continuum at 200 nm. One of the atoms formed at 200 nm is in an
excited state, which lies 8000 cm-1 above its ground state. Calculate
the bond dissociation energy of A2.
12. (a) Which of the following molecules may show an infrared
vibrational absorption spectrum?
(i) C12
(ii) HCI
(iii) NH3
(iv) CO2
(v) CH4
(b) If the two methyl proton resonances in the proton NMR spectrum of methyl
acetate (CH3COOCH3) are 320 Hz apart in an instrument
operating at 200 MHz, calculate the difference in frequency (Hz) for the two
signals in the spectrum of an instrument operating at 500 MHz.
(c) By predicting the appearance of their proton NMR spectra, show how 1,3,5
trinitrobenzene can be distinguished from 1,2,4-trinitrobenzene. Sketch the low
resolution NMR spectrum of each molecule.
(d) How would you distinguish between n → p* and
p → p* transitions in a
carbonyl compound? Give the differences, including effect of increasing solvent
polarity.
13. (a) Calculate the average internal energy per molecule of oxygen
gas at 300 K, using 'principle of equipartition of energy'.
(b) Deduce the reduced equation of state for the van der Waals gas. Mention its
significance.
14. (a) Why is glycerol more viscous than water?
(b) Arrange the following molecules in order of their increasing acid strength,
giving reason :
(i) H3PO4, H3PO3 and H3PO2
(ii) CH3COOH and CF3COOH
(d) Evaluate the commutator [ x, Px].
15. (a) If we mix 700 mL of ethanol with 30.0 mL of water at normal
pressure and temperature, then the total volume will be less than 100.0 mL.
Explain why.






.jpg)